Urticaria - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 23
Title:
Urticaria
Description:
May be caused by systemic response secondary to new medications, ... Kawasaki Disease. Presents with recurrent fever after being diagnosed with URI last week. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:2901
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Urticaria
1
Urticaria
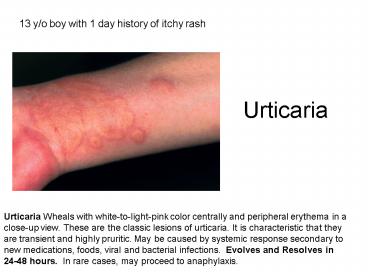
13 y/o boy with 1 day history of itchy rash
Urticaria Wheals with white-to-light-pink color
centrally and peripheral erythema in a close-up
view. These are the classic lesions of urticaria.
It is characteristic that they are transient and
highly pruritic. May be caused by systemic
response secondary to new medications, foods,
viral and bacterial infections. Evolves and
Resolves in 24-48 hours. In rare cases, may
proceed to anaphylaxis.
2
Kawasaki Disease
Presents with recurrent fever after being
diagnosed with URI last week.
- Conjuctival Injection (limbic sparing and no
exudate) - Mucous membrane changes (fissures and no discrete
lesions or exudates) - Morbilliform Rash
- Cervical Lymphadenopathy (50), not generalized
- Edema of palms and soles
3
Lyme Disease
14 y/o boy returns from mountain biking trip near
lake tahoe
Anywhere in continental U.S.A. Erythema Migrans
Expanding annular lesion around original
bite Affected satellite areas /- fever, malaise,
LAD One-month Later Arthritis, neurological
including Bellpalsy, cardiac conduction defects
Serology unreliable in early in course of
disease (false positives). Western Blot is more
specific Tx 8
y/o x 14 days
4
Candida
3 month old with red bottom after Desitin cream
- Confluent erosions, marginal scaling, and
"satellite pustules" in the area covered by a
diaper in an infant - No sparing of gluteal folds
- Atopic dermatitis or psoriasis also occurs in
this distribution and may be concomitant. - Prefers warm/moist areas
- Imidazole cream or nystatitin for 3-4 days after
rash disappears
5
Oral Candida
2 ½ y/o boy with history of persistent asthma
presents to clinic
- White curdlike material on the mucosal surface
the material can be abraded off with gauze
(pseudomembranous), revealing underlying
erythema. - May affect fissures of mouth (perleche)
- Associated with recent, abx, inhaled steroids and
immunosuppression - May be seen with breast feeding (treat mom as
well) - Wash mouth or brush teeth after use of inhaled
steroids - Nystatin 1-2 ml to each check after eating TID
for two days after rash resolves or miconazole gel
6
Molluscum Contagiosum
15 y/o girl presents for sport physical and you
notice these lesions
- Caused by Pox Virus
- Typically, discrete, solid, skin-colored papules,
1 to 2 mm in diameter, with central umbilication
on the face, chest, trunk, axilla, or genitalia - Presents with multiple lesions, usually grouped
- Lesion with an erythematous halo is undergoing
spontaneous regression. - Self-limited. May curette but will leave small
scar, Cantharone Beetle Juice, Aldara
(imiquimod), Retin A 0.1 - Cimetidine PPx if complicated with eczema
7
Rubella
16 y/o presents from low-grade fever, ocular
pain, sore throat, and myalgia.
- Very unlikely if immunized
- Erythematous macules and papules appearing
initially on the face and spreading inferiorly to
the trunk and extremities, usually within the
first 24 h. - Postauricular and posterior cervical lymph
adenopathy - Lesions becoming confluent on the cheeks while
clearing on the forehead. B. Truncal lesions
appear 24 h after onset of facial lesions. - Disappears by fourth day with few symptoms
- Risk of first trimester infection leads to 80
affect rate among infants growth retardation,
cardiac anomalies, cataracts/glaucoma/retinitis,
deafness, encephalitis, thrombocytopenia,
leukopenia, hepatitis, etc.
8
Measles
Overweight 12 y/o with fever, runny nose, cough,
lethargy, photophobia, and pus in both eyes
- Measly look sick
- Erythematous flat papules, first appearing on the
face and neck where they become confluent,
spreading to the trunk and arms in 2 to 3 days
where they remain discrete. - Rash resolves in 6 days
- In contrast, rubella also first appears initially
on the face but spreads to the trunk in 1 day. - Erythematous papules usually become confluent on
the face on the fourth day. - Koplik's (few to countless small white papules on
red base, 1-2 days prior to and after onset of
rash) spots on the buccal mucosa near lower
molars - Complications include bacterial pneumonia,
encephalitis (12000). Year later may develop
subactue sclerosign panencephalitis (1100,000) - Confirm with serology (IgM)
- Break-outs 2/2 poor immunization practices, one
dose - Supportive therapy. Ribavirin for
immunocompromised. - Exposure treated with vaccine and passive PPx
9
HFM- Cocksackie Virus
8 y/o hispanic boy presents low-grade fever,
malaise, sore throat and painful mouth sores
- Multiple, superficial erosions and small,
vesicular lesions surrounded by an erythematous
halo on the lower labial mucosa the gingiva is
normal. - In primary herpetic gingivostomatitis, which
presents with similar oral vesicular lesions, a
painful gingivitis usually occurs as well. - Vesciculopustues on hands are asymptomatic and
evolve into superficial erosions - May have macular papular eruption on buttocks
- Late summer and early fall
- Supportive therapy, magic mouth wash (mylanta,
benadryl)
10
Erythema infectiosum (Fifth Disease)
Happy 7 y/o girl is brought in by worried mom.
- Parvivurys B19
- Stage I Diffuse erythema and edema of the cheeks
with "slapped cheek" facies in a child. - Stage II Discrete, erythematous macules with
ring formation, papules, and urticaria on
extremities and trunk after face rash fades - May be pruitic
- Stage III As portion of rash fade, a retucular
or marbled appearance develops and may last
anywhere from 1 to 8 weeks. - No treatment required but associated with bone
marrow suppresion and reactive arthritis
11
Primary Gingivostomatitis
5 y/o girl with poor dentition presents with
painful mouth lesions.
- Herpes simplex virus
- Multiple, very painful erosions on the lower
labial mucosa with erythema and edema of the
gingiva - Fibrin deposits on teeth, toungue, and gingiva.
- Fever and tender submandibular lymphadenopathy
- /- dysphagia and dehydration
- Commonly under 3 y/o
- Recurrent in immunocomprised patients
- Tx c acyclovir early 10 mg/kg tid x 7 days in
first 48-72 hours
12
Herpetic Whitlow
15 y/o boy with chronic nail biting develops this
lesion
- Herpes simplex virus infection
- Painful, grouped, confluent vesicles on an
erythematous edematous base on the distal finger
were the first (and presumed primary) symptomatic
infection. - Always ask about sick contacts
- Confused with paronychia
- May result in exzema herpeticum, if at risk
- Treat if caught within 72 hours
13
Herpes Simplex Neonatal
Previously healthy 3 week old presents with these
lesions
- Vesicles and crusted erosions on the upper lip
and large geographic ulcerations of the tongue
were the clinical findings in this neonate with
herpetic gingivostomatitis. - Grouped and confluent vesicles with underlying
erythema and edema on the shoulder of a newborn
infant, arising at the inoculation site. - Treat with 20 mg/kg IV acyclovir q 8 hours
for14-21 days
14
Varicella
17 y/o with chronic acne presents with these
lesions
- Incubation period 10-20 days, without exposure
history - Prodrome of 1-3 days of fever, respiratory
symptoms, and headache - Multiple, very pruritic, erythematous papules,
vesicles ("dewdrops on a rose petal"), and
crusted papules on erythematous, edematous
concentrated on face - Dissemination to trunk in random pattern with
multiple papules and vesicles on erythematous
bases - Lesion typically are at different stages of
evolution of individual lesions and crust over
5-6 days. - Once crusted, no longer contagious
- Confirm with Tzank (old), DFIA, Serology,
- Typically, no leukocytosis and mild increase in
LFTs
15
Pityriasis Versicolor (Tinea)
14 y/o presents with these lesions
- Malassezia furfur/pityrosporum orbiculare
- Numerous sharply marginated brown macules on
upper chest, back, proximal arms, and neck with
associated fine scale - May be hyperpigmented, hypopigmented or
brown-orange in color - KOH prep spaghetti and meatballs
- Brown glow with woods lamp
- Tx selenum sulfide (2.5) to whole body x 1 with
repeat in one week - May use topical antifungals
16
Atopic Dermatitis
9 y/o with worsening itching during summer camp
- the itch that rashes."
- The lesions are papular, lichenified plaques,
erosions, crusts, especially on the antecubital
and popliteal fossae - African and Asian children often present with
pruritic follicular papules (follicular eczema) - Erosions moist, crusted. Linear or punctate,
resulting from scratching. - Serum IgE level is usually (85) elevated Atopic
dermatitis childhood-type - Dust mites and pollens, have been shown to cause
exacerbations of AD. - Subset of infants and children have flares of AD
with eggs, milk, peanuts, soybeans, fish, and
wheat.
17
Atopic Dermatitis
6 month old with irritability, difficulty
sleeping, and rash
- Usually, first 2 months of life and by the first
years in 60 of patients. 30 are seen for the
first time by age 5, and only 10 develop AD
between 6 and 20 years of age. - Confluent erythema, papules, microvesiculation,
scaling, and crusting on the face, with similar
involvement (to a lesser degree) of the trunk and
arms. The facial involvement is more severe due
to easier access to scratching. - May involve diaper area
- Risk for superinfection with staph aureas and
herpes simplex - Tx gentle soaps, extra rinse c hypoallergenic
detergent, minimize sweating, oatmeal/baking soda
in baths with immediate occlusive lotions, even
vaseline or crisco shortening. In moderate
cases, may use low-moderate dose steroids
(Hydrocortisone 1 to Triamcinolone 0.01) or tar
preparation in addition to oral anithistamines
18
Infant Atopic Dermatitis
4 month old infant with diaper rash
- Usually, first 2 months of life and by the first
years in 60 of patients. 30 are seen for the
first time by age 5, and only 10 develop AD
between 6 and 20 years of age. - Confluent erythema, papules, microvesiculation,
scaling, with erosions - Risk for superinfection with staph aureas and
herpes simplex - Tx gentle soaps, extra rinse c hypoallergenic
detergent, minimize sweating, oatmeal/baking soda
in baths with immediate occlusive lotions, even
vaseline or crisco shortening. In moderate
cases, may use low dose steroids (Hydrocortisone
1) or tar preparation in addition to oral
anithistamines
19
Atopic Dermatitis
12 y/o cross country runner presents with this
itchy rash
- the itch that rashes."
- The lesions are papular, lichenified plaques,
erosions, crusts, especially on the antecubital
and popliteal fossae - African and Asian children often present with
pruritic follicular papules (follicular eczema) - Erosions moist, crusted. Linear or punctate,
resulting from scratching. - Serum IgE level is usually (85) elevated Atopic
dermatitis childhood-type - Dust mites and pollens, have been shown to cause
exacerbations of AD. - Subset of infants and children have flares of AD
with eggs, milk, peanuts, soybeans, fish, and
wheat.
20
Ichthyosis Vulgaris
9 y/o presents with for physical exam and has
this itchy rash
- Herditary, with onset3 to 12 months
- 50 overlap with atopic dermatitis
- Xerosis (dry skin) with fine, powdery scaling but
also larger, firmly adherent tacked-down scales
in a fish-scale pattern - Usually, diffuse general involvement, accentuated
on the shins, arms, and back but also on the
buttocks and lateral thighs axillae and the
anticubital and popliteal fossae spared - Tx with occlusive or Keratolytic Agents Propylene
glycol-glycerin- lactic acid mixtures (i.e
lac-hydrin)
21
Ichthyosis of the Newborn
Dr. Mannino asks you to see this 6 month old for
well child check and shows you the babys picture
at 1 week of life and now.
- "Collodion baby'' shortly after birth with a
parchment-like membrane covering the entire skin.
The eyes and lips pucker outward, i.e., ectropion
and eclabion. B. - At risk of infection and temperature
dysregulation while healing - May lead to ichthyosis will chronic sequellae
- In some cases, may resolve completely with
minimal residual scale and erythema on the
cheeks.
22
Vitiligo
- Vitiligo knees Depigmented, sharply demarcated
macules on the knees. Apart from the loss of
pigment, vitiliginous skin appears normal. Note
tiny follicular pigmented spots within the
vitiligo areas that represent repigmentation.
23
Hypermelanosis
- Hypermelanosis with acne This condition is a
major complaint of this 18-year-old African
American (skin phototype V). The acne is not the
problem now it is the disfiguring
hypermelanosis. This hyperpigmentation can be
markedly reduced with topical hydroquinone
solution, 3, applied daily. During the
depigmentation, the patient must use an opaque
sunblock daily to prevent the pigment darkening
that occurs with daily sun exposure.