LIGHT REACTION OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 63
Title:
LIGHT REACTION OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS
Description:
LIGHT REACTION OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS. 1. Photosynthetic reaction. 1) 6 ... P960 (special pair) bacteriochlorophyll (BChl) bacteriopheophytin b (BP) QA (quinone) QB ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:298
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: LIGHT REACTION OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS
1
LIGHT REACTION OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS
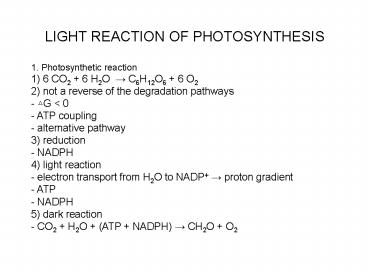
1. Photosynthetic reaction 1) 6 CO2 6 H2O ?
C6H12O6 6 O2 2) not a reverse of the
degradation pathways - ?G lt 0 - ATP coupling -
alternative pathway 3) reduction - NADPH 4) light
reaction - electron transport from H2O to NADP ?
proton gradient - ATP - NADPH 5) dark reaction -
CO2 H2O (ATP NADPH) ? CH2O O2
2
(No Transcript)
3
2. Chloroplast 1) stroma - dark reaction 2)
thylakoid membrane - 40 galactolipids - 10
phospholipids - 4 sulfolipids - conversion of
light to chemical energy 3) chlorophyll -
magnesium porphyrin - photoreceptor - chlorophyll
a 400 - 700 nm - visible light 4 - 80 kcal/mole
4
4) photosynthetic bacteria - cyanobacteria -
purple bacteria 5) endosymbiosis - chloroplasts
semiautonomous organelles - chloroplast DNA -
ancestor of a cyanobacterium
5
(No Transcript)
6
(No Transcript)
7
(No Transcript)
8
(No Transcript)
9
(No Transcript)
10
(No Transcript)
11
(No Transcript)
12
3. Electron transfer 1) photoinduced charge
separation - D A ? D A- 2) electron transfer
at the reaction center - donor molecule ?
chlorophyll ? acceptor molecule
13
(No Transcript)
14
(No Transcript)
15
- 4. Bacterial photosynthetic reaction center
- 1) Rhodopseudomonas viridis
- - a purple bacteria
- - homologous to photosystem II
- four polypeptides (L, M, H, C) L and
- M, transmembrane proteins
- 2) atomic resolution
- P960 (special pair) ? bacteriochlorophyll (BChl)
? - bacteriopheophytin b (BP) ? QA (quinone) ? QB ?
- cytochrome bc1 ? cytochrome c2 ? P960
16
(No Transcript)
17
(No Transcript)
18
(No Transcript)
19
(No Transcript)
20
(No Transcript)
21
(No Transcript)
22
5. Photosystem II 1) two photosystems - lt 680 nm
(photosystem II), lt 700 nm (photosystem I) 2) a
core with a reaction center - D1, D2
transmembrane proteins - P680 chlorophyll
dimer - P680 ? pheophytin (Ph) ? QA
(plastoquinone) ? QB ? QH2 3) an oxygen-evolving
complex - P680 cation a very strong oxidant -
extraction of electrons from water the Mn
center a cluster of four manganese ions, a
charge accumulator - 4 photons for one oxygen
molecule
23
(No Transcript)
24
(No Transcript)
25
(No Transcript)
26
(No Transcript)
27
(No Transcript)
28
(No Transcript)
29
(No Transcript)
30
(No Transcript)
31
- 6. Photosystem I
- 1) electron-tranfer from QH2 to photosystem I
- QH2 ? (cytochrome bf complex) ? plastocyanin
(PC) ? - photosystem I
- 2) cytochrome bf complex 4 subunits
- cytochrome f, cytochrome with 2 b-type hemes,
- a Fe-S protein, a 17-Kd polypeptide
- - Q-cytochrome c oxidoreductase in mitochondria
- - electron-transfer from QH2 to plastocyanin Q
cycle - - two proton pumping per QH2 oxidation ? ATP
synthesis - 3) plastocyanin
- - a water soluble protein
- - a copper ion (Cu1 ? Cu2)
32
4) psaI and psaII - P700 - A0 (an acceptor
chlorophyll) - A0 ? A1 (quinone) ? 4Fe-4S
clusters 5) reduction of ferredoxin (Fd) - a
water-soluble protein - a 2Fe-2S cluster -
PC(Cu) ferrodoxinox. ? PC(Cu2)
ferrodoxinred. 6) ferredoxin-NADP reductase -
FAD-FADH2-mediated electron transfer - NADP
2Hstroma 2e-? NADPH
33
(No Transcript)
34
(No Transcript)
35
(No Transcript)
36
(No Transcript)
37
(No Transcript)
38
(No Transcript)
39
(No Transcript)
40
7. ATP synthesis 1) proton-motive force - 3.5 pH
units -?p - 0.06(?-3.5) 0.20 V 4.8
kcal/mol - the major factor pH gradient -
thylakoid membrane (quite permeable to Mg2 and
Cl-) 2) thylakoid lumen - acidic (pH ?4) 3) ATP
synthase - CF1-CF0 complex - 2 NADPH in stroma
12 H in lumen by 8 photons
41
(No Transcript)
42
(No Transcript)
43
(No Transcript)
44
(No Transcript)
45
(No Transcript)
46
(No Transcript)
47
- 8. Cyclic electron flow
- 1) an alternative pathway
- P700 ? ferredoxin (Fd) ? cytochrome bf complex ?
- plastocyanin ? P700
- 2) cyclic phosphorylation
- - a high ratio of NADPH to NADP
- - no O2 generation
48
(No Transcript)
49
(No Transcript)
50
9. Accessory pigments 1) accessory pigments -
450 - 650 nm of the visible regions - relative
low density of chlorophyll a molecules at the
active center - additional chlorophyll a
molecules - other classes of molecules
chlorophyll b, lycopene, ß-carotene -
transfer the absorbed energy to a reaction
center 2) light-harvesting complexes - the
26-kd subunit of a light-harvesting complex
(LHC-II) 7 chlorophyll a, 6 chlorophyll b, 2
carotenoid - bacterial light-harvesting
complexes 8 polypetides (3 chlorophyll, 1
carotenoid)
51
(No Transcript)
52
(No Transcript)
53
(No Transcript)
54
(No Transcript)
55
(No Transcript)
56
(No Transcript)
57
(No Transcript)
58
(No Transcript)
59
10. Localization of photosystems, cytochrome bf,
and ATP synthase 1) separation of
photosystem II from photosystem I - direct
electron-transfer from photosystem II to
photosystem I 2) photosystem I in unsacked
regions - direct access to stroma - NADPH 3) ATP
synthase in unsacked regions - direct access to
stroma - a large size of CF1 4) photosystem II in
sacked regions - H2O - plastoquinone (a highly
lipid-soluble electron carrier)
60
(No Transcript)
61
- 11. Herbicides
- 1) photosystem II
- - diuron (urea derivatives), atrazine (triazine
derivatives) - - the QB site of D1
- 2) photosystem I
- paraquat accept electrons from photosystem I to
become - a radical
62
(No Transcript)
63
(No Transcript)