Chapter 4, Module 3 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 64
Title: Chapter 4, Module 3
1
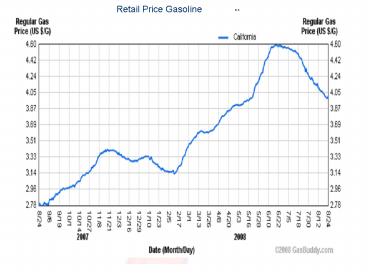
Retail Price Gasoline
2
- Soaring gas prices turned into massive profits
for big oil, shareholders of these companies are
cashing in. - In July, BP reported a staggering 63 surge in
first quarter net profit to 7.6 billion, and
Royal Dutch Shell posted a 25 increase to 9.1
billion. Last week, ConocoPhillips reported a 16
rise in net income to 4.1 billion.
3
Why?
- Massive global demand overpowering a finite
supply, aggravated by - Uncertainty about oil supplies in the Middle
East, Nigeria and Venezuela.
4
What should the government do about it?
- Let markets determine prices freely? (Free market
economics) - Control prices to protect consumers? What should
be the price of gasoline?
5
What is a market?
Examples commodities market, stock market,
classified advertising section of the newspaper,
e-bay, market for cocaine...
- Any environment in which buyers and sellers
communicate to exchange goods or services.
6
Quantity Demanded
- The number of units an individual is willing and
able to purchase at each price holding constant
all other factors that may influence his/her
decision.
7
The Law of Demand
And ONLY the price changes
Demand Curves Slope DOWN to the right.
Implies that
8
The Law of Demand
What if at the same time the price drops, your
income drops too?
What if because the price dropped, you no longer
want to buy this good?
What if at the same time that the price drops,
the prices of similar goods also drop?
What if the price drops because a new version is
coming into the market soon?
9
The Ceteris Paribus Assumption
- Other things constant means that all other
factors that affect the analysis are assumed to
remain constant, whether they actually remain
constant or not.
10
The Law of Demand
- When the price goes down ceteris paribus - the
quantity demanded increases and vice versa.
11
The Law of Demand
- When the price goes down and everything else
remains the same - the quantity demanded
increases and vice versa.
12
The Demand Curve
- The demand curve is the graphic representation of
the law of demand. - The demand curve slopes downward and to the
right. - As the price goes up, the quantity demanded goes
down and vice versa.
13
The Demand Curve
Price (per unit)
She will buy 0 units
- The Quantity Demanded is
- The number of units a household would buy at each
market price
10
She will buy 3 units
5
She will buy 7 units
4
D0
If the market price is 4
3
7
0
If the market price is 5
Quantity Demanded (Number of Units Purchased)
If the market price is 10
14
When other things do NOT remain constant
- A households decision about how many units of a
product to demand is also affected by - Prices of Other Goods (P)
- INCOME available (Y)
- TASTES AND PREFERENCES (T)
- EXPECTATIONS with respect to future income,
wealth, and prices (E)
As price drops, all other things constant, the
quantity demanded increases
ceteris paribus
15
Annas Demand Schedule
150
120
100
50
D
30
0
0
6
10
20
24
30
16
Changes in Quantity Demanded vs. Changes in
Demand
Important Distinction!
Changes in quantity demanded are the result of
price changes.
Moving Along a Demand Curve
Changes in demand are the result of changes in
all other determinants of demand (PYTE)
Shift the Demand Curve
17
Price Changes represent a Movement Along the
Demand Curve
150
A drop in price from 100 to 50
120
A movement Along
100
Caused a change in quantity demanded
from 10 to 20
50
30
D
0
20
10
0
6
24
30
18
Determinants of Quantity Demanded
- Prices ONLY!
- Changes in prices cause changes in quantity
demanded - A movement along the demand curve.
19
What is wrong with this sentence?
- When the price goes up demand goes down
20
When Income Increases
At each price now she can afford to buy more units
The entire line shifts!
150
A shift in Demand
120
100
50
30
0
6
10
20
24
30
0
11
17
21
31
35
41
Instead of 24
Instead of 30
Instead of zero units
Instead of 6
Instead of 10
Instead of 20
21
Determinants of Demand
- 1. Income
- Changes in Income cause changes in Demand
- A shift of the Demand curve.
22
Consider the Demand for Gasoline.
Suppose consumer incomes rise. What will happen
to the demand for gasoline?
23
Demand for gasoline
Price
Demand shifts to the right.
D2
D1
0
Quantity demanded
24
Normal Goods
- Goods that people buy more when their income
increases - Goods that people buy less when their income
decreases - Most goods we buy are Normal Goods
Demand for Normal Goods changes in the same
direction as income changes
25
Demand for Normal Goods Increases when Income
Increases
Price
Demand shifts to the right.
D2
D1
0
Quantity demanded Normal Good
26
Inferior Goods
- Goods that people are forced into buying when
incomes drop. - Goods that people buy less or stop buying when
income increases. - Inferior goods are bought only out of necessity
Store Brand Products
Demand for Inferior Goods changes in the opposite
direction as income changes
Generic Products
27
Demand for Inferior Goods Decrease when Income
Increase
Price
Demand shifts to the left.
D1
D2
0
Quantity demanded Inferior good
28
Consider the Demand for Cars.
Suppose consumer incomes rise. What will happen
to the demand for cars?
29
Demand for cars
Price
Demand shifts to the right.
D2
D1
0
Quantity demanded
30
Demand for Public Transportation
Demand for public transportation decreases
Price
A shift to the left.
D1
D2
0
Quantity demanded
31
Determinants of Demand
- Income
- Changes in Income cause changes in Demand
- A shift of the Demand curve.
Demand for normal goods shift to the right
When Income Increases
Demand for inferior goods shifts to the left
Demand for normal goods shift to the left
When Income decreases
Demand for inferior goods shifts to the right
32
Determinants of Demand
- Prices of Related goods Substitute Goods
- Goods that can serve as replacements for one
another - When one of the goods becomes more expensive,
demand for the other good increases. - Perfect substitutes are identical products
from the point of view of the buyer.
33
Substitute Goods
- Fuel oil, natural gas (used for heating or
electricity), coal, nuclear fuels, windmills, etc - Butter and margarine
- Wood and bricks
- Cellular phones and public pay phones
- Compact discs and cassettes
- Zip disks, memory sticks, CDs.
- Different brands of the same product.
34
Consider the Demand for MP3 players.
Suppose price of an Apple Ipod increases. What
will happen to the demand for all other MP3
players?
35
Demand for MP3 Players
Price
Demand shifts to the right.
D2
D1
0
Quantity demanded
36
Determinants of Demand
- Prices of Other Goods Complements
- Goods that are used together
- When one becomes more expensive, we buy fewer
units of both goods. - When the price of one increases, demand for the
other decreases.
If the price of a complement of good X
increases, Demand for X will decrease the demand
curve for X shifts to the left.
37
Complement Goods
- Ipods and songs
- Video game console and video games
- Computers and software/printers/internet service
- Printers and ink cartridges.
- Hamburgers and French fries
- Cars and gasoline
- Phone service and phones
38
Consider the Demand for Songs at the Itunes Music
Store.
Suppose price of an Apple Ipod decreases. What
will happen to the demand for Itunes songs?
39
Consider the Demand for Itunes Songs.
Price
Demand shifts to the right too
D2
D1
0
Quantity demanded
40
Determinants of Demand
- Income
- Changes in Income cause changes in Demand
- A shift of the Demand curve In the same
direction if Normal, in the opposite direction if
inferior. - Prices of Related Goods
- Changes in prices of related goods cause changes
in Demand - An increase in the price of a substitute causes
an increase in Demand (shift to right) for the
good. - An increase in the price of a complement, causes
a decrease in Demand (shift to left) for the
good.
41
Determinants of Demand
- Expectations consumer beliefs about what will
happen in the future. - When consumers expect an increase in price of a
good in the future, they will increase their
purchases of the good TODAY.
An Increase in Demand
A shift to the right in the demand for good A
42
Will this announcement cause a shift in Demand
for Toshiba Notebooks? OR A Movement Along the
demand for Notebooks?
- By the end of next month, Toshiba is expected to
bring into the market a new cheaper version of
their thin notebooks
43
Will the announcement cause a shift in Demand for
French Wine? OR A Movement Along the demand for
French wine?
- The current trade agreement between the US and
France will expire at the end of next month. With
no new agreement in the works, markets are
preparing for the re-establishment of tariffs and
other trade barriers on French goods.
44
Determinants of Demand
- Expectations
- When consumers expect an increase in their
incomes in the future, consumers increase their
purchases of normal goods TODAY.
An Increase in Demand
A shift to the right in the demand for normal
goods
45
News of an impending recession hit Wall Street
as expected
What is the effect of an expected downturn in the
economy on demand for stocks?
46
Determinants of Demand
- Tastes and Preferences
- When consumers tastes and preferences change,
their demand for goods also changes even though
prices remain unchanged. - Consumers become concerned about the safety of
eating imported poultry.
A Decrease in Demand
A shift to the left in the demand for poultry
47
What is wrong with this sentence?
- When the price goes up demand goes down thus we
shift the demand line left
48
Choose the arrow that best represents the effect
and whether it reflects a change in DEMAND or a
change in Quantity Demanded and why?
a
c
b
d
49
- The rental price of a video movie falls. What is
the effect of this price drop on the demand for
rented videos? - The rental price of a video movie falls. What is
the effect of this price drop on the demand for
movie tickets? - The price of VCRs decreases. What is the effect
of this price change on demand for rented videos? - The price of a movie ticket increases. What is
the effect of this price change on demand for
VCRs? - The price of soybeans decrease. What is the
effect of this price change on demand for
soybeans? - As the season progresses, it is clear that the
Chicago Bulls will make it to the playoffs. What
is the effect of this event on the market for
tickets to the Chicago Bulls games?
50
- Per capita incomes in China have risen. What is
the effect of this event on the market for
computers? - A recent report established that Vioxx, a popular
drug used for Arthritis, may increase patients
risk of heart attack, stroke and kidney failure.
What is the effect of this event on the market
for Vioxx? - A recent report established that Vioxx a popular
drug used for Arthritis may increase patients
risk of heart attack, stroke and kidney failure.
What is the effect of this event on the market
for Arthritest and other Arthritis medications?
51
- Consumers consider crab meat and lobster
substitute goods. Suppose that the price of crab
meat increases. What is the effect of this event
on the market for lobster? What is the effect of
this event on the market for crab meat? - Gasoline prices will continue to rise in the
future. What is the effect of this event on the
market for large size vehicles in the U.S? What
is the effect of this event on the demand for
gasoline? What is the effect of this event on the
market for small size vehicles in the U.S? - In 1996 the mad cow disease scare kept
Americans from beef and beef products. What was
the effect of this event on the market for beef
in the U.S? - Synthetic fibers became available. What is the
effect on demand for natural fibers?
52
Market Demand
- Demand for a good or service can be defined for
an individual household, or for a group of
households that make up a market. - Market Demand is the sum of all the quantities of
a good or service demanded per period by all the
households buying in the market for that good or
service
53
To determine the market demand from the
individual demand curves
Price
Price
DA
3.50
1.50
54
Draw the Market Demand
55
(No Transcript)
56
What happens to the Market Demand if we add one
more consumer to the market?
57
(No Transcript)
58
What happens to the Market Demand if we add one
more consumer to the market?
The market demand increases, and the market
demand curve shifts to the right
One more determinant of demand Number of
Consumers in the market.
59
Determinants of Demand
- Prices of related goods
- Incomes
- Tastes and Preferences
- Expectations
- Number of consumers in the market.
60
Prices are Determined by Supply and Demand
Price Changes are the RESULT of either a change
in supply alone, a change in demand alone or a
simultaneous change in both demand and supply .
61
Competitive Markets
- Buyers and sellers are price takers There are so
many buyers and sellers, that no single buyer or
seller has the ability to influence the market
price. - Smallness each buyer/seller is so small relative
to the size of the market, that changes in
production have no influence on the market price
or on the actions of other firms. - No barriers to entry or exit.
- Each firms output is indistinguishable from any
other firms. - Consumers have all necessary information about
prices, products and available technology no
firm or consumer have an advantage over another. - Firms are in business to earn profits.
62
Why should exit be costless?
- There are barriers to exit when exiting the
industry is not costless. This happens when to
enter, a firm would have to purchase assets with
no alternative use (say a nuclear power plant). - Sunk costs are costs that are unavoidable once
they have been committed at a particular moment
in time - An example is the money that the telecoms spent
to win mobile phone licenses at auction in 2000.
These costs are sunk. Exit is no longer
costless, in which case exiting the industry
requires that you lose your investment.
63
Environmentalist
- We must cut demand for fossil fuels because we
are going to run out.
64
http//www.oil-price.net/