Electric Flux - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Electric Flux
The magnitude of the electric filed at a point outside the sphere ... Example 24.6: The electric field due to a thin spherical shell ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Title: Electric Flux
1
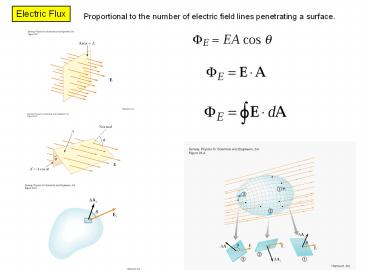
Electric Flux
Proportional to the number of electric field
lines penetrating a surface.
O
2
Gausss Law
3
Gausss Law
- Example 24.3
- What happens to the total flux through The
surface if - The charge is tripled
- The radius of the sphere is doubled
- The surface is changed to a cube
- The charge is moved to a another location inside
the surface
4
Application of Gausss Law
- Determine a surface such that
- 1.Value of the electric field is constant over
the surface - 2. The dot product between E and dA can be
expressed as a simple algebraic product
because E and dA are parallel - 3. The dot product is zero because E and dA are
perpendicular - 4. The field is zero over the surface.
Example 24.4 Electric field due to a point
charge
5
- Example 24.5 An insulating solid sphere of
radius a carries a total charge Q. calculate - The magnitude of the electric filed at a point
outside the sphere - The magnitude of the electric filed at a point
inside the sphere
6
Example 24.6 The electric field due to a thin
spherical shell
7
Example 24.7 Find the electric field a distance
r from a line of positive charge of infinite
length and constant linear charge density l
8
Example 24.8 Find the electric field due to a
non-conducting , infinite plane of positive
charge with uniform surface charge density s
9
Conductors in Electrostatic equilibrium
10
(No Transcript)
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics, the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.