The Computer System - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 82
Title:
The Computer System
Description:
A computer is an electronic device, operating under the control of instructions ... virtually any type of video device, such as VCRs, televisions, and camcorders. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:235
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: The Computer System
1
The Computer System
2
What is a Computer?
- A computer is an electronic device, operating
under the control of instructions stored in its
own memory unit, that can accept data (input),
process data arithmetically and logically,
produce results (output), and store the results
for future use.
3
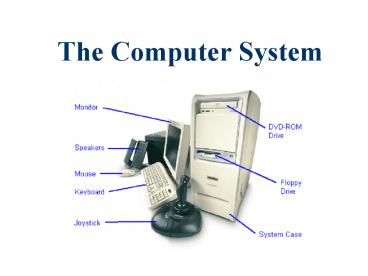
Components of a computer
- Basic Components
- Input Devices
- System Unit
- Output Devices
- Storage Devices
- Other Components
- Peripheral Devices
- Communication Devices
4
(No Transcript)
5
Strengths of Computers
- Speed
- Reliability
- Accuracy
- Storage
- Communication/Connectivity
6
Types of Computer
- Microcomputer (PC)
- Workstation
- Minicomputer
- Mainframe Computer
- Supercomputer
Increasing speed processing power!
7
Data Representation
- Bits
- off or on digital value, short term for binary
digits. - Bytes
- a group of eight bits, a unique code can be
assigned to 256 different data possibilities.
(e.g. 01000001 represents the letter A.)
8
Coding Scheme
- ASCII (American Standard Code for Information
Interchange) - 8 bits used in many PC minicomputer.
- EBCDIC (Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange
Code) - 8 bits used in Mainframe Computer
- Unicode
- 16 bits
- can represent gt 65000 characters
9
1. System Unit
10
Components of System Unit
- Motherboard
- Central Processing Unit (CPU)
- Memory
- Upgrade sockets
- Co-processor
- Buses
- Expansion Slot
- Ports connectors
11
The Central Processing Unit
- It is the brain of a computer system
- The CPU
- receives input.
- interprets instructions provided by programs.
- directs other components of the system to act.
- processes data.
- controls output.
12
The Central Processing Unit
- Control Unit
- It coordinates the flow of data and instructions.
It contains a clock that generates a uniform
stream of electrical pulses that synchronize the
operating of the CPU and other computer components
Note The control unit controls the computer by
repeating 4 operations, called the machine cycle.
The 4 operations are fetching program
instructions from memory decoding the
instructions into commands that the computer can
process executing the commands and storing the
results in memory
13
The Central Processing Unit
- Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU)
- It performs calculations and comparisons of data.
14
The Central Processing Unit
- Registers
- They hold program instructions, data values, and
memory locations as the computer executes a
program.
15
The Central Processing Unit
Buses They are electrical pathways that carry
signal (bits) between a CPUs components and
outside devices.
16
Multiprocessing
- Large computer systems, as well as newer
workstations and network servers, frequently
contain more than one central processing unit. - Multiple CPUs enable the computer to execute more
than one instruction or process more than one
program, at the same time.
17
Main Memory
- Before programs are executed or data processed,
they must first enter into main memory. - Main memory holds information read from disk or
captured by input devices. - The CPU then moves information from the main
memory into its registers for processing.
ROM
CACHE
RAM
18
Random Access Memory (RAM)
- Integrated circuit containing data that can be
read and written by the microprocessor or other
devices. - Volatile - programs data stored in RAM are
erased when the power is off.
19
Read Only Memory (ROM)
- Chips that store information or instructions that
can be read and used, but cannot be changed. - Non-volatile - retains its contents even the
power is turned off. - The instructions to start the computer are on a
special chip known as a ROM BIOS chip (Basic
Input/Output System).
20
Cache Memory
- Cache memory is a specialized chip used with the
computer's memory. - Cache chips are faster and more expensive than
regular RAM chips. - The computer stores the most frequently used
instructions and data in cache. Cache has a
relatively small storage capacity but can
significantly increase the system's speed.
21
In summary, memory
- accepts and holds program instruction and data
- acts as the CPUs source for data and
instructions and as a destination for operation
results - holds the final processed information until it
can be sent to the desired output or storage
devices, such as printer or disk drive
22
Motherboard
- A circuit board that contains most of the
electronic components of the system unit.
CPU Slot (PII)
BIOS Chip
DIMM Sockets for Memory
23
Internet References How microprocessor works
(http//www.intel.com/education/mpuworks/index.htm
) Introduction to PC (http//www.pcguide.com/intro
/index.htm) Computer Hardware (http//www.ied.edu.
hk/has/comp/component/index.htm) Toms Hardware
Guide (http//www.tomshareware.com/guides/cpu.html
) Multimedia Tutorials (Available in SLCSS
Intranet Only) Lab 1 Computer Fundamentals Lab
2 Central Processing Unit
24
2. Input Devices
25
Input Devices
- Input devices, such as keyboards or scanners, are
hardware components that capture, collect, and
transmit data and programs to the computer in a
form that computer can understand. - Input devices transmit the input to the computer
in a series of electronic pulses representing
bits, or digits, of the binary code.
26
Types of Input
- Data
- raw facts that a computer receives and processes
to produce information - Programs
- instructions that direct the computer operations
- Commands
- key words that direct the computer to perform
certain activities - User Responses
- data a user enters to respond to a question or
message.
27
A. Keyboard
- The most commonly used input devices.
- Contains alphanumeric, cursors and function keys.
28
- Function Keys, labeled from F1 to F12, allow user
to quickly access commands and functions, such as
saving a document or calling up a programs Help
feature. - Cursor-control Keys govern the movement of the
cursor on the screen. They include Up Arrow, Down
Arrow, Left Arrow and Right Arrow key on the
keyboard. - Special Purpose Keys are used in conjunction with
other keys to enter commands into a computer.
Control (Ctrl), Alternate (Alt) and Shift keys
are example of special purpose keys.
29
- Toggle Keys are keys that, when pressed,
activates a certain mode or condition, and when
pressed again, deactivates the condition. The Num
Lock key, Cap Lock key and the Scroll Lock key
are examples of toggle keys. (For example,
pressing the Cap Lock key will cause all the
alphanumeric characters to appear in capitals
without holding down the Shift key.) - Numeric Keypad, located in the far right portion
of the keyboard, is used for entering numbers
quickly and for performing the same operations as
a calculator.
Not all keyboards have the same layout. Most
keyboards have adopted the so-called QWERTY
layout for the alphanumeric keys.
30
Types of Keyboard
31
B. Pointing Devices
- Many people use pointing devices instead of
keyboards whenever possible. - Pointing devices minimize the amount of typing
(and the number of errors).
32
Mouse
- Palm-sized pointing devices
- a ball on the bottom senses its movement
- various actions can be preformed by moving the
pointer and then pressing one of the buttons on
top of the mouse.
33
Types of Mouse
34
Mouse Interfaces
35
Trackball
- Up-side down mouse
- user rotates the ball itself while clicking
nearby buttons
36
TrackPoint
Touchpad
The mouse is not practical for people using a
notebook computer in a small space. Track Point
or Touch pad is therefore used instead to control
the pointer.
37
Touch-Sensitive Screens
- Touch screens enable the user to select an option
by pressing a specific part of the screen. - Touch screens are commonly used in grocery
stores, fast-food restaurants, and information
kiosks.
38
Joysticks
- Use the movement of a vertical stem to direct the
pointer.
39
C. Pen Input Devices
- Input data with hand written characters, select
items by pressing the pen against the screen, and
use gestures, which are special symbols, to issue
commands.
40
Light Pen
- Used to select processing options or to draw on
the screen
The tip of a light pen contains a highly
sensitive photoelectric cell. When the light pen
is pointed close to the screen, the photoelectric
cell detects the light emitted from the exact
spot the pen is touching. This accuracy makes
light pens very popular among engineers and
draftsmen who use computer-aided design (CAD)
software to create blueprints and drawings of
products or construction projects.
41
Digitizing Tablet
- A digitizing tablet consists of a grid on which
designs and drawings can be entered. - Most tablets are pressure-sensitive, and the
user draws directly on the tablet using a special
pen called a stylus.
- Digitizing tablets are used to design cars,
buildings, medical devices, and robots.
42
Chinese Handwriting Recognition Device
- Used for inputting and recognizing Chinese
handwriting
Nowadays, sophisticated Chinese handwriting
recognition system also contains voice
recognition function.
43
D. Scanning Devices
44
Image Scanner
- Electronically capture an entire image convert
it into digital form that can be processed by a
computer
45
(No Transcript)
46
Bar Code Reader
- Bar code consists of a set of vertical lines and
spaces of different widths - Universal Product Code (UPC) is very common
47
Magnetic Ink Character Recognition (MICR)
- Use a special ink that can be magnetized during
processing - MICR is used by the banking industry as a means
of processing checks it receives in every day.
48
Optical Character Recognition
- a system of producing machine-readable code on a
data source item and reading that code by means
of optical scanning devices.
- OCR software can be installed in a computer to
perform character recognition.
49
Optical Mark Recognition
- Optical marks are the filled-in shape, usually
ovals or rectangles, on scan sheets. - The data collected on the scan sheets are
translated into binary form by an optical mark
reader (OMR)
Use lead pencil to mark on scan sheet
Feed the scan sheets into the OMR
50
Smart Card
- A smart card, often the size of a credit card,
contains a built-in microprocessor and memory
that identify the card (and its owner) and
assists in financial and other transactions. - Its primary advantage is increased security the
information can only be read by an authorized
user with appropriated password.
51
E. Multimedia Input Devices
52
Voice Input Devices
- A voice input device has two functions
- First, it can simply record and play back the
voice inputted by the user. - Secondly, it can record a human voice, then with
appropriate voice recognition software, convert
the voice input to ASCII characters.
53
Digital Camera
- Record images in a form that can be stored by a
computer. - Some digital cameras resemble traditional cameras
and are portable. Some are connected directly to
a computer.
54
Video digitizers
- Video digitizers can capture input from virtually
any type of video device, such as VCRs,
televisions, and camcorders. - Audio digitizers can digitize music or voice from
a microphone.
55
Internet References Jans Illustrated Computer
Literacy 101 (http//www.jegsworks.com/Lessons/les
sonintro.htm) Introduction to PC
(http//www.pcguide.com/intro/index.htm) Computer
Hardware (http//www.ied.edu.hk/has/comp/compnent/
index.htm) Toms Hardware Guide
(http//www.tomshardware.com/guides/cpu.html) Mul
timedia Tutorials (Available in SLCSS Intranet
Only) Lab 3 Input/Output Devices
56
Storage Devices
57
Storage Devices
- Also called secondary storage
- store data programs permanently for future use
- can be used as both input output devices
58
Magnetic Disk Storage
- Most widely used storage medium
- consists of a round piece of plastic or metal,
the surface on which is covered by a magnetic
materials. - e.g. floppy disks, hard disks and removable disk
cartridge
59
Floppy Disk
- Random-access storage medium
- provides storage of 1.44MB data
- A circular piece of thin plastic that is coated
with magnetic material - the circular piece of plastic is enclosed by a
rigid plastic shell - Formatting prepares a floppy disk for storage by
defining the tracks, cylinders, and sectors on
the disk surface - time required to locate data and transfer it to
memory is called the access time.
60
Data is recorded on disk in concentric circular
bands called tracks. The tracks on a disk are
similar to the grooves on a phonograph record.
Each track is divided into pie-shaped wedges
called sectors. Two or more sectors combine to
form a cluster.
61
Most computers maintain on the disk a table with
the sector and track locations of data. This
table, the file allocation table (FAT), enables
the computer to locate data easily.
62
Structure of a Floppy Disk
63
Hard Disks
- Fixed in the System Unit
- Consists of one or more rigid platters coated
with a magnetic material - the platters, read/write heads, and the access
arms that move the heads across the disk surface
are all enclosed in an airtight, sealed case
64
- Access time for a hard disk is significantly less
than that for a floppy disk because a hard disk
spins faster and unlike a floppy disk, a hard
disk is spinning constantly (7200 revolutions per
minute). - hard disks are permanently encased within the
disk drive in a sealed environment free from dust
and dirt. The disk can spin very rapidly, with
the read/write head "floating" above the disk's
surface.
65
Hard Disk Interfaces
- To connect a hard disk to a microcomputer
motherboard, you must have a hard disk interface.
- This component includes circuitry that conforms
to a standard recognized by both the hard disk
and the motherboard manufacturer. - Common standards are Integrated Drive Electronics
(IDE) and Small Computer System Interface (SCSI).
66
Removable Disks
- Provide both the storage capacity and fact access
time of hard disk and the probability of floppy
disks. - Examples
- Iomegas ZIP (100, 250, 750 MB)
- Imations Superdisk (120MB)
- Sonys MO Disk (49GB)
67
Maintaining Stored Data
- To prevent loss of data, 2 procedures should be
performed regularly - Backup
- process of creating a copy of important programs
and data - Defragmentation
- process of reorganizing data stored on a disk so
that files are located in contiguous (adjacent)
clusters.
68
CD-ROM and Optical Disks
- By using laser technology, optical disk can store
large quantities of data - a high power laser writes data on an optical disk
by burning microscopic holes on the disk surface - a lower power laser reads the data by reflecting
light off the disk surface. The reflected light
is converted into a series of bits
69
- CD-ROM
- CD-Read Only Memory
- can store 650 MB data
- suitable for reference material such as
encyclopedias, catalogs and pictures - CD-R
- CD-Recordable
- write once, read many
- CD-RW
- CD-Rewritable
- erasable write many, read many
- MO
- Magneto-Optical
- Floptical (Optical Magnetic)
70
Magnetic Tape
- Consists of a thin ribbon of plastic, one side of
which is coated with a material that can be
magnetized to record binary data. - A sequential storage media (must write and read
records on after another) - usually cartridge tape
- serves as a primary means of
- backup,
- a method of transferring data between system, and
- a cost-effective way to store data that does not
have to be accessed immediately
71
Other types of Storage Devices
- PC Cards (PCMCIA)
- Compact Flash Memory Card
- Memory Stick
- Smart Card
72
Output Devices
73
Types of Output
- Output is data that has been processed into a
useful form called information. - Report
- Computer Graphics
- Audio Output
- Video Output
74
Types of Output
- Most output can be divided into 2 categories
Soft copy hard copy. - Soft copy is what you see on the monitor. Soft
copy is temporary. - Hard copy can be touched and carried. Hard copy
is usually some form of paper output.
75
Monitors
- A visual output device of a computer.
- Monitor output is a most common form of soft copy.
CRT Monitor
Flat-panel Monitor
76
Resolution of Display
- Images on the screen are created by
configurations of dots called pixels (picture
elements) - The more the pixels, the better the resolution of
the image - SVGA pixel configuration of 800 by 600
- XVGA pixel configuration of 1024 by 768
77
Printers
- Produce permanent output (hard copy)
- consists of 2 main types impact non-impact
78
Impact Printers
- Line printers
- they can produce only text--no graphics.
- Chain printers
- Dot Matrix Printers
- The most common character printers create images
by using a dot pattern.
79
Non-impact Printers
- Laser Printer
- work in the same manner as copy machines a laser
beam creates electrical charges that attract
toner to form an image and transfer it to paper.
Color Laser Printer
Laser Printer
80
- Inkjet Printers
- significantly less expensive than laser printers
- relatively low resolution
- Electronically charged ink is sprayed through a
jet nozzle and passed through an electronic
field, which deflects the ink to form a
dot-matrix character
81
Other Output Devices
- Plotter
- produce high-quality line drawings
- A continuous-curve plotter is used to draw maps
from stored data.
82
- LCD Projectors
- project a computer image onto screen
- Voice Output Devices
- generate spoken words from text
- Computer Output microfilm (COM)
- records output as microscopic images on roll
film. - Facsimile (FAX) Machine
- transmit receives document over telephone line.
- Multifunctional Devices (MFD)
- can print, copy and fax