Basics of Genetics - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Basics of Genetics
Description:
Animal Biotech- 3rd Yr- Unit 5- Stem Cell and Gene Therapy – PowerPoint PPT presentation – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:166
Updated: 28 January 2020
Slides: 39
Provided by:
theabhijitdn
Category:
Medicine, Science & Technology
Tags:
Title: Basics of Genetics
1
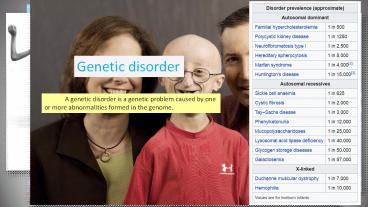
Genetic disorder
A genetic disorder is a genetic
problem caused by one or more abnormalities
formed in the genome.
2
(No Transcript)
3
What will be Todays Agenda???
Lecture 1
- An overview of Gene Therapy
- An Overview of Stem Cells
- Back to Basics
Lecture 2
- Gene Therapy
Lecture 3
- Stem Cells Therapy
4
Lecture 1
- Agenda 1 An overview of Gene Therapy
- Agenda 2 An Overview of Stem Cells
- Agenda 3 Back to Basics
5
An Overview of Gene Therapy
Todays Agenda 1
6
What is the Most Common thing in all these
diseases???
- Gene therapy is an experimental technique that
uses Genes to treat or prevent disease.
- The First Success Story of Gene Therapy
- The first human to receive gene therapy treatment
was a 4 year old girl with severe
immune-deficiency disease. - This disease is caused by a faulty gene that
fails to produce a vital enzyme. - In the therapy procedure, they extracted some of
the girl's white blood cells. - Then, they exposed them to a genetically
engineered virus that had lost its virulence but
still carried normal versions of the gene that
was not functioning correctly in the girl. - The virus invaded the white blood cells, and then
these cells were transfused back into the girl. - Once back inside the girl's bloodstream, the
cells began producing the proper enzyme. - Although the girl still needs follow-up
treatments, she now leads a relatively normal
life following the gene therapy. - This is one of the success stories of gene
therapy.
- In this to treat a disorder a gene is inserted
into a patient's cells instead of using drugs or
surgery.
- The first attempt at modifying human DNA was
performed in 1980 by Martin Cline
- But the first successful nuclear gene transfer in
humans was approved by the National Institutes of
Health, was performed in May 1989.
Gene Therapy
- The first therapeutic use of gene transfer as
well as the first direct insertion of human DNA
into the nuclear genome was performed by French
Anderson in a trial starting in September 1990.
- Between 1989 and February 2016, over 2,300
clinical trials were conducted, with more than
half of them in phase I
7
An Overview of Stem Cell Therapy
Todays Agenda 2
8
Confusion Between Totipotent vs. Pluripotent vs.
Multipotent?
What are the different types of stem cells?
What are the Stem Cells Throughout the Human
Lifecycle
What is Stem Cell?
What is Stem Cell Therapy?
What is the Most Common thing in all these
diseases???
- Embryonic Stem Cells (ESCs) This is the only
controversial stem cell type. ESCs are derived
from blastocysts, a stage in the developing
embryo. They can become any cell type within the
human body. - Perinatal Stem Cells These cells are obtained
during the period immediately before and after
birth. Collection of these cell types does not
impact the development of the fetus or newborn,
so they are non-controversial. - Adult Stem Cells These are non-controversial
cells found in living adults. Everyone has stem
cells present in their bone marrow, fat (adipose
tissue), and many other sites. - Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPS Cells) iPS
cells were discovered in 2006. They are
non-controversial because they are adult cells
that are genetically reprogrammed in a lab. Like
embryonic stem cells, they can become any cell
within the body. - Cancer Stem Cells (CSCs) Cancer stem cells are
a type of stem cell that biotech and pharma
companies are exploring because they play a role
in facilitating the formation of tumors.
Companies exploring CSCs are interested to
discover how to manage and prevent cancer.
- Embryonic stem cells Stem cells derived from
embryos (controversial). - Pre-natal stem cells Stem cells derived from
the fetus or supporting structures
(non-controversial). - Post-natal stem cells Stem cells derived from a
recent newborn (non-controversial). - Adult stem cells Stem cells derived from living
humans (non-controversial). Common adult stem
cell types include mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs),
hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), and neural stem
cells (NSCs), among others.
- Totipotent stem cells Cells that have the
capacity to form an entire organism. - Pluripotent stem cells Can give rise to most,
but not all, tissues within an organism. - Multipotent stem cells Undifferentiated cells
that are limited to giving rise to specific
populations of cells.
Stem Cell therapy
Ans Stem-cell therapy is the use of stem cells
to treat or prevent a disease or condition.
Ans Stem cells are cells with the potential to
develop into many different types of cells in the
body. They are part of the repair system for the
body.
9
Why do scientists want to use stem cell lines?
- The reason scientists want to use stem cells is
twofold - They hope to grow these stem cells into tissues,
afflicted by certain diseases, to better assess
what causes these diseases and how to create
effective treatments and - scientists can use stem cells to repair or patch
damaged cells in people with various diseases.
10
How Are Stem Cells Being Used in Medicine?
- Today, most clinics that offer stem cell
treatments administer Mesenchymal stem cells
(MSCs), which they source from fat tissue or bone
marrow. - Mesenchymal stem cells are a type of multipotent
stem cell that is being explored for use in the
orthopedic repair, pain management, arthritis,
asthma, and many other applications. - MSCs tend to exert effects on other cells and
tissues within the human body, which is called
paracrine signaling. - Another stem cell type that is commonly used is
the hematopoietic stem cell (HSC). HSC
transplantation has been used for decades as a
means of rebuilding the immune system after a
patient undergoes radiation or chemotherapy.
11
- Success Stories of Stem Cell Therapy
- Blindness
- On July 12, 2011, scientists injected retinal
cells, derived from embryonic stem cells, into
the eyes of two patients suffering from
progressive blindness. The patients who received
the therapy currently exhibit no signs of adverse
effects from the treatment and are reporting
small improvements in their vision. The
transplanted retinal pigment cells have
integrated into the eye tissue and are aiding
photoreceptor cells to function again.
- Parkinsons Disease
- Scientists are currently treating some patients
with Parkinsons disease with stem cell therapy.
So far, the two patients treated to date are
showing no ill effects from the therapy, which is
being studied in a phase 1 trial involving 12
Parkinsons disease sufferers conducted by
researchers at the Royal Melbourne Hospital in
Australia.
- Spinal-Cord Injury
- In the June 2017 issue of Forbes magazine, they
disclose a couple of the current findings in the
field of stem cell science and medicine. As part
of a 2016 trial, neurologist Charles Liu, infused
ten million stem cells into a paralyzed patients
spinal cord. Within months, the patient could
lift weights, write his name and feed himself.
Although Lius study is not complete, and the
treatment is not standard therapy, researchers
were encouraged enough by the results to extend
the treatment to people with less-severe spinal
injuries who would have been too risky to include
in initial tests.
12
(No Transcript)
13
(No Transcript)
14
Now the Biggest Question!
- How Does Gene Therapy and Stem Cell Therapy Work?
(Technically)?
- What are the Different types of cells?
- What are the Different types of Tissues?
- How does all they are inter connected?
ANS To Understand We have to decode the chapter
from the basics to Applied level
15
Back to Basics
Todays Agenda 3
16
Some Basics
- Our Human Body having 11 Systems
Infrastructure Systems
Regulation Systems
Energy Systems
1. Skeletal system -stores calcium -frame work for the body -protects vital organs -produces red blood cells
2. Muscular system -generates heat -creates movement -maintains posture -uses energy
3. Cardiovascular system or Circulatory System- - transportation of nutrients and gas waste -supports immune function
4. Nervous System -Sensory input -interpretation of input or thought -elicit and signal responses -coordination of muscles
5. Endocrine system -secrets hormones that regulate growth, metabolism and general body function.
6. Integumentary system/ Exocrine system -largest sensory organ -vitamin D syntheses -protects deeper tissue -regulates fluid and blood loss
7. Lymphatic system / Immune system -picks up fluids leaked from the capillaries -supports immune systems houses white blood cells -portions of many different systems that fight disease
8. Renal system/ Urinary system -get rid of nitrogenous waste out of blood -regulated electrolytes, fluid and pH balance
9. Respiratory System -portions moistens and heats air -gas exchange
10.Digestive System -breaks down food into the building blocks for the body
11. Reproductive system -production off spring -production of hormones
17
Some Basics
- Our Human Body having 11 Systems
Infrastructure Systems
Regulation Systems
Energy Systems
1. Skeletal system -stores calcium -frame work for the body -protects vital organs -produces red blood cells
2. Muscular system -generates heat -creates movement -maintains posture -uses energy
3. Cardiovascular system or Circulatory System- - transportation of nutrients and gas waste -supports immune function
4. Nervous System -Sensory input -interpretation of input or thought -elicit and signal responses -coordination of muscles
5. Endocrine system -secrets hormones that regulate growth, metabolism and general body function.
6. Integumentary system/ Exocrine system -largest sensory organ -vitamin D syntheses -protects deeper tissue -regulates fluid and blood loss
7. Lymphatic system / Immune system -picks up fluids leaked from the capillaries -supports immune systems houses white blood cells -portions of many different systems that fight disease
8. Renal system/ Urinary system -get rid of nitrogenous waste out of blood -regulated electrolytes, fluid and pH balance
9. Respiratory System -portions moistens and heats air -gas exchange
10.Digestive System -breaks down food into the building blocks for the body
11. Reproductive system -production off spring -production of hormones
18
Some Basics
- Our Human Body having 11 Systems
Infrastructure Systems
Regulation Systems
Energy Systems
1. Skeletal system -stores calcium -frame work for the body -protects vital organs -produces red blood cells
2. Muscular system -generates heat -creates movement -maintains posture -uses energy
3. Cardiovascular system or Circulatory System- - transportation of nutrients and gas waste -supports immune function
4. Nervous System -Sensory input -interpretation of input or thought -elicit and signal responses -coordination of muscles
5. Endocrine system -secrets hormones that regulate growth, metabolism and general body function.
6. Integumentary system/ Exocrine system -largest sensory organ -vitamin D syntheses -protects deeper tissue -regulates fluid and blood loss
7. Lymphatic system / Immune system -picks up fluids leaked from the capillaries -supports immune systems houses white blood cells -portions of many different systems that fight disease
8. Renal system/ Urinary system -get rid of nitrogenous waste out of blood -regulated electrolytes, fluid and pH balance
9. Respiratory System -portions moistens and heats air -gas exchange
10.Digestive System -breaks down food into the building blocks for the body
11. Reproductive system -production off spring -production of hormones
19
Some Basics
- Our Human Body having 11 Systems
Infrastructure Systems
Regulation Systems
Energy Systems
1. Skeletal system -stores calcium -frame work for the body -protects vital organs -produces red blood cells
2. Muscular system -generates heat -creates movement -maintains posture -uses energy
3. Cardiovascular system or Circulatory System- - transportation of nutrients and gas waste -supports immune function
4. Nervous System -Sensory input -interpretation of input or thought -elicit and signal responses -coordination of muscles
5. Endocrine system -secrets hormones that regulate growth, metabolism and general body function.
6. Integumentary system/ Exocrine system -largest sensory organ -vitamin D syntheses -protects deeper tissue -regulates fluid and blood loss
7. Lymphatic system / Immune system -picks up fluids leaked from the capillaries -supports immune systems houses white blood cells -portions of many different systems that fight disease
8. Renal system/ Urinary system -get rid of nitrogenous waste out of blood -regulated electrolytes, fluid and pH balance
9. Respiratory System -portions moistens and heats air -gas exchange
10.Digestive System -breaks down food into the building blocks for the body
11. Reproductive system -production off spring -production of hormones
20
Some Basics
- Our Human Body having 11 Systems
Infrastructure Systems
Regulation Systems
Energy Systems
1. Skeletal system -stores calcium -frame work for the body -protects vital organs -produces red blood cells
2. Muscular system -generates heat -creates movement -maintains posture -uses energy
3. Cardiovascular system or Circulatory System- - transportation of nutrients and gas waste -supports immune function
4. Nervous System -Sensory input -interpretation of input or thought -elicit and signal responses -coordination of muscles
5. Endocrine system -secrets hormones that regulate growth, metabolism and general body function.
6. Integumentary system/ Exocrine system -largest sensory organ -vitamin D syntheses -protects deeper tissue -regulates fluid and blood loss
7. Lymphatic system / Immune system -picks up fluids leaked from the capillaries -supports immune systems houses white blood cells -portions of many different systems that fight disease
8. Renal system/ Urinary system -get rid of nitrogenous waste out of blood -regulated electrolytes, fluid and pH balance
9. Respiratory System -portions moistens and heats air -gas exchange
10.Digestive System -breaks down food into the building blocks for the body
11. Reproductive system -production off spring -production of hormones
21
Some Basics
- Our Human Body having 11 Systems
Infrastructure Systems
Regulation Systems
Energy Systems
1. Skeletal system -stores calcium -frame work for the body -protects vital organs -produces red blood cells
2. Muscular system -generates heat -creates movement -maintains posture -uses energy
3. Cardiovascular system or Circulatory System- - transportation of nutrients and gas waste -supports immune function
4. Nervous System -Sensory input -interpretation of input or thought -elicit and signal responses -coordination of muscles
5. Endocrine system -secrets hormones that regulate growth, metabolism and general body function.
6. Integumentary system/ Exocrine system -largest sensory organ -vitamin D syntheses -protects deeper tissue -regulates fluid and blood loss
7. Lymphatic system / Immune system -picks up fluids leaked from the capillaries -supports immune systems houses white blood cells -portions of many different systems that fight disease
8. Renal system/ Urinary system -get rid of nitrogenous waste out of blood -regulated electrolytes, fluid and pH balance
9. Respiratory System -portions moistens and heats air -gas exchange
10.Digestive System -breaks down food into the building blocks for the body
11. Reproductive system -production off spring -production of hormones
22
Some Basics
- Our Human Body having 11 Systems
Infrastructure Systems
Regulation Systems
Energy Systems
1. Skeletal system -stores calcium -frame work for the body -protects vital organs -produces red blood cells
2. Muscular system -generates heat -creates movement -maintains posture -uses energy
3. Cardiovascular system or Circulatory System- - transportation of nutrients and gas waste -supports immune function
4. Nervous System -Sensory input -interpretation of input or thought -elicit and signal responses -coordination of muscles
5. Endocrine system -secrets hormones that regulate growth, metabolism and general body function.
6. Integumentary system/ Exocrine system -largest sensory organ -vitamin D syntheses -protects deeper tissue -regulates fluid and blood loss
7. Lymphatic system / Immune system -picks up fluids leaked from the capillaries -supports immune systems houses white blood cells -portions of many different systems that fight disease
8. Renal system/ Urinary system -get rid of nitrogenous waste out of blood -regulated electrolytes, fluid and pH balance
9. Respiratory System -portions moistens and heats air -gas exchange
10.Digestive System -breaks down food into the building blocks for the body
11. Reproductive system -production off spring -production of hormones
23
Some Basics
- Our Human Body having 11 Systems
Infrastructure Systems
Regulation Systems
Energy Systems
1. Skeletal system -stores calcium -frame work for the body -protects vital organs -produces red blood cells
2. Muscular system -generates heat -creates movement -maintains posture -uses energy
3. Cardiovascular system or Circulatory System- - transportation of nutrients and gas waste -supports immune function
4. Nervous System -Sensory input -interpretation of input or thought -elicit and signal responses -coordination of muscles
5. Endocrine system -secrets hormones that regulate growth, metabolism and general body function.
6. Integumentary system/ Exocrine system -largest sensory organ -vitamin D syntheses -protects deeper tissue -regulates fluid and blood loss
7. Lymphatic system / Immune system -picks up fluids leaked from the capillaries -supports immune systems houses white blood cells -portions of many different systems that fight disease
8. Renal system/ Urinary system -get rid of nitrogenous waste out of blood -regulated electrolytes, fluid and pH balance
9. Respiratory System -portions moistens and heats air -gas exchange
10.Digestive System -breaks down food into the building blocks for the body
11. Reproductive system -production off spring -production of hormones
24
Some Basics
- Our Human Body having 11 Systems
Infrastructure Systems
Regulation Systems
Energy Systems
1. Skeletal system -stores calcium -frame work for the body -protects vital organs -produces red blood cells
2. Muscular system -generates heat -creates movement -maintains posture -uses energy
3. Cardiovascular system or Circulatory System- - transportation of nutrients and gas waste -supports immune function
4. Nervous System -Sensory input -interpretation of input or thought -elicit and signal responses -coordination of muscles
5. Endocrine system -secrets hormones that regulate growth, metabolism and general body function.
6. Integumentary system/ Exocrine system -largest sensory organ -vitamin D syntheses -protects deeper tissue -regulates fluid and blood loss
7. Lymphatic system / Immune system -picks up fluids leaked from the capillaries -supports immune systems houses white blood cells -portions of many different systems that fight disease
8. Renal system/ Urinary system -get rid of nitrogenous waste out of blood -regulated electrolytes, fluid and pH balance
9. Respiratory System -portions moistens and heats air -gas exchange
10.Digestive System -breaks down food into the building blocks for the body
11. Reproductive system -production off spring -production of hormones
25
Some Basics
- Our Human Body having 11 Systems
Infrastructure Systems
Regulation Systems
Energy Systems
1. Skeletal system -stores calcium -frame work for the body -protects vital organs -produces red blood cells
2. Muscular system -generates heat -creates movement -maintains posture -uses energy
3. Cardiovascular system or Circulatory System- - transportation of nutrients and gas waste -supports immune function
4. Nervous System -Sensory input -interpretation of input or thought -elicit and signal responses -coordination of muscles
5. Endocrine system -secrets hormones that regulate growth, metabolism and general body function.
6. Integumentary system/ Exocrine system -largest sensory organ -vitamin D syntheses -protects deeper tissue -regulates fluid and blood loss
7. Lymphatic system / Immune system -picks up fluids leaked from the capillaries -supports immune systems houses white blood cells -portions of many different systems that fight disease
8. Renal system/ Urinary system -get rid of nitrogenous waste out of blood -regulated electrolytes, fluid and pH balance
9. Respiratory System -portions moistens and heats air -gas exchange
10.Digestive System -breaks down food into the building blocks for the body
11. Reproductive system -production off spring -production of hormones
26
Some Basics
- Our Human Body having 11 Systems
Infrastructure Systems
Regulation Systems
Energy Systems
1. Skeletal system -stores calcium -frame work for the body -protects vital organs -produces red blood cells
2. Muscular system -generates heat -creates movement -maintains posture -uses energy
3. Cardiovascular system or Circulatory System- - transportation of nutrients and gas waste -supports immune function
4. Nervous System -Sensory input -interpretation of input or thought -elicit and signal responses -coordination of muscles
5. Endocrine system -secrets hormones that regulate growth, metabolism and general body function.
6. Integumentary system/ Exocrine system -largest sensory organ -vitamin D syntheses -protects deeper tissue -regulates fluid and blood loss
7. Lymphatic system / Immune system -picks up fluids leaked from the capillaries -supports immune systems houses white blood cells -portions of many different systems that fight disease
8. Renal system/ Urinary system -get rid of nitrogenous waste out of blood -regulated electrolytes, fluid and pH balance
9. Respiratory System -portions moistens and heats air -gas exchange
10.Digestive System -breaks down food into the building blocks for the body
11. Reproductive system -production off spring -production of hormones
27
Some Basics
- Our Human Body having 11 Systems
Infrastructure Systems
Regulation Systems
Energy Systems
1. Skeletal system -stores calcium -frame work for the body -protects vital organs -produces red blood cells
2. Muscular system -generates heat -creates movement -maintains posture -uses energy
3. Cardiovascular system or Circulatory System- - transportation of nutrients and gas waste -supports immune function
4. Nervous System -Sensory input -interpretation of input or thought -elicit and signal responses -coordination of muscles
5. Endocrine system -secrets hormones that regulate growth, metabolism and general body function.
6. Integumentary system/ Exocrine system -largest sensory organ -vitamin D syntheses -protects deeper tissue -regulates fluid and blood loss
7. Lymphatic system / Immune system -picks up fluids leaked from the capillaries -supports immune systems houses white blood cells -portions of many different systems that fight disease
8. Renal system/ Urinary system -get rid of nitrogenous waste out of blood -regulated electrolytes, fluid and pH balance
9. Respiratory System -portions moistens and heats air -gas exchange
10.Digestive System -breaks down food into the building blocks for the body
11. Reproductive system -production off spring -production of hormones
28
Some Basics
- Our Human Body having 11 Systems
Infrastructure Systems
Regulation Systems
Energy Systems
- All different systems are made up of several
types of Tissues
1. Skeletal system -stores calcium -frame work for the body -protects vital organs -produces red blood cells
2. Muscular system -generates heat -creates movement -maintains posture -uses energy
3. Cardiovascular system or Circulatory System- - transportation of nutrients and gas waste -supports immune function
4. Nervous System -Sensory input -interpretation of input or thought -elicit and signal responses -coordination of muscles
5. Endocrine system -secrets hormones that regulate growth, metabolism and general body function.
6. Integumentary system/ Exocrine system -largest sensory organ -vitamin D syntheses -protects deeper tissue -regulates fluid and blood loss
7. Lymphatic system / Immune system -picks up fluids leaked from the capillaries -supports immune systems houses white blood cells -portions of many different systems that fight disease
8. Renal system/ Urinary system -get rid of nitrogenous waste out of blood -regulated electrolytes, fluid and pH balance
9. Respiratory System -portions moistens and heats air -gas exchange
10.Digestive System -breaks down food into the building blocks for the body
7. Lymphatic system / Immune system -picks up fluids leaked from the capillaries -supports immune systems houses white blood cells -portions of many different systems that fight disease
11. Reproductive system -production off spring -production of hormones
29
Some Basics
- Our Human Body having 11 Systems
Infrastructure Systems
Regulation Systems
Energy Systems
- All different Systems are made up of several
types of Tissues
- All different type of Tissues are made up of
different types of Cells
30
1.1 Some Basics
What is the difference between Nucleotides, Gene,
chromosome, Genome Protein?
- Our Human Body having 11 Systems
- From smallest to largest Nucleotide, Gene,
Chromosome, Genome. - Nucleotides are the smallest building blocks of
DNA. There are four nucleotides (A, G, T, C)
which arrange in pairs to form the long double
strands typical of DNA molecules. - A Gene is a segment of DNA which codes for the
amino acid sequence of a particular protein. A
gene is therefore composed of many pairs of
nucleotides. Eg. APOE e4 Gene appears to increase
the risk of Alzheimer Disease.
Infrastructure Systems
Regulation Systems
Energy Systems
- All different Systems are made up of several
types of Tissues
- All different type of Tissues are made up of
different types of Cells
- A Chromosome is a long strand of DNA which is
coiled up with various proteins. A chromosome
contains many genes. - .
- The Genome is all the DNA of a particular
organism. All of an organism's chromosomes
compose the organism's genome. - .
NM_000041
31
1.1 Some Basics
What is the difference between Nucleotides, Gene,
chromosome, Genome Protein?
- Our Human Body having 11 Systems
- From smallest to largest Nucleotide, Gene,
Chromosome, Genome. - Nucleotides are the smallest building blocks of
DNA. There are four nucleotides (A, G, T, C)
which arrange in pairs to form the long double
strands typical of DNA molecules. - A Gene is a segment of DNA which codes for the
amino acid sequence of a particular protein. A
gene is therefore composed of many pairs of
nucleotides. Eg. APOE e4 Gene appears to increase
the risk of Alzheimer Disease.
- How Proteins are Made?
Infrastructure Systems
Regulation Systems
Energy Systems
- All different Systems are made up of several
types of Tissues
Ans Proteins are made From DNA by Transcription
and Translation!
- All different type of Tissues are made up of
different types of Cells
- Facts-
- Thee are
- 37.2 trillion cells in Human Body!
- 23 chromosome pairs with a total of about 3
billion DNA base pairs - About 25,000 genes are present in Human Genome
about 20,000 of these genes are protein-coding
genes! - Humans make at least 20,000 proteins!
- Amino acids are the building blocks these
Proteins! - Total 21 Amino acids
- A Chromosome is a long strand of DNA which is
coiled up with various proteins. A chromosome
contains many genes. - .
- The Genome is all the DNA of a particular
organism. All of an organism's chromosomes
compose the organism's genome. - .
- A protein is composed of one or more long chains
of amino acids, the sequence of which corresponds
to the DNA sequence of the gene that encodes it.
NM_000041
32
What is the difference between Nucleotides, Gene,
chromosome, Genome Protein?
- Genome as being composed of a collection of
chromosomes - Chromosomes as being a collection of Genes
- Genes are being composed of Nucleotides (ATGC)
- Nucleotides are the monomeric unit of DNA
- DNA makes m-RNA by Transcription
- mRNA makes Amino Acids by Translation
- Amino Acids are the Building Block of Protein
How all these Human Gene and Genome were
Discovered/ Identified?
Ans Human Genome Project (HGP)
33
Background of Human Genome Project
- Francis Collins, former director of the Human
Genome Project, which began its mission in 1990. - A parallel, private sequencing effort was
undertaken by the Celera Corporation under Craig
Venter
34
Human Genome Project
35
Timeline of Genetics Charles Darwin to HGP
36
Timeline of Genetics Charles Darwin to HGP
37
Timeline of Genetics Charles Darwin to HGP
38
Timeline of Genetics Charles Darwin to HGP
39
Timeline of Genetics Charles Darwin to HGP
https//wellcomelibrary.org/collections/digital-co
llections/makers-of-modern-genetics/genetics-timel
ine/28106