Preparation of Tissues for Transmission Microscopy - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Preparation of Tissues for Transmission Microscopy
Description:
Preparation of Tissues for Transmission Microscopy – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:654
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Preparation of Tissues for Transmission Microscopy
1
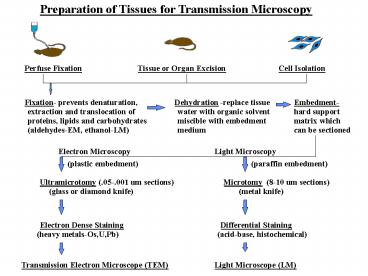
Preparation of Tissues for Transmission Microscopy
Perfuse Fixation
Tissue or Organ Excision
Cell Isolation
Fixation- prevents denaturation,
Dehydration
-replace tissue
Embedment-
extraction and translocation of
water with organic solvent
hard support
proteins, lipids and carbohydrates
miscible with embedment
matrix which
medium
(aldehydes-EM, ethanol-LM)
can be sectioned
Electron Microscopy
Light Microscopy
(plastic embedment)
(paraffin embedment)
Ultramicrotomy (.05-.001 um sections)
Microtomy
(8-10 um sections)
(glass or diamond knife)
(metal knife)
Electron Dense Staining
Differential Staining
(heavy metals-Os,U,Pb)
(acid-base, histochemical)
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
Light Microscope (LM)
2
Chemical Constituents of Cells and Tissues
3
Histological Stains based on Acid-Base Reactions
4
Hematoxylin and Eosin (HE)
Nuclei (DNA) and Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
(ribosomes-RNA) are acids and
basophilic and stain blue with hematoxylin.
Cytoplasmic proteins (acidophilic at neutral
pH) stain pink with eosin.
5
Heidenhahns Iron Hematoxylin
Chemical specificities are uncertain but stains
cell membranes, secretory granules
and skeletal muscle striations.
Zymogen Secretory Granules in Pancreas
Striations in Skeletal Muscle Fiber
6
Mallorys and Massons Trichrome
Combines several acidic dyes- collagen and
reticular fibers stain blue, nuclei and cytoplasm
stain red and elastic fibers stain yellow or pink
Tracheal Epithelium
Dense, Regular, Elastic Connective Tissue
7
Golgis Silver Stain
Selective for nerve cells-neurons blacken when
silver is reduced. Only a few cells stain which
is useful for determing relations between nerve
cell processes.
Pyramidal Cell in Cerebral Cortex
Synaptic Boutons on Purkinje Cell
8
Cajals Gold Method
Purkinje Cells in
Cerebellum
9
Weigerts Potassium Dichromate
Stains lipid in myelin sheath of
nerve axons
Myelinated Axons and Node of
Ranvier
10
Metachromasia
Property of cell components to take on a
different color than that of the dye with which
they are stained (e.i. metachromatic granules)
Metachromatic Histamine Granules in Mast
Cells
11
Histochemical Stains
Stains mucopolysaccharides (intestinal mucosa
liver glycogen) and glycoproteins
Glycogen in Liver Cells
Intestinal Mucosa
Goblet Cells
12
Histochemical Stains
Feulgen Reaction- Mild acid hydrolysis removes
RNA but not DNA and unmasks aldehyde groups of
deoxyribose. Free aldehyde groups react with
Schiffs reagent. Nuclei and chromatin are
Feulgen positive and cytoplasm is Feulgen
negative.
Spermatogonia and Spermatids in
Seminiferous Tubule
spermatid
Spermatogonium
13
Lysosomes-Light Micrograph
Lysosomes- Electron Micrograph
14
ELECTRONS AND RESOLUTION
LIGHT MICROGRAPH
ELECTRON MICROGRAPH
15
Transmission Electron Microscope
16
CONTRAST IN TRANSMISSION ELECTRON MICROSCOPY
Electron
Dense
Electron
Transparent
Electron
Transluscent
17
Magnification with the Transmission
Electron Microscope
Lung Tissue (LM) 100 X
Lung Alveolus (TEM)- 3000 X
18
Scanning Electron Microscope
19
Depth of Focus with the Scanning Electron
Microscope
Light Micrograph of Ants Head
Scanning EM of Ants Head
20
Three Dimensionality in Scanning Electron
Microscopy
Kidney Glomerulus-Light Micrograph
Kidney Glomerulus- Scanning EM
21
Freeze Fracturing
Fracturing
Transmission EM of Replica
Replication
22
Split
Membranes
Gap Junction - TEM
Gap Junction - Freeze Fracture
Tight Junction
Tight Junction
TEM
Freeze-Fracture
23
TEM Section and Freeze Fracture
Comparason
Section Through Apical Region of
Freeze-Fracture Replica of Apical
Intestinal Adsorptive Cell
Region of Intestinal Adsorptive Cell
Tight Junctions