Homogeneous representation - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 44
Title:
Homogeneous representation
Description:
Vision infers world properties form images. How do images depend on ... [W/sr = cd (candela)] Stefano Soatto (c) UCLA Vision Lab. 26. Isotropic Point Source ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:98
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Homogeneous representation
1
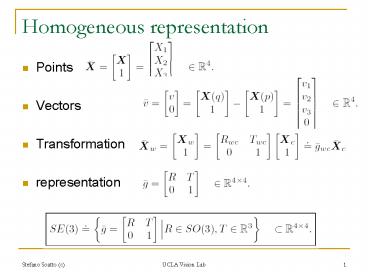
Homogeneous representation
- Points
- Vectors
- Transformation
- representation
2
Lecture 4 Image formation
3
Image Formation
- Vision infers world properties form images.
- How do images depend on these properties?
- Two key elements
- Geometry
- Radiometry
- We consider only simple models of these
4
Image formation (Chapter 3)
5
Representation of images
6
Similar triangles ltPFSgt,ltROFgt and ltPSFgtltQOFgt ?
7
Pinhole model
8
Forward pinhole
9
Distant objects are smaller
(Forsyth Ponce)
10
Parallel lines meet
Common to draw image plane in front of the focal
point. Moving the image plane merely scales the
image.
(Forsyth Ponce)
11
Vanishing points
- Each set of parallel lines meets at a different
point - The vanishing point for this direction
- Sets of parallel lines on the same plane lead to
collinear vanishing points. - The line is called the horizon for that plane
12
Properties of Projection
- Points project to points
- Lines project to lines
- Planes project to the whole image or a half image
- Angles are not preserved
- Degenerate cases
- Line through focal point projects to a point.
- Plane through focal point projects to line
- Plane perpendicular to image plane projects to
part of the image (with horizon).
13
Orthographic projection
14
(No Transcript)
15
Cameras with Lenses
(Forsyth Ponce)
16
(No Transcript)
17
Assumptions for thin lens equation
- Lens surfaces are spherical
- Incoming light rays make a small angle with the
optical axis - The lens thickness is small compared to the radii
of curvature - The refractive index is the same for the media on
both sides of the lens
18
(No Transcript)
19
Blur circle
Points a t distance are brought into focus
at distance
is imaged at point
A point at distance
from the lens
and so
Thus points at distance will give rise to a
blur circle of diameter
with d the diameter of the lens
20
Interaction of light with matter
- Absorption
- Scattering
- Refraction
- Reflection
- Other effects
- Diffraction deviation of straight propagation in
the presence of obstacles - Fluorescenceabsorbtion of light of a given
wavelength by a fluorescent molecule causes
reemission at another wavelength
21
Refraction
n1, n2 indexes of refraction
22
Solid Angle
hemisphere
radian
dq
q
Sphere 4p
23
Radiometric Terms
24
Irradiance and Radiance
Irradiance Definition power per unit area
incident on a surface
W/m2 lux
Radiance Definition power per unit area and
projected solid angle
W/m2sr
25
Radiant Intensity
Definition flux per unit solid angle
? Radiant flux W
W/sr cd (candela)
?
26
Isotropic Point Source
27
Isotropic Point Source
? Radiant flux W
All directions solid angle 4p
- Radiant flux per
- unit solid angle W/sr
r
Radiant intensity
- Note inverse square law fall off.
28
Isotropic Point Source
? Radiant flux W
All directions solid angle 4p
- Radiant flux per
- unit solid angle W/sr
r
Radiant intensity
h
- Note cosine dependency.
29
Isotropic Point Source
Point source at a finite distance
r
h
- Note inverse square law fall off.
- Note cosine dependency.
30
Irradiance from Area Sources
31
Hemispherical Source
L
32
Reflectance
The surface becomes a light source
Li(x,wi)
qi
Ei
dLrfr dEi
Reflectance ratio of radiance to irradiance
33
BRDF
34
BRDF
35
Reflection Equation
36
qi
Perfectly Diffuse Reflection
- Perfectly Diffuse Surface
- Appears equally bright from all viewing
directions (qr, fr) - Reflects all incident light, i.e.,
37
qi
Common Diffuse Reflection
- Normal Diffuse Surface
- Appears almost equally bright from most viewing
- directions (qr, fr), qr ltlt
90 - Reflects only a fraction of incident light, i.e.,
Reflectance Albedo
38
Perfectly Diffuse Reflection
Distant point light source
Lambertian cosine Law
39
Law of Reflection
40
Perfectly Specular Reflection
From the definition of BRDF, the surface radiance
is
To satisfy
41
Lambertian Examples
Lambertian sphere as the light moves. (Steve
Seitz)
Scene (Oren and Nayar)
42
Lambertian Specular Model
43
Lambertian specular
- Two parameters how shiny, what kind of shiny.
- Advantages
- easy to manipulate
- very often quite close true
- Disadvantages
- some surfaces are not
- e.g. underside of CDs, feathers of many birds,
blue spots on many marine crustaceans and fish,
most rough surfaces, oil films (skin!), wet
surfaces - Generally, very little advantage in modelling
behaviour of light at a surface in more detail --
it is quite difficult to understand behaviour of
LS surfaces (but in graphics???)
44
LambertianSpecularAmbient
(http//graphics.cs.ucdavis.edu/GraphicsNotes/Shad
ing/Shading.html)