Lecture 09: OLAP - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Lecture 09: OLAP
Description:
Data is up-to-date. Mostly updates. Need to support high levels of update transactions ... date, country. product, date, country. 0-D(apex) cuboid. 1-D cuboids ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:93
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Lecture 09: OLAP
1
Lecture 09OLAP
- www.cl.cam.ac.uk/Teaching/current/Databases/
2
22
/ Microsoft SQL Server 2005 // By the way,
it is just VHVyaW5nIG1hY2hpbmU -) /WITH
SubQuery(t, s, a, b) AS( SELECT 0, 's', CAST
('lt' AS VARCHAR(8000)), CAST ('110110' AS
VARCHAR(8000)) UNION ALL SELECT t 1,
newS, CASE mv WHEN 'l' THEN
SubString(curr.a, 1, Len(curr.a) - 1) WHEN
's' THEN SubString(curr.a, 1, Len(curr.a) - 1)
newZ WHEN 'r' THEN SubString(curr.a, 1,
Len(curr.a) - 1) newZ Left(b '_', 1)
ELSE '?' END, CASE mv WHEN 'l' THEN
newZ b WHEN 's' THEN b WHEN 'r' THEN
SubString(b, 2, ((Len(b)-1)Abs(Len(b)-1))/2)
ELSE '?' END FROM SubQuery AS curr,
( SELECT 's', 'lt', '1', 'lt', 'r' UNION
ALL SELECT '1', '1', '1', '1', 'r' UNION ALL
/ find 0 / SELECT '1', '_', 'a', '0', 's'
UNION ALL SELECT '1', '0', '2', '0', 's'
UNION ALL SELECT '2', '0', '2', '0', 'r'
UNION ALL / find 1 left / SELECT '2',
'_', 'a', '_', 's' UNION ALL SELECT '2',
'1', '3', '1', 'l' UNION ALL SELECT '3',
'0', '4', '1', 's' UNION ALL / 0 -gt 1 /
SELECT '4', '1', '4', '1', 'r' UNION ALL / find
0 or _ left / SELECT '4', '_', '5', '_',
'l' UNION ALL SELECT '4', '0', '5', '0', 'l'
UNION ALL SELECT '5', '1', '6', '0', 's'
UNION ALL / 1 -gt 0 / SELECT '6', '1', '6',
'1', 'l' UNION ALL / rewind / SELECT '6',
'0', '6', '0', 'l' UNION ALL SELECT '6',
'lt', 's', 'lt', 's' / restart / )
AS prog(currS, currZ, newS, newZ, mv) WHERE
curr.s currS AND Right(curr.a, 1)
currZ)SELECT CharIndex('0', a b) - 2FROM
SubQueryWHERE s 'a'OPTION (MAXRECURSION
0)/ SELECT t, s, a '.' b FROM SubQuery
OPTION (MAXRECURSION 0) /
David Srbecky
3
Acknowledgments
- DB2/400 Mastering Data Warehousing Functions.
(IBM Redbook) Chapters 1 2 only.
http//www.redbooks.ibm.com/abstracts/sg245184.htm
l - Data Warehousing and OLAPHector Garcia-Molina
(Stanford University)http//www.cs.uh.edu/ceick/
6340/dw-olap.ppt - Data Warehousing and OLAP Technology for Data
Mining Department of ComputingLondon
Metropolitan Universityhttp//learning.unl.ac.uk/
csp002n/CSP002N_wk2.ppt
4
Buzz Words Buzz Words Buzz Words Buzz Words Buzz
Words
- Data Warehouse (DW)
- Decision Support (DS)
- Data Marts (DM)
- Data Mining (DM)
- Enterprise Dashboard (ED)
- Multi-Dimensional Modeling (MDM)
- Online Analytic Processing (OLAP)
- Extract, Transform, and Load (ETL)
- MOLAP vs. ROLAP
- Three Letter Acronym (TLR)
- Drill Down, Roll up (DDRU)
- Data vs. Knowledge (DvK)
- Data Cube vs. Sugar Cube (DCvSC)
Dont be surprised to see this sort of BDB
(Blah-Dee-Blah) in the trade press The ED lets
you transform enterprise data into knowledge with
at-a-glance DS/DM and MDM, allowing
interactive DD/RU over large DCs.
5
OLTP vs. OLAP
- Database is operational
- Data is up-to-date
- Mostly updates
- Need to support high levels of update
transactions - Normal form schemas are important
- Database is for analysis
- Data is historical
- Mostly reads
- Need to efficiently support complex queries, and
only bulk loading of data - Schema optimized for query processing
6
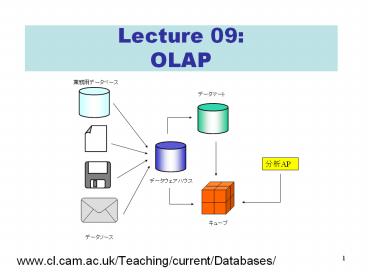
Decision Support Systems
Information Sources
Data Warehouse Server (Tier 1)
OLAP Servers (Tier 2)
Clients (Tier 3)
e.g., MOLAP
Analysis
Semistructured Sources
serve
Extract Transform Load
Query/Reporting
Data Warehouse
serve
e.g., ROLAP
Data Mining
serve
Operational DBs
Data Marts
From Enrico Franconi CS 636
7
xOLAP
- Multi-dimensional OLAP (MOLAP)
- A k-dimensional matrix based on a non relational
storage structure. Agrawal et al - Relational OLAP (ROLAP)
- A relational back-end wherein operations of the
data are translated to relational queries.
Agrawal et al - Hybrid OLAP (HOLAP)
- Integration of MOLAP with ROLAP.
- Desktop OLAP (DOLAP)
- Simplified versions of MOLAP or ROLAP.
- ZOLAP
- Speak with your chemist (normally only prescribed
for death march victims)
8
Beware of Data Warehouse Death March
Death March projects use a forced march imposed
upon relatively innocent victims, the outcome of
which is usually a high casualty rate.
Edward Yourdon, 1997, Death March The Complete
Software Developers Guide to Surviving Mission
Impossible Projects
Data Warehouses and Decision Support systems are
among the most complex and demanding in the IT
world. Failure rates are very high.
9
Relational data model
- based on a single structure of data values in a
two dimensional table - CUSTOMER ORDER
10
Data warehousing ___Multidimensional Data
- Sales volume as a function of product, month, and
region
Region
Dimensions Product, Location, Time
Product
Month
11
A Sample Data Cube
Total annual sales of TV in U.S.A.
12
A Concept Hierarchy for Dimension Location
all
all
Europe
North_America
...
region
Mexico
Canada
Spain
Germany
...
...
country
Vancouver
...
...
Toronto
Frankfurt
city
M. Wind
L. Chan
...
office
13
Cuboids Corresponding to the Cube
all
0-D(apex) cuboid
country
product
date
1-D cuboids
product,date
product,country
date, country
2-D cuboids
3-D(base) cuboid
product, date, country
14
Multidimensional Data A University Sample Data
Cube
Module
Average Mark of Abraham in Year 1.
Computing
Avg
Art
Business
Design
Student
Abraham
Year 1
Bridget
Caroline
Avg
Year 2
Time
Year 3
Avg
- Students marks as a function of student,
department, and year
15
Data Warehousing
- A data warehouse is a subject-oriented,
integrated, time-variant, and nonvolatile
collection of data in support of managements
decision-making process. - W. H. Inmon
16
OLAP Operations
- Roll up (drill-up) summarize data
- by climbing up hierarchy or by dimension
reduction - Drill down (roll down) reverse of roll-up
- from higher level summary to lower level summary
or detailed data, or introducing new dimensions - Slice and dice
- project and select
- Pivot (rotate)
- reorient the cube, visualization, 3D to series of
2D planes. - Other operations
- drill across involving (across) more than one
fact table - drill through through the bottom level of the
cube to its back-end relational tables (using SQL)