I' Microscopy - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 24
Title:
I' Microscopy
Description:
I. Microscopy. magnification. resolving power. Ocular x Objective. Electron Microscopes: ... SEM beam scans the surface of a specimen coated with a thin layer of gold ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:36
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: I' Microscopy
1
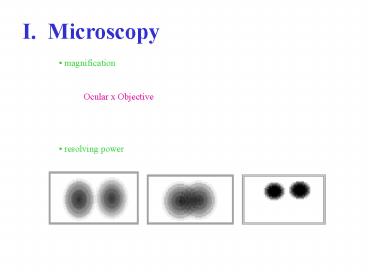
I. Microscopy
- magnification
Ocular x Objective
- resolving power
2
Electron Microscopes
Better resolving power than light microscopes
TEM ? aims an electron beam at a thin stained
section
Used to study internal cell structure
3
SEM ? beam scans the surface of a specimen coated
with a thin layer of gold
- Visualized entire image
- Creates a 3-D image
4
BUT, EMs can only view dead cells
PHASE CONTRAST ? allow unstained, living tissues
to be observed
CELL FRACTIONATION ? using a centrifuge to
separate cell components based on
DENSITY
5
PROKARYOTIC vs. EUKARYOTIC
- found in Kingdoms Protista, Fungi, Plantae,
Animalia
- found only in Kingdom Monera
- no true nucleus lacks nuclear envelope
- true nucleus bounded by nuclear envelope
- genetic material in nucleoid region
- genetic material within the nucleus
6
PROKARYOTIC vs. EUKARYOTIC
- contains cytoplasm w/ cytosol and membrane-bound
organelles
- no membrane-bound organelles
- have a plasma membrane and usually a cell wall
- usually smaller than eukaryotes
7
PROKARYOTIC vs. EUKARYOTIC
8
CELL SIZE is limited by
- metabolic requirements
- surface area to volume ratio
II. PARTS of the CELL
9
- nucleus
histones
10
- cytoplasm
- cytosol
- nucleolus
- ribosomes
- endoplasmic reticulum
11
- Golgi apparatus
- lysosomes
- intracellular digestion
- apoptosis
12
- vacuoles
- peroxisomes
13
- mitochondria
14
- Cytoskeleton
- microtubules
- intermediate filaments
- microfilaments
15
- cell walls
16
- glycocalyx
- Intercellular Junctions
- tight junctions
- desmosomes
17
- gap junctions
18
IV. MEMBRANES
- Singer-Nicolson Fluid Mosaic Model
19
- Selective Permeability
20
- Water Potential
- hypoosmotic environments
- isotonic environments
- hyperosmotic environments
21
- Diffusion and Osmosis
22
- Facilitated Diffusion
- Active Transport
23
- Forms of Active Transport
- ATP Pump
- Symport
- Antiport
24
- Receptor-mediated endocytosis