Embedded MT Systems - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Embedded MT Systems
Description:
Embedded MT Systems ... Embedded MT System Design. Platforms with Plug and Play ... noisy input (degraded documents, human spelling errors) - multimodal input ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:35
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Embedded MT Systems
1
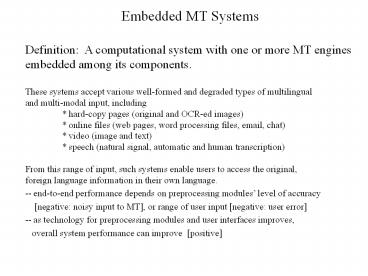
Embedded MT Systems
Definition A computational system with one or
more MT engines embedded among its
components. These systems accept various
well-formed and degraded types of
multilingual and multi-modal input, including
hard-copy pages (original and OCR-ed images)
online files (web pages, word processing files,
email, chat) video (image and text) speech
(natural signal, automatic and human
transcription) From this range of input, such
systems enable users to access the original,
foreign language information in their own
language. -- end-to-end performance depends on
preprocessing modules level of accuracy
negative noisy input to MT, or range of user
input negative user error -- as technology for
preprocessing modules and user interfaces
improves, overall system performance can
improve positive
2
Examples of Embedded MT Systems
- Background to Special Issue
- AMTA98 Workshop Diplomat (CMU), CyberTrans
(Mitre), FALCon (ARL), LinguaNet (CBS) - NAACL/ANLP00 Workshop Closed-Caption MT (Simon
- Frasier U),CLIR (JHU et al.), Riptides
(Cornell et al.) - Papers in Special Issue - Grouped by System
Designs - Preprocessor MT engine Postprocessor
- (Bangalore Riccardi, Gao et al., Lee et al.)
- User interface front end MT engine back end
- (Langlais et al., Dorr et al.)
- Informant interface MT build module MT engine
- (Levin et al., Nirenberg et al.)
- Platforms with Plug and Play Components, multiple
MT engines - (Hansen Sorenson, Voss Fisher)
3
Embedded MT System DesignPreprocessor MT
engine Postprocessor
- - Preprocessing of noisy (non-character) input
necessary - Cascading of errors through modules
4
System Design Preprocessor MT engine
Postprocessor
Bangalore Riccardi
noise
postprocess
MT Engine
Call Routing
Transcribed speech
preprocess
MT Engine
Speech Recog
Ltd domain speech
Composed FST Models
5
System Design Preprocessor MT engine
Postprocessor
Gao et al.
preprocess
postprocess
MT Engine
Speech Recog
Speech Generation
Ltd domain speech
Lee et al.
preprocess
postprocess
MT Engine
Speech Recog
Speech Generation
Read speech
noise
6
Embedded MT System DesignUser interface front
end MT engine back end
Back End
- - MT engine resides on Back End,
- User Interface is Front End GUI
- Room for further development of GUI
- that enables system developers to
- monitor how the user is making use
- of the system how to improve it
- - feedback loop developed, task-oriented MT
- all input typed by user (manual text entry
- is bottleneck, need human error correction
- or prediction or completion or constraints)
MT Engine
Front End
7
System Design User interface front end MT
engine back end
Back End
Statistical Engine
User Lexicon
Front End
L1
L2
Langlais et al. TransType
8
System Design User interface front end MT
engine back end
L2
L2
IR
Back End
MT Engine
MT Engine
Lexical Resources
L1 -gt L2
L2 -gt L1
Front End
L1
User query
Dorr, Levow and Lin
9
Embedded MT System Design Elicitation module MT
build module MT engine
- informant participates in elicitation process
during development time - vs. MT engine build-time vs. MT engine run-time
- -- MT system is built based on elicited
knowledge provided - by bilingual informant
- -- pre-established sequencing of guided
elicitation is critical - -- Standalone MT engine is result
- feedback loop allows for MT output to be viewed
by - bilingual informant system developers who can
- modify MT engine (via rules, features,
depending on engine design) - focus experimental methodology
- For low resource languages
- (these are research systems at early stage of
development) - linguistically motivated choice of elicited
knowledge
10
McShane et al. Expedition
System Design Elicitation module MT build
module MT engine
L1
MT Build Module
Elicitation Module
Learned Transfer rules
MT Engine
Language Corpus, Dictionaries
Hand- crafted Rules, forms
Interface
L2
Computational Linguist/ Computer Scientist
bilingual Informant (L1, L2)
11
Probst et al. Avenue Project
L1
MT Elicitation Module MT
Rule Learning Module Engine
Control Process
Elicitation Corpus, Dictionaries,
Parsing
Learning Process
Transfer Rules
Word-aligned, HT, elicited minimal pairs
Transfer
Learned Transfer rules
Handcrafted Rules, forms
Generation
Elicitation Interface
HT Human Translation
L2
Computational Linguist/ Computer Scientist
Bilingual Informant (L1, L2)
12
Embedded MT System Design Platforms with Plug and
Play Components, multiple MT engines
- customized for user groups during integration
time, - augmented user-specific lexicons/glossaries
- noisy input (degraded documents, human spelling
errors) - - multimodal input
- iterative development of design, includes user
feedback - focus extensibility of platform via new
technologies, - upgraded components
- multiple languages
- (these are operational systems with specific
applications) - user-provided domain knowledge (text, images,
databases)
13
Platform with Plug and Play Components, multiple
MT engines
Point-to-point communication
Back End
MT Engines
Table Translation
Knowledge Bases
Front End
L2
L1 L2
Hansen Sorenson LinguaNet
L1
14
Platform with Plug and Play Components, multiple
MT engines
Hardcopy documents
preprocess
postprocess
DocEx tasks
scan
N
OCR
MT Engines
Camera capture
Scene or View of Text
Voss et al. FALCon