PURPOSE - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 1
Title:
PURPOSE
Description:
Containment of the deforming femoral head in the acetabulum will improve the spherocity. ... to redirect the femoral head into the acetabulum or a Salter innominate ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:31
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: PURPOSE
1
The influence of the Proximal Femoral Growth
Plate on the Remodeling of the Hip Joint
Following Shelf Acetabuloplasty for
Perthes Disease. Marcin Domzalski (1),
MD Muharren Inan (2), MD Joe Glutting (2), PhD
Jay Kumar (2), MD (1) Dept. of Orthopaedics,
Medical University of Lodz, POLAND (2) A.I.
duPont Hospital for Children, Wilmington, DE, USA
RATIONALE
CONCLUSIONS
RESULTS
Containment of the deforming femoral head in the
acetabulum will improve the spherocity.
Containment can be achieved by performing a
proximal femoral derotation osteotomy to redirect
the femoral head into the acetabulum or a Salter
innominate osteotomy to redirect the acetabulum
to contain the femoral head anteriorly and
laterally or by a buttressing procedure called
shelf acetabuloplasty. In 1996, Yasuda and Tamura
described a simple radiographic measurement
involving the growth plate of the proximal femur
in Perthes disease and found a very good
correlation between their measurement and the
final outcome
The growth plate involvement index is a reliable
and reproducible method of measurement and may be
used as a useful prognostic factor to predict
radiographic outcome. Lower (lt0.25) values of
GPII are associated with good radiographic
outcomes. Optimal timing for shelf
acetabuloplasty based on the GPII is within 6-12
months after onset of symptoms in children older
than 5 years of age. Following containment at
least 3 years of an open growth plate is
necessary for a good radiographic result.
Involvement of the growth plate increases with
the course of the disease (Tab. 1) (Fig. 3).
Significant difference in the extent of growth
plate involvement at the time of surgery was
found between the Stulberg groups. A growth plate
involvement index below 0.25 resulted in a good
radiographic outcome( Stulberg Groups I and II),
while an index exceeding 0.25 was associated with
unsatisfactory results (Groups III and IV)(Tab.
2). This showed sensitivity of 93.2 and
specificity of 100 in predicting Stulbergs
outcomes. The results for intra- class
coefficients showed 0.89 for complete agreement
rule, and 0.95 for consistency. Growth plate
remained open longer when GPII was lower (lt0.25)
at the time of surgery (Fig. 4).
PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to assess the
extent of involvement of the growth plate in the
early stages of the disease, and try to establish
patterns of involvement that related to the final
radiological outcome after shelf acetabuloplasty,
and also to evaluate the reliability and
reproducibility of the method of measurement of
the extent of involvement of the growth plate.
Figure 3 Graph showing changes in the growth
plate involvement index with progression of the
disease
Table 1. Comparison of growth plate involvement
at the time of surgery at different stages of the
disease
METHODS
69 patients with unilateral Perthes disease were
analyzed. The mean age at the time of shelf
acetabuloplasty was 9 years. The involvement of
the growth plate was assessed on all available
radiographs from the time of onset of the disease
to the time of surgery. From these measurements a
new index (GPII) was formulated (Fig. 1 and 2).
Involvement of the growth plate was classified
into two types depending on this index. The
duration the growth plate remained open after
surgery was noted. Radiographic results were
classified by the Stulbergs criteria. Inter-
observer reliability was assessed for the method
of measurement of the extent of growth plate
involvement.
(X) Results from the ANOVA were significant
(F30.5, df 3.65, p0.001) Post hoc
analysis showed that all comparisons between
groups were significant at plt0.01)
Table 2. Comparison of growth plate involvement
at the time of surgery at different stages of the
disease
(X) Results from the ANOVA were significant
(F57.27, df 2.66, p0.001) Post hoc
analysis showed that GPII was lower in Groups I
and II then in group III (plt0.001) and group IV
(plt0.001). Difference between groups III and IV
was not significant at p5.9)
Figure 4 Time growth plate remained open after
surgery.
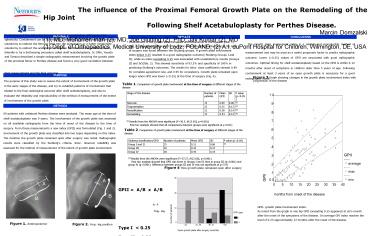
GPII A/B x A/B A- P frog- leg Type I
lt 0.25 Type II gt 0.25
GPII- growth plate involvement index. As noted
from the graph in one hip GPII exceeding 0.25
appeared at sixs month after the onset of the
symptoms of the disease. On average GPI index
reaches the level of 0.25 approximately 12 months
after the onset of the disease.
Figure 1. Anteroposterior
Figure 2. Frog- leg position