VI. Other Agents - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 22
Title: VI. Other Agents
1
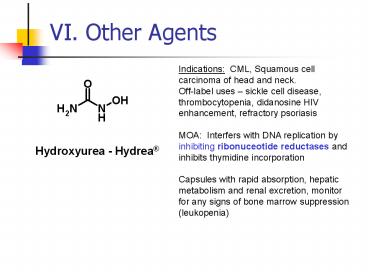
VI. Other Agents
Indications CML, Squamous cell carcinoma of
head and neck. Off-label uses sickle cell
disease, thrombocytopenia, didanosine HIV
enhancement, refractory psoriasis MOA
Interfers with DNA replication by inhibiting
ribonuceotide reductases and inhibits thymidine
incorporation Capsules with rapid absorption,
hepatic metabolism and renal excretion, monitor
for any signs of bone marrow suppression
(leukopenia)
2
Ribonucleotide Reductase
NADPH H
Can you name another anticancer agent that
interferes with this enzyme?
Gemcitabine HCl - Gemzar
Also Fludribine Pentostatin
3
Other Agents
Indication Treatment of inoperable adrenal
cortical carcinoma MOA adrenal cytotoxic agent
that suppresses adrenal function and production
of adrenal steroids both directly at the adrenal
cortex and via peripheral metabolism of
steroids Discontinue use in cases of shock and
severe trauma Tablets, highly lipid soluble and
can be detected for up to 10 weeks, hepatic
metabolism - use caution in impairment Can cause
brain damage and depression Indications
Esophageal and endobronchial non-small cell lung
cancer Photodynamic therapy in which drug and
laser light are administered at the same time,
tumor tissue harbors the agent selectively and
for longer periods than normal tissue MOA
porfimer is a photosensitizing agent that is
injected into the tissue followed by 630 nm laser
light generating oxygen free radicals (singlet
oxygen), superoxide and hydroxide radicals
causing tissue damage and tumor death Last resort
drug for palliative treatment
4
Other Agents
- Enzymes - Asparaginase - Elspar and
PEG-Asparaginase - Oncaspar - Asparaginase is produced by overexpression in
Eschericia coli or Erwinia carotovora accordingly
it is a foreign protein with high antigenicity - The immunogenicity of the protein is decreased by
covalently binding polyethylene glycol to the
protein - Indications Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL),
Adult ALL, Chronic ALL - MOA Asparginase is responsible for the
hydrolysis of L-asparagine (a non-essential amino
acid) to L-aspartic acid ?ALL tumor cells lack
L-asparagine synthase, the enzyme that produces
L-asparagine from L-aspartic acid and
L-glutamine. So, ALL tumor cells can only get
L-asparagine by diffusion from the environment
PEG-asparaginase depletes L-asparagine from the
tumor cell resulting in cytotoxicity - Some toxicity does occur to rapidly dividing
normal cells that are dependent on exogenous
L-asparagine, Resistance arises due to tumor
cells inducing production of asparagine
synthetase so they can produce their own
L-asparagine - Half-life (t1/2) of PEG-modified enzyme and
normal Asparaginase PEG modified enzyme 2.6
to 7.1 days, Normal bacterial enzyme 0.6 to 1.2
days - Adverse reactions and contraindications too
many to list - Drug interactions Note Can decrease the
effects of methotrexate (Rhumatrex), - Administration with vincristine (Oncovin) ?
severe erythropoiesis disruption and neuropathy
5
Other Retinoids
Indications Induction of remission of acute
promyelocytic leukemia containing the PML/RARa
gene translocation genetic defect MOA a
non-cytolytic agent that induces maturation of
primitive promyelocytes derived from the leukemic
clone cell that decreases proliferation. Allows
for repopulation of normal periperal blood cells
and hematopoietic cells achieving complete
remission Retinoid toxicity headache, fever,
weakness, fatigue Teratogenic USE
contraception Indications Cutaneous T-cell
lymphoma MOA binds retinoid receptors that
function as transcription factors that regulate
genes that promote cellular differentiation and
proliferation - inhibits growth and induces tumor
regression Hepatic metabolism with heptobiliary
excretion routesuse caution in hepatic
impairment, Retinoid toxicity headache, fever,
weakness, fatigue Teratogenic USE
contraception
6
Newer agents TK inhibitors
- Imatinib mesylate GleevecTM
- Indications chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) in
blast crisis, accelerated phase or in chronic
phase after failure of interferon-alpha therapy - MOA Tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TK controls cell
growth and differentiation). Induces apoptosis
in CML cells that express an abnormal Bcr-Abl TK - Metabolism hepatic CYP3A4 is the major CYP mode
that demethylates the drug followed by primarily
fecal elimination - Drug interactions CYP3A4 inhibitors increase
plasma levels, imatinib is a potent competitive
inhibitor of CYP 2C9, 2D6, 3A4, - Side effects fluid retention and edema, GI
irritation, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia,
hepatotoxicity (monitor liver enzymes), allergic
reactions, decreased urination - Supplied as 100 mg capsules (400 mg daily),
contraindicated is breast feeding
7
Newer agents - TK inhibitors
- Gefitinib Iressa (AstraZeneca)
- Non Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
- NSCLC expresses high levels of epidermal growth
factor receptor (EGFR) on its cell surface - EGFR is a surface receptor with a tyrosine kinase
? stimulate growth and proliferation of cancer
cells - MOA unknown believed to have activity against
EGFR tyrosine kinases - Diarhea (48), rash (43), acne (25), dry skin
(13), NV (12) - Undergoes extensive hepatic metabolism primarily
through CYP3A4 Many drug interactions! - Bleeding with warfarin!
- 250mg once daily. 30 pills 1750
8
Monoclonal Antibody
9
(No Transcript)
10
Monoclonal Antibodies
- Trastuzumab - Herceptin
- Indication Breast carcinoma
- A recombinant DNA-derived humanized monoclonal
antibody specific for the HER2 protein located on
the surface of metastatic breast carcinomas - Metastatic tumors of the breast are large
overexpressors of the HER2 protein a
transmembrane protein related to epidermal growth
factor - The term humanized means the antibody contains
more human protein sequence and is therefore less
immunogenic in nature - Overexpressed/produced in Chinese hamster ovary
cell cultures - Binding to the HER2 protein invokes antibody
dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity via natural
killer cells and monocytes and prevents tumor
cell proliferation - IV use only
- Contraindication Presence of Human Anti-Human
antibody
11
Monoclonal Antibodies
- Rituximab - Rituxan
- Indication non-Hodgkins lymphoma (B-Cell
Lymphomas) - Murine/tumor monoclonal antibody specific for
CD20 antigen located on the surface of B-cell
precursor and mature B lymphocytes gt90 of the
B-cell non-Hodgkins lymphomas - CD20 regulates early activation process for cell
cycle initiation and differentiation, may
actually be a calcium ion channel - The Fab portion of the antibody recruits immune
functions that mediate cell lysis or apoptosis,
blocking CD20 prevents cell cycling and
differentiation - Overexpressed/produced in Chinese hamster ovary
cell cultures - IV use only
- Contraindication Presence of Human Anti-Human
antibody or Human Anti-Chimeric antibody - Drug interactions Patients taking
antihypertensives should discontinue use 12 hrs
before infusion to prevent hypotension
12
Monoclonal Antibodies
- Gemtuzumab Ozogamicin- Mylotarg
- Indication acute myeloid leukemia (AML)
- A murine/humanized monoclonal antibody
covalently linked with the cytotoxic antitumor
antibiotic calicheamicin (isolated by Drew
Minnick from the fermentation goop of the
bacterium Micromonospora echinospora sp.
calichensis) - Highly toxic agent severe anemias
- MOA Antibody portion binds selectively to the
CD33 antigen present on gt80 of the human
leukemias - The bound complex is taken into leukemia cells
where lysozyme releases the calicheamicin which
binds to the minor groove of DNA resulting in DNA
double strand breaks and cell death - IV slow infusion only
- Contraindication Presence of Human Anti-Human
antibody or Human Anti-Chimeric antibody - Drug interactions unknown
13
Immunostimulants
- Alter host response to Cancer
- Promotes non-malignant growth
- Interferon a-2a (Roferon-A) Interferon a-2b
(Intron-A) - Naturally occurring proteins (viral stimulus)
- Recombinant DNA proteins
- Enhance immune response to cancer
- Alter gene expression (keep cells dormant)
- Best with hematologic cancers
- I.M. or S.C. administration
- Flu-like symptoms
14
Immunostimulants - Interleukins
- Interleukin-2 is also known as T-cell growth
factor - This compound results in the direct activation of
cytotoxic T-lymphocytes and natural killer cells
- immunosurveillance to removed foreign,
viral-infected and cancer cells - Antagonists or antibodies to IL-2 may prove
useful as immunosuppressive agents for
transplantation of organs - Products
- Aldesleukin - Proleukin
- Non-glycosylated version of the natural IL-2 with
several amino acid changes - Extremely toxic agent
- Interaction with the IL-2 receptor on immune
cells leads to a cascade release of many
interferons, interleukins and tumor necrosis
factor which leads to a proliferation of B- and
T-killer cells - Indications acute myelogenous leukemia, bone
marrow transplant, HIV, leprosy, malignant
melanoma, non-Hodgkins lymphoma, renal cell
carcinoma - IV or SC administration
15
Immunostimulants - Interleukins
- Denileukin Deftitox - Ontak
- A cytotoxic fusion protein produced in an E. coli
expression system - Consists of the highly toxic fragments A and B of
diphtheria toxin covalently linked genetically to
recombinant IL-2 - Indications cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, mycosis
fungoides, non-Hodgkins lymphoma, psoriasis - Mechanism of action this toxin linked IL-2
analog is cytotoxic against cells that express
certain high-affinity IL-2 receptors containing a
three protein complex designated
CD25/CD122/CD137. Upon binding to these
receptors, the IL-2 toxin complex is internalized
by endocytosis. The A-fragment of diphtheria
toxin is cleaved and inhibits cellular protein
synthesis leading to cell death in hours.
Accordingly, this drug is active against
malignancies and cells that express the high
affinity IL-2 receptor. - Drug Interactions None known at this time---has
no effect of Cytochrome P450 enzymes
16
Immunostimulants
Indications adjunctive treatment along with
5-FU after surgical resections in Dukes stage C
colon cancer MOA Immunomodulator that restores
depressed immune function by stimulating antibody
production, enhances T-cell responses, increases
phagocytosis, chemotaxis and mobility of
neutrophils, macrophages and monocytes Tablet
dose form, extensively hepatically metabolized
with renal excretion, monitor blood constituents
and hepatic function---may cause
agranulocytosis Avoid alcohol use due to
disulfiram like reaction Notify MD of any
flu-like symptoms or malaise
17
Immunostimulants
BCG, intravesical (live, attenuated mycobacteria
Bacillus of Clamette and Guerin strain of
Mycobacterium bovis) Pacis, TICE BCG,
TheraCys Indications Carcinoma in situ in the
urinary bladder with papillary tumors Caution
health care workers have been infected due to
needle sticks and lacerations treat this
material as a biohazardous agent with respect to
handling and disposal MOA Intravesical
delivery in the bladder results in infection that
promotes local acute inflammatory responses and
sub-acute granulomatous reaction with macrophage
and lymphocyte infiltration results in a
T-lymphocyte based anti-tumor activity If a
cough develops contact MD immediately due to
systemic BCG infection notify MD of any increase
in normal symptoms of the patients disease Do
not use in UTI, feverclosely monitor for
infections Always void while in the seated
position (no standing guys) into undiluted bleach
to prevent spreading the organisms to other
people
18
Angiogenesis Inhibitors
- Promising Research Area
- Fights primary tumor only!
- Decrease tumor growth
- Inhibit new blood vessel growth
- angiopoietin-1
- basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF)
- vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF).
- Angiostatin - protein
- Binds ATP synthase receptors
- Inhibits metasteses (mice)
- Endostatin - protein
- Causes primary tumor regression (mice)
19
Radiopharmaceuticals
- 1. Chromic Phosphate (32P) - Phosphocol P32
- Indications intracavity injection for treatment
of peritoneal or pleural effusions in metastatic
cancer, also interstitial injection, NOT for IV
use - MOA b-particle radiation emission with a t1/2
of 14.3 days - Side effects transitory radiation sickness,
N/V, bone marrow depression - 2. Sodium iodide (131I) - Iodotope
- Indications Selected cases of thyroid cancer
(only certain cell types will take up) or
treatment of hyperthyroidism - MOA oral use 90 b-particle and 10
g-particle radiation emission with a t1/2 of 8
days - kidney excreted - Drug uptake is decreased by recent iodine
ingestion or via contrast agents - Side effects transitory radiation sickness -
N/V, temporary hair thinning, sore throat, cough,
hematological depression possiblewatch for
infections - May take up to three months for positive results
to appear in treatment of hyperthyroidism - 3. Sodium phosphate (32P) - generics
- Indications Leukemias and skeletal metastatic
disease - MOA injection only b-particle radiation
emission with a t1/2 of 14.3 days - Side effects transitory radiation sickness -
hematological depression possiblewatch for
infections
20
Radiopharmaceuticals
- 4. Strontium-89 Chloride - Metastron
- Indications painful skeletal metastatic disease
- IV injection only
- MOA pure b-particle radiation emission with a
t1/2 of 50.5 days - 2/3 excreted in the urine and 1/3 fecal excretion
with bone turnover rate of every 14 days---use
caution in renal failure - Side effects transitory radiation sickness,
N/V, bone marrow depression - Bone pain worst first 2-3 days following therapy
- increase pain meds - Use a normal toilet (not a urinal) to prevent
spread of radiation the first week - 5. Samarium Lexidronam (153Sm) - Quadramet
- Indications painful skeletal metastatic disease
confirmed by bone scans, rheumatoid arthritis,
ankylosing spondylitis - IV injection only
- MOA b-particle radiation emission (640-810 keV)
and g-particle radiation emission - Renally excreted within 24 hours
- Side effects transitory radiation sickness,
N/V, bone marrow depression - Use a normal toilet to prevent spread (12 hours),
store contaminated clothing for several weeks ?
radiation decay - Always verify dosage before giving any of these
agents to a patient
21
Radiopharmaceuticals
- Brachytherapy radioactive implants
- The implants or seeds are tiny, sealed capsules
that contain precise dosages of a radioactive
element - Typically 60-100 seeds are implanted into the
cancerous tissue in a procedure called
interstitial brachytherapy - Trade name is PharmaSeed sold by Syncor
International Corporation - Contain either Iodine-125 or Palladium-103
- Indicated for prostate cancer therapy
22
Radiopharmaceuticals
- Indium-111 or Yttrium-90 radiolabled Ibritumomab
Tiuxetan Zevalin - First (approved March 26, 2002) Smart bomb
approach to targeting radiation directly to
cancer cells - The first radioimmunotherapy drug which is a 3
part immunoconjugate consisting of 3 parts - Ibritumomab (a murine IgG1 kappa monoclonal
antibody targeted against the antigen CD20
present on the surface of normal and malignant B
lymphocytes) - The antibody is coupled via a stable thiourea
covalent bond to the linker-chelator group called
Tiuxetan - The radioisotope 111In (electron capture decay
producing a gamma ray 2.81 day half-life) or
90Y (Beta particles 5 mm distance 2.67 day
half-life) - Indications Resistant or recurrent form of
non-Hodgkin lymphoma called low-grade or
follicular lymphoma Two treatment shots a test
shot to see if the lymphoma is responsive and one
week later a real dose - Toxicity possible Infection due to loss of
white cells and platelets requiring transfusions
and a possible first dose fatal infusion reaction
(80 of the patients) hypoxia, pulmonary
infiltrates - ARDS, MI, cardiogenic shock - the
antibody portion is produced in Chinese hamster
ovary cells