Chapter 20: Transition Metals - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 8
Title:
Chapter 20: Transition Metals
Description:
Exhibit similarities within a period as well as a group, whereas representative ... luster, variable oxidation state, many paramagnetic ions, many colored ions ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:144
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Chapter 20: Transition Metals
1
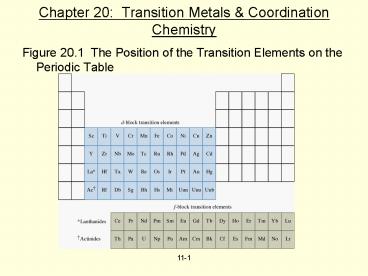
Chapter 20 Transition Metals Coordination
Chemistry
- Figure 20.1 The Position of the Transition
Elements on the Periodic Table
2
- Transition Metal has partially filled
d-orbitals in metal or common oxidation states
(d1 d9) - Inner Transition Metal has partially filled
f-orbitals - Exhibit similarities within a period as well as a
group, whereas representative metals exhibit
similarities only within a group. - Properties most hard strong, good electrical
thermal conductivity, metallic luster, variable
oxidation state, many paramagnetic ions, many
colored ions
3
- Complex Ions transition-metal ion covalently
bonded to a number of Lewis bases (ligands) - Ni2 6 NH3 ? Ni(NH3)62
- Co2 4 Cl ? CoCl42
- Recall from lab FeSCN2, Co(H2O)62
- Electron Configurations recall Aufbau principle
(section 7.11) - Sc Ar4s23d1
- Cr Ar4s13d5
- Cu Ar4s13d10
4
- Electron Configurations of Ions
- Lose es of highest n-value first.
- Sc2 Ar3d1
- Cr2 Ar3d4
- Oxidation States see Table 20.2
- Exs V 2, 3, 4, 5
- Mn 2, 3, 4, 7
- Co 2, 3
- Ionization Energies see Figure 20.2
5
Figure 20.2Plots of the First (Red Dots) and
Third (Blue Dots) Ionization Energies for the
First-Row Transition Metals
6
- Reducing Strength Table 20.3
- M(s) ? Mn(aq) n e
- Lower E indicates stronger reducing agent
- Sc3 3 e ? Sc E 2.08 V
- Cu2 2 e ? Cu E 0.34 V
- All metals with negative E will dissolve in acid
to release H2 - Fe(s) 2 H(aq) ? Fe2(aq) H2(g)
- ?E 0.00 (0.44) 0.44 V
7
- Atomic Radii
- Main groups increase down a group, decrease
across a period as Z increases - Transition metals decrease across a period,
increase from 3d to 4d, but 4d 5d metals - Lanthanide contraction 5d metals smaller than
expected due to the presence of the lanthanides
and addition of 14 protons immediately before
starting 5d series - 4d 5d metals very similar in behavior
8
Figure 20.3Atomic Radii of the 3d, 4d , and 5d
Transition Series