MODEL - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 13
Title: MODEL
1
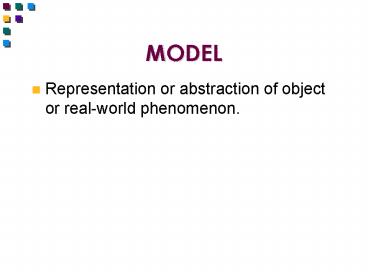
MODEL
- Representation or abstraction of object or
real-world phenomenon.
2
Types of Models
- Iconic - physical representation that actually
looks like the object it represents - analog - represents dynamic situations statically
- symbolic - represents problem by a system of
symbols or mathematical relationships
3
SIMULATION
- A numerical technique of experimentation to
determine the dynamic behavior
of a management system.
4
The Process of Simulation
Define the Problem
Introduce important variables
Construct simulation model
Specify the values to be tested
Conduct the simulation
Examine the results
Select best course of action
5
Advantages of Simulation
- Simulation
- 1. is very flexible, and relatively
straightforward - 2. can be used to analyze large and complex
real-world problems for which closed form
analytical solutions are not possible - 3. allows for the inclusion of real-world
complications which most other techniques do not
permit - 4. make possible Time compression
- 5. allows one to ask what if type questions
- 6. does not interfere with the real-world system
- 7. allows us to study the interactive effect of
individual components or variables
6
Disadvantages of Simulation
- Simulation
- 1. may be very time consuming and expensive
- 2. does not generate optimal solutions
- 3. requires that management generate parameters
describing the conditions to be studied and the
constraints on the system activity - 4. produces a unique model which may not be
transferable to another problem
7
The Monte Carlo Simulation Technique
- 1. Setup probability distribution for important
variables - 2. Build cumulative distribution for each
variable - 3. Establish interval of random numbers for each
variables - 4. Generate random numbers
- 5. Simulate a series of trials
8
Graphical Representation of the Cumulative
Probability
00
Represents 4 items Demanded
86
85
66
65
Cumulative Probability
Random Numbers
36
35
Represents 1 item Demanded
16
15
06
05
01
Daily Demand for Radials
9
52 37 82 69 98 96 33 50 88 90 50 27 45 81 66 74 30
59 67 60 60 80 53 69 37
06 63 57 02 94 52 69 33 32 30 48 88 14 02 83 05 34
55 09 77 08 45 84 84 77
50 28 68 36 90 62 27 50 18 36 61 21 46 01 14 82 87
72 80 46 19 86 49 12 13
88 02 28 49 36 87 21 95 50 24 18 62 32 78 74 82 01
33 98 63 29 99 63 94 10
53 74 05 71 06 49 11 13 62 69 85 69 13 82 27 93 74
62 99 71 36 02 26 51 02
30 35 94 99 78 56 60 44 57 82 23 64 49 74 76 09 11
13 25 69 72 34 65 36 18
10 24 03 32 23 59 95 34 34 51 08 48 66 97 03 96 46
74 77 44 30 87 72 17 31
47 03 11 10 67 23 89 62 56 74 54 31 62 37 33 33 82
68 50 22 27 08 84 02 19
99 29 27 75 89 78 68 64 62 30 17 12 74 45 11 52 59
22 03 03 50 86 85 15 32
37 60 79 21 85 71 48 39 31 35 12 73 41 31 97 78 94
44 32 85 64 84 63 29 85
66 74 90 95 29 72 17 55 15 36 80 02 86 94 59 13 25
42 36 14 85 49 26 16 31
91 85 87 90 21 90 89 29 40 85 69 68 98 99 81 06 34
09 63 48 72 76 02 52 94
35 90 92 94 25 57 34 30 90 01 24 00 92 42 72 28 32
32 65 69 75 24 75 56 81
32 73 41 38 73 01 09 64 34 55 84 16 98 49 00 30 23
46 75 13 29 08 26 43 43
00 59 09 97 69 98 93 49 51 92 92 16 84 27 64 94 17
71 94 30 87 01 92 26 31
84 55 25 71 34 57 50 44 95 64 16 46 54 64 61 23 01
79 19 50 05 86 62 22 58
57 17 36 72 85 31 44 30 26 09 49 13 33 89 13 37 58
45 95 33 75 29 40 09 33
07 60 77 49 76 95 51 16 14 85 59 85 40 42 52 39 73
89 88 24 01 11 67 62 51
R A N D O M N U M B E R S
T A B L E O F
10
Flow Diagram for Inventory simulation
Begin day of simulation.
Increase current inventory by quantity ordered.
Yes
Has order arrived?
No
Select random number to generate todays demand.
Is demand greater than beginning inventory?
Yes
Record number of lost sales.
No
Compute ending inventory Beginning inventory -
Demand
Record ending inventory 0
Is ending inventory less than reorder point?
Has order been placed that hasnt arrived yet?
Yes
No
Place order
Have enough days of this order policy
been simulated?
Yes
No
No
Select random number to generate lead time.
Yes
Compute average ending inventory, average lost
sales, average number of orders placed, and
corresponding costs.
End
11
SERVICE WINDOW EXAMPLE
TIME BETWEEN ARRIVALS
SERVICETIME
PROBABILITY
PROBABILITY
.2 .3 .3 .2
1 2 3
.3 .5 .2
1 2 3 4
Random number for arrivals 14, 74, 27, 03 Random
numbers for service times 88, 32, 36, 24 Window
opens at 11 am. What time does the fourth
customer leave the system?
12
SERVICE WINDOW EXAMPLE
Answer
TIME BETWEEN ARRIVALS
SERVICETIME
PROB.
PROB.
RN
RN
.2 .3 .3 .2
1 2 3
.3 .5 .2
1 2 3 4
01-20 21-50 51-80 81-00
01-30 31-80 81-00
13
SERVICE WINDOW EXAMPLE
First arrival (RN 14) at 1101. Service time
3 (RN 88). Leaves at 1104. Second arrival
(RN 74) at 1104 (3 minutes after 1st). Service
time 2 (RN 32). Leaves at 1106. Third
arrival (RN 27) at 1106. Service time 2 (RN
36). Leaves at 1108. Fourth arrival (RN
03) at 1107. Must wait 1 minute for service to
start. Service time 1 minute (RN 24).
Leaves at 1109.