Chapter 13 Unsaturated Hydrocarbons - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 26
Title:
Chapter 13 Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
Description:
Physical Properties of Alkenes. Similar to those of alkanes ... Chemical and physical properties are similar to alkenes. Nomenclature: Replace 'ane' with 'yne' ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:539
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Chapter 13 Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
1
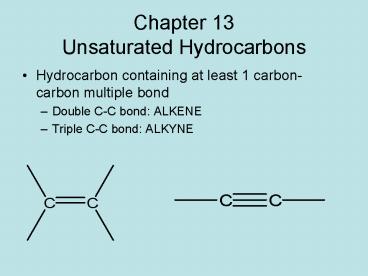
Chapter 13Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
- Hydrocarbon containing at least 1 carbon-carbon
multiple bond - Double C-C bond ALKENE
- Triple C-C bond ALKYNE
2
Unsaturated Hydrocarbons contd
- Fig. 13.1
- In ethene, the atoms are in a flat rather than a
tetrahedral arrangement.
3
Alkene/alkyne Nomenclature
- Identify longest chain CONTAINING DOUBLE (TRIPLE)
BOND - Number from end closest to double (triple) bond
- Name and number of substituents BEFORE alkene
(alkyne) name - Name cyclic alkenes as cyclo(alkene)
- Two double bonds are called diene 3. triene
4
Nomenclature Examples
1 ? 8
3,5,7-trimethyl-3-octene
5 ? 1
2,3-dimethyl-1,3-pentadiene
5
Nomenclature ExamplesCycloalkenes
6
Isomerism in Alkenes
7
Cis-Trans Isomerism
- Fig. 13.3
- Cis-trans isomers Different representatives of
the cis and trans isomers of 2-butene.
8
Cis-Trans Isomerism and Vision
9
Physical Properties of Alkenes
- Similar to those of alkanes
- Low density
- Insoluble in water
- Soluble in non-polar solvents
- Alkenes generally have lower BP and MP than
corresponding alkanes
10
Chemistry of Alkenes
- Addition reactions atoms or groups are added to
both carbons of a double bond - Symmetrical addition
- Same atoms or groups are added to each carbon
- Asymmetrical addition
- Different atoms or groups are added to each
carbon
11
Symmetrical Additions
- Hydrogenation H2 is added to double bond
- Halogenation X2 is added to double bond (where X
halogen)
12
Unsaturated Hydrocarbons contd
- Fig. 13.9
- A bromine in water solution is reddish brown.
When a small amount of such a solution is added
to an unsaturated hydrocarbon, the added solution
is decolorized.
13
Asymmetrical Additions
- Hydrohalogenation Hydrogen is added to one
carbon halogen to the other - Hydration Hydrogen is added to one carbon
- -OH is added to the other
14
Asymmetrical Additions, continued
- Markovnikovs rule The rich get richer (in
terms of hydrogen)
15
Alkene Reactions
Markovnikov The rich get richer
16
Polymerization
- Repetitive bonding of monomers to form long,
repeating molecule
17
(No Transcript)
18
Unsaturated Hydrocarbons contd
CAG 13.1
19
Alkynes
- Chemical and physical properties are similar to
alkenes - Nomenclature Replace ane with yne
- Follow rules for naming alkenes
20
Aromatic Hydrocarbons
21
Benzene
22
Nomenclature of Aromatic Hydrocarbons
23
Nomenclature of Aromatic HydrocarbonsDi-substitut
ed Benzene Derivatives
24
Nomenclature of Aromatic HydrocarbonsTri-substitu
ted Benzene Derivatives
25
Nomenclature of Aromatic HydrocarbonsBenzene as
a substituent (Phenyl group)
2-phenyl-2-benzene
26
Chemical Reactions of Aromatic Hydrocarbons
- Alkylation
- Halogenation