Outcomes from external or internal environment analyses - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 29
Title:
Outcomes from external or internal environment analyses
Description:
Shows primary activities that move product from raw-material stage to the final customer ... activities in which the firm itself can create and capture value ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:79
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Outcomes from external or internal environment analyses
1
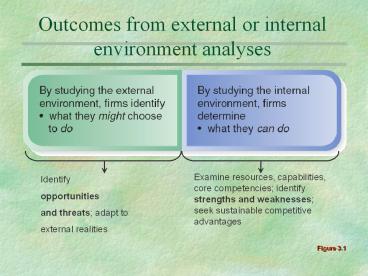
Outcomes from external or internal environment
analyses
Examine resources, capabilities, core
competencies identify strengths and weaknesses
seek sustainable competitive advantages
Identify opportunities and threats adapt to
external realities
Figure 3.1
2
Conditions contributing to the challenge of
identifying strengths and weaknesses
-UncertaintyComplexityOrganizational
conflicts(Time pressure)
3
Useful attributes for pragmatically identifying
strengths and weaknesses -
4
Facilitating internal analysis via . . .
5
Components of internal analysis
Figure 3.2
6
Resources, capabilities and core competencies
- Resources - what the firm has
- basic source of a firms capabilities, but alone,
do not yield competitive advantage - Tangible resources
- Intangible resources
7
Which type of resources are likely to play a
stronger role in creating a sustainable
competitive advantage? Why?
- Tangible resources? Intangible resources?
8
Resources, capabilities and core competencies
- Capabilities - what firm can do with what it has
- Emerge over time through complex interactions
among tangible and intangible resources - Often based in specific functional areas, such as
. .
9
Examples of notable capabilities
10
Resources, capabilities and core competencies
- Core Competencies
- Resources and capabilities that serve as a source
of a firms competitive advantage - Distinguish a company from its competitors
- (NOT just the same as competitors)
11
Building sustainable competitive advantage
- Valuable capabilities
- Help a firm neutralize threats or exploit
opportunities - Are valued by the marketplace
- Rare capabilities
- Are not possessed by many others
12
Building sustainable competitive advantage
Difficult to imitate capabilities, from
- Historical company origins
- Ambiguous cause-effect sequences in key
activities - Social complexity
13
Building sustainable competitive advantage
- Nonsubstitutable Capabilities
- No strategic equivalent
- (or, organizationally accessible capabilities)
14
Outcomes from combinations of the criteria for
sustainable competitive advantage
Table 3.5
15
Core/distinctive competencies So what? Who
cares?
- Identify and protect core competencies!
- Use your core competencies
- rely on in competitive strategies
- Continually develop and renew core competencies
beware of core rigidities - Leverage core competencies into new areas of
opportunity stay on the ball!
16
Components of internal analysis
Figure 3.2
17
Value chain analysis
- The primary tool for comprehensive internal
analysis - A template that firms use to systematically
- identify strengths, weaknesses, and core
competencies throughout the firms structure,
resources, and activities - identify relative cost position in each activity
area - contemplate alternative ways to implement
strategies
18
The Basic Value Chain
Service
Marketing and Sales
Human Resource Management
Outbound Logistics
Technological Development
Firm Infrastructure
Operations
Procurement
Inbound Logistics
19
Value chain analysis (contd)
- Value chain
- Shows primary activities that move product from
raw-material stage to the final customer - Shows facilitating orgl support activities
- To be a source of competitive advantage, a
resource or capability must allow the firm - To perform an activity in a manner that is
superior to the way competitors perform it, or - To perform a value-creating activity that
competitors cannot complete
20
The value-creating potential of primary activities
- Inbound logistics
- Activities used to receive, store, and
disseminate inputs to a product (materials
handling, warehousing, inventory control, etc.) - Operations
- Activities necessary to convert the inputs
provided by inbound logistics into final product
form (machining, packaging, assembly, etc.) - Outbound logistics
- Activities involved with collecting, storing, and
physically distributing the product to customers
(finished goods warehousing, order processing,
etc.)
21
The value-creating potential of primary
activities (contd)
- Marketing and sales
- Consider all 4 Ps! plus marketing research
- Service
- Activities designed to enhance or maintain a
products value (repair, training, adjustment,
etc.) - Each activity should be examined relative to
competitors abilities and rated as superior,
equivalent or inferior
22
The value-creating potential of support activities
- Procurement
- Activities completed to purchase the inputs
needed to produce a firms products (raw
materials and supplies, machines, laboratory
equipment, etc.) - Technological development
- Activities completed to improve a firms product
and the processes used to manufacture it (process
equipment, basic research, product design, etc) - Human resource management
- Activities involved with recruiting, hiring,
training, developing, compensating, retaining all
personnel
23
The value-creating potential of support
activities (contd)
- Firm infrastructure
- Top and upper management, organizational
structure, financial situation, specialized
functions, orgl culture - Each activity should be examined relative to
competitors abilities and rated as superior,
equivalent or inferior
24
Use of value chain analysis
- Advantages?
- Disadvantages?
25
Outsourcing
- Why?
- Trend?
- Issues?
26
Outsourcing decisions
A firm may outsource all or only part of one or
more primary and/or support activities.
Service
Marketing and Sales
Human Resource Management
Outbound Logistics
Technological Development
Firm Infrastructure
Operations
Procurement
Inbound Logistics
27
Outsourcing advice
- Outsource only to strong vendors
- Do not outsource activities in which the firm
itself can create and capture value - Do not outsource activities that are central to
the firms core competencies and development of
potential new core competencies - Realize the importance of effective and ongoing
management of outsourcing arrangements
28
SWOT analysis
- External analysis of
- general environment,
- industry environment,
- 5 forces of competition,
- strategic groups,
- competitive intelligence, key success factors
- to identify
- OPPORTUNITIES
- and THREATS
- Internal analysis of
- Resources, capabilities, core competencies, and
competitive advantages - (using value chain analysis, functional audits,
financial analysis, or other tools) to identify - STRENGTHS and
- WEAKNESSES
29
Using the SWOT analysis
- Create strategies that
- Are consistent with orgl mission
- Rely on internal strengths
- Pursue external opportunities
- Achieve external strategic fit
- Buffer external threats (both offensive and
defensive approaches are desirable) - Minimize the effects of internal weaknesses
- Achieve internal strategic fit