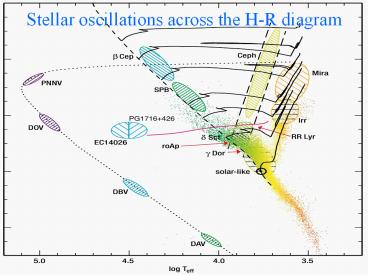
Stellar oscillations across the H-R diagram - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Stellar oscillations across the H-R diagram
Description:
Sun-as-a-star data from VIRGO experiment, SPM and LOI instruments ... 105 square degrees just above galactic plane in the constellation Cygnus ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:113
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Stellar oscillations across the H-R diagram
1
Stellar oscillations across the H-R diagram
2
Helioseismology
- Millions of independent oscillation frequencies
excited simultaneously - Each mode samples the interior in a different and
complementary way - This provides a detailed calibration of the
physics of standard solar models
Larger
Smaller
? Surface spatial scale ?
Shallower
? Interior sampled ?
Deeper
3
Calibrating solar physics
- New radiative opacities significantly improved
standard solar models - Models with settling of heavy elements agreed
even more closely - Remaining discrepancies in the outer layers were
resolved by a new EOS
Dziembowski et al. (1992)
Bahcall et al. (1997)
4
Asteroseismology
- New opportunities to probe the fundamental
physics of the models - Understanding the solar evolution in a broader
context from stellar ages - Only the lowest degree modes are detectable in
distant stars (l lt 3)
Bedding Kjeldsen (2003)
5
Observing techniques
Light variation
Appourchaux et al. (2008)
Velocity variation
Bouchy et al. (2004)
6
Solar-like oscillations
7
Mission SOHO
- SOlar and Heliospheric Observatory, launched in
December 1995 - Sun-as-a-star data from VIRGO experiment, SPM and
LOI instruments - 5.5-cm aperture, silicon photodiode detectors
8
Stellar density and age
Elsworth Thompson (2004)
- Large frequency spacing ltDngt scales with average
density of the star - Small frequency spacing ltdngt sensitive to
interior gradients, proxy for age - Probe evolution of activity and rotation as a
function of stellar mass and radius
Christensen-Dalsgaard (2004)
9
Mission WIRE
- Wide-field InfraRed Explorer, launched in March
1999 - Primary instrument failed shortly after launch
due to complete loss of coolant - 5.2-cm star tracker with CCD camera mounted to
side of main instrument
10
Radial differential rotation
- WIRE 50-day time series of a Cen A has resolved
the rotational splitting - Splitting as a function of radial order can
indirectly probe differential rotation - Even low-degree modes allow rough inversions of
the inner 30 of radius
Fletcher et al. (2006)
Gough Kosovichev (1993)
11
Mission MOST
- Microvariability and Oscillations of STars,
launched in June 2003 - 15-cm primary mirror, two CCD cameras with Fabry
lens array for stability - Up to two months per target, 100 duty cycle, few
ppm photometry
12
Surface differential rotation
- Three seasons of precise MOST photometry for the
solar-type star k1 Ceti - Latitudinal differential rotation pattern has
same functional form as Sun - Kepler will obtain similar rotation measurements
for 105 solar-type stars
Ca HK period
Walker et al. (2007)
13
Mission CoRoT
- French-led ESA mission, successfully launched in
December 2006 - 28-cm primary mirror, two science CCDs for planet
transits and seismology - Interleaved 1-month and 5-month runs for 2.5 yrs,
100 duty cycle
14
Convection zone depth
- Expected seismic signal from a CoRoT 5-month
observation of HD 49933 - Second differences (d2n) measure deviations from
even frequency spacing - Base of the convection zone and He ionization
create oscillatory signals
Baglin et al. (2006)
15
Mission Kepler
- NASA mission currently scheduled for launch in
March 2009 - 105 square degrees just above galactic plane in
the constellation Cygnus - Single field for 4-6 years, 100,000 stars 30
minute sampling, 512 at 1 minute
16
Oscillations and magnetic cycles
- Solar p-mode shifts first detected in 1990,
depend on frequency and degree - Even the lowest degree solar p-modes are
shifted by the magnetic cycle - Unique constraints on the mechanism could come
from asteroseismology
Libbrecht Woodard (1990)
17
Cycle-induced frequency shifts
- Solar p-mode shifts show spread with degree and
frequency dependence - Normalizing shifts by our parametrization removes
most of the dependencies - Kepler will document similar shifts in hundreds
of solar-type stars
Metcalfe et al. (2007)
18
Red supergiants
Kiss et al. (2006)
19
(p-)ressure and (g-)ravity
Montgomery Winget (1999)
20
Excitation mechanisms
Dutch Open Telescope
21
Intermediate-mass pulsators
22
d Scuti stars
Breger et al. (2005)
23
g Dor stars
Rowe et al. (2007)
24
roAp stars
Kurtz et al. (2002, 2005)
25
Massive pulsators
26
SPB stars
Aerts et al. (2006)
27
b Cep stars
Aerts et al. (2006)
28
Subdwarf variables
29
sdB stars
Fontaine et al. (2007)
Schuh et al. (2006)
30
White dwarf variables
31
DOV stars
Winget et al. (1991)
32
DBV stars
Sullivan et al. (2008)
33
DAV stars
Kanaan et al. (2005)
34
(No Transcript)