Physics of Sound - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 25
Title: Physics of Sound
1
Physics of Sound
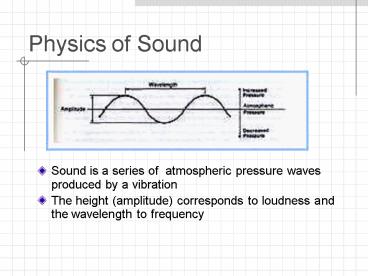
- Sound is a series of atmospheric pressure waves
produced by a vibration - The height (amplitude) corresponds to loudness
and the wavelength to frequency
2
Physics of Sound
- Loudness is determined by the amount of pressure
produced by a wave measured in decibels - An increase of 10 decibels equals twice the
volume - Threshold of hearing is the softest audible
sound, threshold of pain is 130dB. A normal
conversation is 65 dB above the threshold of
hearing - Dynamic range highest to lowest point
3
Physics of Sound
- Frequency determines the pitch of a sound
- The cycles of waves are measured in hertz (Hz) or
cycles per second. Western instruments use 440
Hz as a standard for the pitch A - Doubling the frequency octave
- Ear is more sensitive to midrange frequencies
than to low or high frequencies
4
Physics of Sound
- Frequency response refers to how an audio system
or microphone responds to various frequencies - Good audio recorders are capable of flat or equal
response to all frequencies, consumer camera mics
may not be - Using equalizers to change the frequency response
for given ranges of any sound changes the nature
of that sound
5
Sound Equipment
- Camcorder mics work well for short distances, the
inverted square rule - Professional camcorders give you audio level
control, consumer ones often dont - Using mics outside the camcorder offers more
flexibility in shot choice and the chance to have
a master soundtrack
6
Sound Equipment
- Microphone types
- - dynamic or moving coil are quite rugged,
resistant to hand noise, require no battery - - condenser mics are more sensitive and require
a power source - - electret condenser mics have a permanently
charged capacitor and may be small and require no
power supply
7
Sound Equipment
- Microphone directionality
- - omni-directional mics respond equally to
sounds from any direction - - cardioid mics are most sensitive to sounds
comimg from the front, less to the sides, and
least to the back - - super-cardioid mics are insensitive to sounds
not coming from the front
8
Sound Equipment
- Microphone directionality
- - polar diagrams show sensitivity from above
- - hyper/super cardiod (shotgun) mics do not
magnify sound, but exclude it
9
Sound Equipment
- Lavalier mics or lapel mics
- - useful for recording individuals in noisy
environments - - the resonation of sound in the chest can make
the voice sound low and unnatural
10
Sound Equipment
- Stereo Mics
- - X-Y configurations are usually built into
camcorders - uses two cardioid mics each pointed 45 to the
side
11
Sound Equipment
- Stereo mics
- - M-S (mid-side) mics uses a cardioid mic facing
forward and a figure 8 mike for the sides - - useful for mixing down if you have good
editing equipment
12
Recording Techniques !
- Controlling microphone noise
- - wind across the microphone creates loud
rumbles, crackle, and pops - - wind screens and blocking objects help
- - handling of the microphone or touching of the
camera and vibrations from the tripod can also
create noise
13
Recording Techniques
- Microphone distance
- - ideally 1-3 feet, camcorder mics record speech
accurately up to about 5 or six feet - - too close, breathing, s sounds, pops, bass
tone proximity effect - - to far away means more ambience sound
- - compromised sound perspective can be adjusted
with reverb
14
Recording Technique !
- Digital recording levels and overmodulation
- - overmodulated (too loud) analog sounds becomes
crackly, with digital recording, it is distorted
and clipped off - - digital recordings should be concerned more
with recording too loud, though camcorders dont
overmodulate easily
15
Recording Technique
- Camcorders and Automatic Level Control
- - ALC or automatic gain control works by
adjusting the recording level based on the signal
it receives - - test the sound signal in your environment to
see of any radical level changes take place
16
Recording Technique
- Ambient sound
- - the background sound in any production can be
minimized by turning off appliances, choosing
quiet times and spaces, or using sound blankets - - record about a minute of room tone at every
location - - ambient sound should be consistent from one
shot to the next
17
Recording Technique !
- Noisy locations
- - get the mic as close to the source as possible
- - use lavalier mics
- - use directional mics like shotgun mics and
position your subject outside of a major noise
source - - ideal to have two sound sources, subject and
background
18
Recording Technique !
- Acoustic space
- - live spaces reflect sound and cause echos,
such as empty rooms with hard smooth walls and
floors - - dead spaces absorb the sound, such as carpeted
rooms with lots of furniture and irregular walls.
- - outdoor spaces can be dead because they have
no reflecting surfaces
19
Recording Technique
- Controlling reflected sound
- - a live room can produce a muddled
reverberating sound - - you can minimize reverberation
- - close directional
- - deaden walls and floor with
curtains/blankets - - you may use reflected sound to your advantage
20
Recording Techniques
- Position mics to avoid reflected sound from the
camera
21
Recording Technique
- Narration
- - voice over tracks are ideally recorded in
sound proof environments. A make shift one can
be made out of sound blankets - - off screen narration gives the video a sense
of omniscience, objectivity, and predestination
22
Recording Technique !
- Capturing sound effects
- - sounds directly captured from the environment
- - sounds from a sound library or from the
internet - - foley sounds
23
Sounds Impact on Image
- High pitch tension, suspense
- Low pitch less tension, mystery
- Loud sounds intense, threatening
- Quiet sounds delicate, hesitant
- Fast tempo more tension
- Silence highlights, isolates image, can
represent death, sticks out if a mistake
24
Sounds Impact on Image !
- Sound effects both atmospheric and diagetic
- Off screen sounds can expand the film world
beyond the frame - Sounds can be used like motiffs and serve
symbolic functions - Sounds can be used as to aid transitions and
foreshadow action
25
Sounds Impact on Image !
- Music
- - sets a mood
- - suggest historical references, a time period
- - can suggest locales, classes or ethnic groups
- - used as foreshadowing and musical warnings
- - atonal music can create anxiety
- - can reference other settings of music
- - music can provide ironic contrasts with image