Fungi - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 36
Title:
Fungi
Description:
Hyphae grow from their tips. Mycelium = extensive, feeding web of hyphae ... Grow rapidly. Fig 31.6 Rhizopus on strawberries. Fig 31.7 Life cycle of Rhizopus ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:218
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Fungi
1
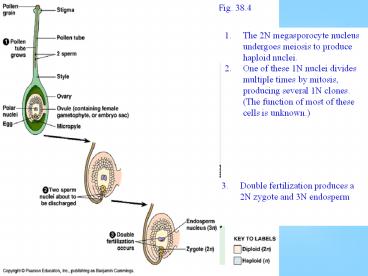
Fig. 38.4
- The 2N megasporocyte nucleus undergoes meiosis to
produce haploid nuclei. - One of these 1N nuclei divides multiple times by
mitosis, producing several 1N clones. (The
function of most of these cells is unknown.)
- Double fertilization produces a 2N zygote and 3N
endosperm
2
Kingdom Fungi
3
Characteristics of Fungi
- Briefly describe an example in each of the
following fungal lifestyles - decomposers
- parasites
- symbionts
- Fungi are NOT plants
- Absorptive heterotrophs
- Reproduce by spores
- reproductive bodies are often the most visible
- Ecologically active
- hyphae tubular units of construction
- secrete exoenzymes
Justify this statement
4
Fig 31.1
fruiting bodies
both are composed of hyphae
mycelium
5
?
(Protista)
Fig 32.2
Proposed Phylogeny of Eukaryotes
Fig 28.8
6
Fig 31.4
asci
zygosporangia
basidia
Where do chytrids live?
Classification in these three phyla is based on
sexual reproductive structures
motile spores
7
Hyphae
Septate hypha
- tubular
- hard wall of chitin around the cell membrane
- septa (perforated cross-walls) may form
compartments ( cells) - multinucleate
Coenocytic hypha
Haustoria
80 of plant diseases are caused by fungi
What do you think is the purpose of perforated
cross-walls?
8
Hyphal growth
Where would you find the hyphae of most fungi?
- Hyphae grow from their tips
- Mycelium extensive, feeding web of hyphae
- Mycelia are the ecologically active bodies of
fungi
Why is SA important?
This wall is rigid
Only the tip wall is plastic and stretches
9
What does absorptive heterotrophic nutrition look
like?
- Fungi get their energy and raw materials from
organic sources in their environment - The products of digestion diffuse back into hyphae
Products
Enzymatic breakdown
Nucleus hangs back and directs metabolism
Enzymes
Products diffuses back into hyphae for use
10
Modifications of hyphae
Fig 30.2 (dont worry about the terms we dont
discuss in class)
11
Reproduction by spores
- Spores are reproductive cells
- Sexual
- Asexual
- Produced
- fruiting bodies
- inside sporangia
- directly on hyphae
What is the primary purpose of spores?
Classification of fungi is based on which mode of
spore production?
Penicillium hyphae (Ascomycota)
Pilobolus sporangia (Zygomycota)
Amanita fruiting body (Basidomycota)
12
Fungal Ecology
- Saprobes
- Decomposers
- Mostly of plants, some animals
- Parasites
- Harm host
- Mostly on plants, some animals
- Mutualists
- Lichens
- Mycorrhizas
13
Zygomycota zygote fungi
- Sexual - zygosporangia
- Asexual spores - common
- Hyphae have no cross walls
- Grow rapidly
Fig 31.6 Rhizopus on strawberries
14
Sexual zygsporangium with one zygospore
Asexual sporangium with spores inside
Fig. 31.7
Fig 31.7 Life cycle of Rhizopus You are not
responsible for the details of this life cycle.
Life cycle is predominantly haploid
15
Ascomycota sac fungi
- Sex. asci
- Asex. common
- Cup fungi, morels, truffles
- Important plant parasites saprobes
- Yeast - Saccharomyces
- Most lichens
A cluster of asci with spores inside
16
Ascomycota sac fungi
17
1 cm
Aleuria
18
Fig 31.9b Tuber melanosporum The black french
truffle
19
Basidiomycota club fungi
- Sex basidia
- Asex not so common
- Long-lived mycelia
- Rusts smuts primitive plant parasites
- Mushrooms, puffballs
- Enzymes decompose wood
- Mycorrhizas
SEM of basidia and spores See Fig. 31.12
20
Marasmius oreades - Fairy Ring
From http//botit.botany.wisc.edu/toms_fungi/mar2
003.html
21
A rust growing on a currant leaf 0.5 cm
22
Amanita, death angel
Inocybe, contains muscarine
Boletus edulis
Cantharellus, the chanterelle
23
Fomitopsis
24
Mushroom Life Cycle
Hyphal fusion of haploid mycelia
mycelium and fruiting body are dikaryotic
haploid mycelium
N 2N NN
Meiosis
Nuclear fusion in basidium
Fig 31.12
young basidia - the only diploid cells
25
Alternative fungal lifestyles
- Yeasts
- Molds
- Mycorrhizas
- Lichens
26
Yeasts
- Single celled fungi
- Adapted to liquids
- Plant saps
- Water films
- Moist animal tissues
Candida
Saccharomyces
27
Molds
- Rapidly growth
- Asexual spores
- Many of human importance
- Food spoilage
- Food products
- Antibiotics, etc.
Noble Rot - Botrytis
Fig 31.21 Antibiotic activity
28
Mycorrhizas
- Fungus roots
- Mutualism between
- Fungus (nutrient water uptake for plant)
- Plant (carbohydrate for fungus)
- Several kinds
- Zygomycota hyphae invade root cells
- Ascomycota Basidiomycota hyphae invade root
but dont penetrate cells - Extremely important ecological role of fungi!
29
Lichens
- Mutualism between
- Fungus structure
- Alga or cyanobacterium provides food
- Form a thallus
- Foliose
- Fruticose
- Crustose
By what process do these symbionts produce food
for the fungus?
Fig 31.16
30
Lichen internal structure
What do the fungi provide in this symbiotic
relationship?
Lobaria
Fig 31.17
31
Lichens as biomonitors
- Thalli act like sponges
- Airborne dust, minerals, etc. adsorb to the
lichen surface - Some species more sensitive
- Which species are present can indicate air
quality - Most resistant species can also be analyzed for
pollutants
32
Lichen diversity
- These photos taken by Fred Rhoades
- Visit Fred Rhoade's Lichen Page
33
Caloplaca Verrucaria
34
Two species in the fruticose lichen of the genus,
Cladonia
35
Peltigera
36
1 cm
Basidiomycote lichen, Omphalina