Dynamics of Learning - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 1
Title:
Dynamics of Learning
Description:
Dynamics of Learning & Distributed Adaptation. Santa Fe Institute: James P. Crutchfield, P.I. ... Monitor emergence of cooperation in agent collectives ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:92
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Dynamics of Learning
1
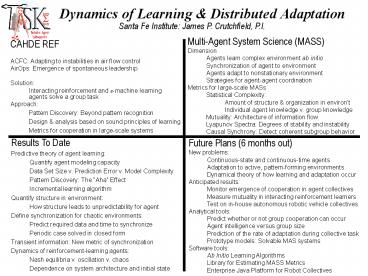
Dynamics of Learning Distributed Adaptation
Santa Fe Institute James P. Crutchfield, P.I.
Multi-Agent System Science (MASS) Dimension Agents
learn complex environment ab initio Synchronizati
on of agent to environment Agents adapt to
nonstationary environment Strategies for
agent-agent coordination Metrics for large-scale
MASs Statistical Complexity Amount of structure
organization in environt Individual agent
knowledge v. group knowledge Mutuality
Architecture of information flow Lyapunov
Spectra Degrees of stability and
instability Causal Synchrony Detect coherent
subgroup behavior
- CAHDE REF
- ACFC Adapting to instabilities in air flow
control - AirOps Emergence of spontaneous leadership
- Solution
- Interacting reinforcement and ?-machine learning
agents solve a group task - Approach
- Pattern Discovery Beyond pattern recognition
- Design analysis based on sound principles of
learning - Metrics for cooperation in large-scale systems
Future Plans (6 months out) New
problems Continuous-state and continuous-time
agents Adaptation to active, pattern-forming
environments Dynamical theory of how learning and
adaptation occur Anticipated results Monitor
emergence of cooperation in agent
collectives Measure mutuality in interacting
reinforcement learners Test on in-house
autonomous robotic vehicle collectives Analytical
tools Predict whether or not group cooperation
can occur Agent intelligence versus group
size Prediction of the rate of adaptation during
collective task Prototype models Solvable MAS
systems Software tools Ab Initio Learning
Algorithms Library for Estimating MASS
Metrics Enterprise Java Platform for Robot
Collectives
- Results To Date
- Predictive theory of agent learning
- Quantify agent modeling capacity
- Data Set Size v. Prediction Error v. Model
Complexity - Pattern Discovery The Aha Effect
- Incremental learning algorithm
- Quantify structure in environment
- How structure leads to unpredictability for agent
- Define synchronization for chaotic environments
- Predict required data and time to synchronize
- Periodic case solved in closed form
- Transient information New metric of
synchronization - Dynamics of reinforcement-learning agents
- Nash equilibria v. oscillation v. chaos
- Dependence on system architecture and initial
state