Membrane Transport - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 30
Title:
Membrane Transport
Description:
Selective- Gated Channels. Gated Channels (Pores) Integral membrane proteins ... Selectivity. Enzymes. Facilitated transport. Receptor-mediated endocytosis ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:106
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Membrane Transport
1
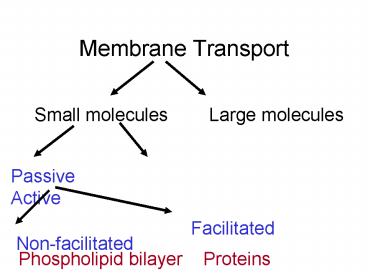
Membrane Transport
Small molecules Large molecules
Passive Active
Facilitated
Non-facilitated
Phospholipid bilayer Proteins
2
What about polar molecules?
-
- Ions - Na, K, Mg, Ca, Cl, H
- Other charged molecules - amino acids
- Uncharged polar - glucose
- Require protein transporters
3
Protein transporters
Selective- Gated Channels
4
Gated Channels (Pores)
- Integral membrane proteins - span membrane
- Selective
- Open only to one side of the membrane at a time
- Conformational change
5
Facilitated Transport
- Passive
- High concentration to low concentration
- No energy required
- Active
- Low concentration to high concentration
- Energy required - ATP
6
(No Transcript)
7
Active transport
- From a low to high concentration
- Energy required - ATP
8
How ATP works
9
Active Transport Summary
- Transport from low to high concentration
- Energy required - ATP
- ATP hydrolyzed
- Phosphate covalently bound to transporter
- Conformational change
10
Sodium-potassium ATPase
- Transports 3 Na ions out
- Transports 2 K ions in
- Hydrolyzes 1 ATP
- Generates a voltage across the membrane -
Electrogenic - Found in almost all animal cells
11
Why is it needed?
12
(No Transcript)
13
Electrogenic pumps
- Voltage across membrane membrane potential
14
An Electrogenic Pump
15
Cotransport
16
Transport of large molecules
- Exocytosis
17
Transport of large molecules
- Exocytosis
- Endocytosis
- Phagocytosis - particle
- Pinocytosis -liquid
- Receptor-mediated endocytosis -
- selective
18
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
19
Ligands bind to receptors
20
Receptors
21
Selectivity
- Enzymes
- Facilitated transport
- Receptor-mediated endocytosis
22
Receptors are trapped in coated pits.
23
Coated pits become coated vesicles.
24
Coated vesicles fuse with lysosomes.
25
Ligand is digested
26
Receptor recycled to surface
27
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
- Ligand binds to receptor
- Ligand-receptor complex is trapped in a coated
pit - The coated pit becomes a coated vesicle
- which fuses with a lysosome
- The ligand is digested and
- the receptor is recycled to the surface.
- New pits form.
28
What happens if something goes wrong?
- Familial hypercholesteremia
- Genetic defect in cholesterol-LDL receptors -
- Cholesterol is not taken up
- Heart attacks and death at a young age.
29
Receptors lack tails
30
Binding sites altered
Wrong shape - ligand does not bind