Electrophilic Addition to Alkenes - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 5
Title:
Electrophilic Addition to Alkenes
Description:
Electrophilic Addition to Alkenes. Electrophile - chemical species that is electron deficient ' ... is one of the best electrophiles - just a proton. This is ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:94
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Electrophilic Addition to Alkenes
1
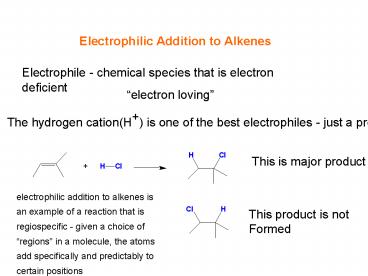
Electrophilic Addition to Alkenes
Electrophile - chemical species that is electron
deficient
electron loving
The hydrogen cation(H) is one of the best
electrophiles - just a proton
This is major product
electrophilic addition to alkenes is an example
of a reaction that is regiospecific - given a
choice of regions in a molecule, the atoms add
specifically and predictably to certain positions
This product is not Formed
2
Mechanism of Electrophilic Addition to Alkenes
The pathway that proceeds through the more stable
carbocation is preferred - This explains the
formation of the Markovnikov Product. Markovnik
ov Addition-The more electronegative atom adds to
the more substituted carbon in alkene addition
reactions.
Pathway 1
Pathway 2
2 carbocation
1 carbocation
3
Energetic Changes in Electrophilic Addition
1 carbocation
2 carbocation
4
Stereochemical Consideration with Addition
Reactions
This could be Top or Bottom Attack of Nucleophile
5
Likely Pathways (Mechanisms) for Alkanes with
Leaving Groups Reacting with Nucleophiles
Strong Bases
Weak Bases
Leaving Groups
H2O, ROH, PR3, NH3, I-, Br-, Cl-, RS-, NC-, RCOO-
HO-, RO-, H2N-, R2N-
H2O, ROH, RCOO- (carboxylate), RSO3- (sulfonate),
RSO4- (sulfate), RPO4-2 (phosphate)
I-, Br-, Cl-,
Weak Nü
Strong Nü
Good Nü
This table will be provided on a quiz