The Semantic Web - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 8
Title:
The Semantic Web
Description:
Translation to Clausal Form. The Semantic Web. Martians Example Revisited... Prove that there is a member of the dancing club who can't jive. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:38
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: The Semantic Web
1
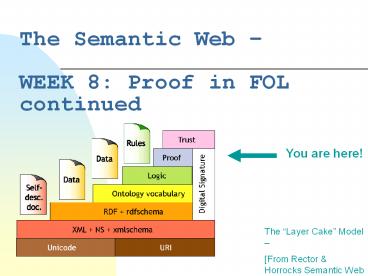
The Semantic Web WEEK 8 Proof in FOL continued
You are here!
The Layer Cake Model From Rector Horrocks
Semantic Web cuurse
2
Recap
- Resolution is a powerful rule of inference. When
used in refutation mode it can be a COMPLETE
proof procedure - Resolution is based on important ideas /
techniques - Unification
- Translation to Clausal Form
3
Martians Example Revisited
- Deep Space 1 travels to Mars and observes many
things about the Martians, including the fact
that some seem very hostile towards humans.
Concrete observations are as follows - (a) All green Martians have antennae.
- (b) A Martian is friendly to humans if all of its
children have antennae. - (c) A Martian is green if at least one of its
parents is green. - On its way back from Mars the robot is hotly
pursued - by a spacecraft containing green Martians only.
Should the robot - suspect it is being attacked? Or can the robot
reason with its observations to answer the
question Are all green Martians friendly?'' - and hence avert an inter-planetary conflict.
4
Systematic Proof Procedure
- Given a set of clauses W ( premises negated
query clauses) we need to find null the empty
clause, indicating a contradiction. - Find the set of all pairs of clauses in W that
can resolve, and resolve them - C child clauses from step 1
- W W U C
- If null is in W finish, else Goto 1.
5
Recall Algorithmic Properties..
- A problem is decidable if there is an algorithm
which can always be trusted to give the correct
answer in finite time. - A problem is of f(n) complexity class if given
any instance of a problem of size n it will
take time/space f(n) to solve it.
6
Problems..
- 1. Resolution (and FOL) is only SEMI-DECIDEABLE.
- That is, if you know that
- Wff1 - Wff2
- Then eventually RR will prove it
- BUT if not the procedure may go on and on
- 2. Proving Wff1 - Wff2 is of exp(n) time
complexity in general, where n is the size of the
Wff set.
7
Problems..
- FOL is thought (by some) to be too powerful for
the ontology/proof level of the Semantic Web (a
contentious point). There are Syntax Conventions
for FOL eg the KIF the Knowledge
Interchange Format - Biggest problems are
- No efficient proof procedures
- No built-in structure for representing classes
8
Summary
- Resolution Refutation is a complete proof
procedure but is intractable in general. Prolog
uses an efficient version of RR. - FOL is perhaps too unrestricted for use in the
Semantic Web - Execises
- 1. Dave and Fred are members of a dancing club in
which no member can both waltz and jive. Freds
dad cant waltz and Dave can do whatever fred
cant do. If a child can do something, then their
parents can do it also. Prove that there is a
member of the dancing club who cant jive. - Answer is on web http//scom.hud.ac.uk/scomtlm/cam
326/logic/logic.html - See section on resolution refutation
- 2. Try out the RR theorem prover in
/local/public/cam326/tp/