Atmospheric Concentrations - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 27
Title:
Atmospheric Concentrations
Description:
Atmospheric Concentrations Source: CDIAC CGE Greenhouse Gas Inventory Hands-on Training Workshop for the Asian Region - Building an Inventory Management System ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:14
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Atmospheric Concentrations
1
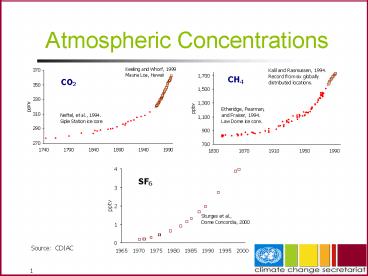
Atmospheric Concentrations
Source CDIAC
2
CGE Greenhouse Gas Inventory Hands-on Training
Workshopfor the Asian Region - Building an
Inventory Management System -Shanghai,
China8-12 February 2005
- Michael Gillenwater
3
(No Transcript)
4
What is an GHG Inventory Program for?
- Meet international obligations and expectations
- Inform international, national, and local policy
making - Enhance credibility of national climate policies
through timely, transparent, and effective
analysis and communication - Foster consistent estimation approaches across
government and private sector programs - Respond to requests for information
- Champion for high quality and objective inventory
information
5
What is quality?
- Transparency
- Completeness
- Comparability
- Consistency
- Accuracy
- Transparency is the most fundamental. If you do
not document, then there is no way to demonstrate
any of the other principles have been met.
6
Who cares?
- A wide audience of stakeholders...
- Decision makers and policy advisors
- International climate change community
- Provincial and local agencies
- The public and interest groups
- Businesses
- Scientists
7
National government
- What are the emissions and removals in other
countries (both Annex I and non-Annex I)? - What are the uncertainties in GHG estimates and
are national inventories verifiable? - What is our countrys contribution to global
emissions removals? - What are current and projected emissions and
removals from key industries?
8
National government (cont.)
- What are the effects of existing or planned
policies and measures (including policies that
aggravate emissions)? - Is our country meeting its UNFCCC obligations?
- Is there consensus among government agencies and
key stakeholders on our emission estimates? - What are the relationships between reducing
greenhouse gas emissions and other environmental
pollutants?
9
International community
- What is the your countrys contribution to global
emissions and removals? - Are your GHG estimates credible and transparent?
- Is your country meeting its UNFCCC obligations?
10
Businesses NGOs
- How do we quantify and get credit for activities
that reduce emissions or sequester carbon? - What activities, industries, companies, or
policies have been responsible for significant
increases or decreases in GHG emissions or
removals?
Scientists
- What are the priorities for research and
measurement? - What are the scientific uncertainties in the
emission and sink estimates?
11
Linkages
Research international scientific community
Trading and projects
LU/LUCF (Sinks policies)
Domestic emission reduction programs
Inventory Program
Negotiations IPCC
Corporate, regional, other inventories
Interest groups the public
Emission projections, climate economic modeling
12
Inventory management systems should...
- Ensure inventory processes are in compliance with
COP decisions (i.e., Non-Annex I Party National
Communications) - Define and apply appropriate procedures for
collecting, processing, communicating, and
archiving inventory data and information - Coordinate with relevant government departments,
national agencies, and other organizations - Provide inventory reports regularly
- Ensure the quality of inventory data
13
Inventory management system
- Inventory planning
- Inventory preparation
- Inventory management
14
Inventory planning
- Appoint national inventory agency
- Allocate responsibilities for inventory
preparation and management - Develop schedule
- Make arrangements to collect data from
statistical agencies, companies, industry
associations, etc. - Create QA/QC plan
- Define formal approval process within government
- Develop review processes
- Integrate continuous improvement
15
Example U.S. Inventory Schedule
Oct - Nov
Late December
April 15th
April - September
Mid October
Nov - Dec
Jan - Feb
Incorporate public comments
Respond to interagency comments
Gather data and prepare initial estimates
Prepare draft report
Expert and interagency review
Submit Inventory to UN
Release for public comment
16
Inventory preparation
- Identify key sources
- Select methods and emission factors (GPG decision
trees) - Activity data collection
- Manage recalculations
- Implement QA/QC plan
- Basic checks should be completed on entire
inventory (Tier 1) (see GPG Ch. 8) - More in-depth investigations into key sources
(Tier 2) - Documentation
17
Key categories
- A key source has a significant influence on a
countrys total inventory in terms of level or
trend in emissions (GPG, Ch.7) - A key source also may be determined through a
qualitative assessment. - A key source category is one that is prioritized
within the national inventory system - In general, countries should focus on key
categories for resources and improvements
18
Inventory management
- Implement inventory review processes (e.g.,
expert review, public review) - Obtain formal approval of final results and
report within government - Submission of report to UNFCCC
- Make inventory information available to
stakeholders and respond to information requests - Archive all documentation and results
- Continuous improvement feedback
19
Uncertainty
- Uncertainty analysis is a subjective exercise, as
it relies to a large extent on expert judgment - Therefore, it is not a valid basis to compare
inventories between countries - Uncertainty analysis should be used as a way to
investigate the quality of your inventory data
and identify ways to improve data quality - You achieve this by investigating data quality
- And communicating with data suppliers (e.g.,
statistical agencies) - Uncertainty investigations should be integrated
within your QA/QC plan!
20
Resources
- IPCC Guidelines
- Revised 1996 IPCC Guidelines
- IPCC Good Practice Guidance
- IPCC LULUCF GPG
- New 2006 IPCC Guidelines
- UNFCCC reporting guidelines
- IPCC Emission Factor Database (EFDB)
- IPCC software
21
Other resources
- Inventory reports from other Parties
- UNFCCC website/GHG Data
- www.unfccc.int
- Inventory related reports from other Parties
- Online network of inventory professionals?
22
Closing remarks
- A greenhouse gas inventory is more than just a
report. It should be viewed as an broader
analytical program. - A cookbook approach to developing a GHG
inventory is not practical. There will always be
a large and essential need for expert judgment at
all levels of the process. - A well constructed inventory should include
enough documentation to allow readers to
understand the underlying assumptions and to
reconstruct the calculations.
23
Please feel free to email me in the
futureMichael GillenwaterEnvironmental
Resources Trustmgillenwater_at_ert.net
- Thank you
24
Flow of Energy Data
EPA
25
Emission Inventory Basics
- An emission inventory is an accounting of the
amount of air pollutants discharged into the
atmosphere. It is generally characterized by the
following factors - The chemical or physical identity of the
pollutants included - The geographic area covered
- The institutional entities covered
- The time period over which emissions are
estimated - The types of activities that cause emissions
26
Inventory Agency Responsibilities
- A single national entity to be responsible for
the overall inventory - Arrangements with collaborating entities that
contribute data, research, estimate emissions or
provide expert reviews - Define legal authority to collect and disseminate
data necessary for the preparation of the
inventory - Ensure inventory processes are in compliance with
COP decisions - Define and apply procedures for collecting data,
preparing inventory, communicating results,
submitting report, and archiving - Liaise among government departments, national
agencies, - Ensure the implementation of QA/QC
27
Goals
- Develop high quality inventory at regular
intervals (e.g., annually, every 2-4 years, etc).
- Resources are focused on the most significant
emission sources in the country