Software Engineering Roadmap: Chapter 9 Focus - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 18
Title:
Software Engineering Roadmap: Chapter 9 Focus
Description:
Adapted from Software Engineering: An Object-Oriented ... Implemen- tation. Test. Jacobson et al: USDP. Prelim. iterations. Iter. #1. Iter. #n. Iter. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:43
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Software Engineering Roadmap: Chapter 9 Focus
1
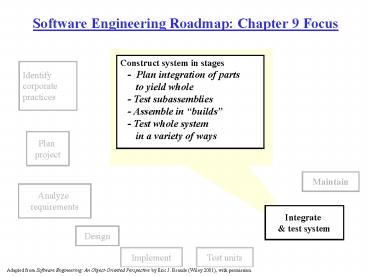
Software Engineering Roadmap Chapter 9 Focus
Construct system in stages - Plan
integration of parts to yield whole -
Test subassemblies - Assemble in builds -
Test whole system in a variety of ways
Identify corporate practices
Plan project
Maintain
Analyze requirements
Integrate test system
Design
Test units
Implement
Adapted from Software Engineering An
Object-Oriented Perspective by Eric J. Braude
(Wiley 2001), with permission.
2
Unified Process for Integration Test
Jacobson et al USDP
Elaboration
Inception
Construction
Transition
Requirements Analysis Design Implemen- ta
tion Test
Integration
Unit Tests
Integration tests ... System tests
Prelim. iterations
Iter. 1
Iter. n
Iter. n1
Iter. m
Iter. m1
Iter. k
..
..
3
Testing for Validation and Verification(After
Myers)
(11) Acceptance tests
Requirements
(10) Installation tests
validation1
(9) Usability tests
(8) System tests
Architecture
verification2
(7) Regression tests
(6) Integration tests
Interface specs
verification2
(5) Interface tests
(1), (4) Function tests
verification2
Detailed design
(2), (3) Module tests
Includes use-cases performance testing
Note 2 Tested against documents indicated
Note 1 Tested against requirements
4
Integration Schedule
Month 1
Month 2
Month 3
Month 4
Month 5
1
2
3
4
1
2
3
4
1
2
3
4
1
2
3
4
1
2
3
4
1
Milestones
Complete prototype
Proto. requirements
Elaboration iterations
Iterations
Inception iteration
Iteration 2 elementary interaction
Iteration 1 view characters in areas
Builds
build 1
build 3
build 2
RolePlaying- Game package
Characters package
GameEn- vironment package
Modules
Encounter Characters package
Encounter- Environ- ment package
EncounterGame package
Integrate test
Integrate test
Integrate test
Adapted from Software Engineering An
Object-Oriented Perspective by Eric J. Braude
(Wiley 2001), with permission.
5
- 1. Understand the architecture decomposition.
- try to make architecture simple to integrate
- 2. Identify the parts of the architecture that
each iteration will implement. - build framework classes first, or in parallel
- if possible, integrate continually
- build enough UI to anchor testing
- document requirements for each iteration
- try to build bottom-up
- so the parts are available when required
- try to plan iterations so as to retire risks
- biggest risks first
- specify iterations and builds so that each use
case is handled completely by one - 3. Decompose each iteration into builds if
necessary. - 4. Plan the testing, review and inspection
process. - see section tbd.
- 5. Refine the schedule to reflect the results.
One way to ...
Plan Integration Builds
Adapted from Software Engineering An
Object-Oriented Perspective by Eric J. Braude
(Wiley 2001), with permission.
6
Factors Determining the Sequence of Integration
- Usage of modules by other modules
- build and integrate modules used
before modules that use them - Defining and using framework classes
- Exercising integration early
- Exercising key risky parts of the application as
early as possible - Showing parts or prototypes to customers
technical (factors)
risk reduction
requirements
Adapted from Software Engineering An
Object-Oriented Perspective by Eric J. Braude
(Wiley 2001), with permission.
7
Plan and Execute Integration Tests
One way to ...
- 1. Decide how and where to store, reuse and code
the integration tests. - show this in the project schedule
- 2. Execute as many unit tests (again) as time
allows - this time in the context of the build
- no drivers or stubs required this time
- prioritize by those most likely to uncover
defects - 3. Exercise regression tests
- to ensure existing capability has not been
compromised - 4. Ensure build requirement are properly
specified - 5. Exercise use cases that the build should
implement - test against the SRS
- 6. Execute the system tests supported by this
build
Adapted from Software Engineering An
Object-Oriented Perspective by Eric J. Braude
(Wiley 2001), with permission.
8
Relationship between Use Cases, Iterations and
Builds
Iteration 5
4
6
5.4
5.2
build 5.3
Use case 7
Use case 14
Use case 23
Use case 9
extends or includes
Adapted from Software Engineering An
Object-Oriented Perspective by Eric J. Braude
(Wiley 2001), with permission.
9
Include og extend use cases
10
Artifacts and Roles for Integration Testing
Component engineer
Integration tester
System tester
Test engineer
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . responsible
for . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . .
Test evaluation
?
Use-case model
Test procedure
Test plan
Test component
Defect management
Test case
Jacobson et al USDP
11
Types of System Tests 1
- Volume
- Subject product to large amounts of input.
- Usability
- Measure user reaction (e.g., score 1-10).
- Performance
- Measure speed under various circumstances.
- Configuration
- Configure to various hardware / software
- e.g., measure set-up time.
- Compatibility
- -- with other designated applications
- e.g., measure adaptation time.
- Reliability / Availability
- Measure up-time over extended period.
see Kit Ki
12
- Security
- Subject to compromise attempts.
- e.g., measure average time to break in.
- Resource usage
- Measure usage of RAM and disk space etc.
- Install-abililty
- Install under various circumstances.
- measure time to install.
- Recoverability
- Force activities that take the application down.
- measure time to recover
- Serviceabililty
- Service application under various situations.
- measure time to service
- Load / Stress
- Subject to extreme data event traffic
Types of System Tests 2
see Kit Ki
13
Key Attributes for Usability Testing
- Accessibility
- How easily can users enter, navigate exit?
- e.g., measure by average time taken to . . .
- Responsiveness
- How quickly does the application allow the user
to accomplish specified goals? - e.g., measure by average time taken
- Efficiency
- Degree to which the number of required steps for
selected functionality is minimal - minimal deduced in theory
- e.g., measure by minimal time / average time
- Comprehensibility
- How easy is the product to understand and use
with documentation and help? - e.g., measure time taken for standard queries
Adapted from Kit Ki.
14
Roadmap for the Transition Iterations
- Define population
- Plan defect collection
- Identify stopping criteria
1. Plan alpha and beta testing.
- Prepare
- Distribute install
- Carry out (users / customers)
- Gather defect reports
- Observe stopping criteria
- Correct defects
2. Conduct alpha testing.
3. Conduct beta testing.
Adapted from Software Engineering An
Object-Oriented Perspective by Eric J. Braude
(Wiley 2001), with permission.
15
Stopping Criteria
- Completing a particular test methodology
- Complete the procedures of a method or tool.
- Estimated percent coverage for each category
- predetermine percent of each how to calculate
- e.g., 95 statement coverage
- Error detection rate
- predetermine rate with given severity level
- e.g., 2 medium severity defects or less per 100
hours of operation - Total number of errors found
- (if possible) computed from a percentage of
remaining defects - predetermine percent
- e.g., 95 of estimated existing defects found
Kit Ki
16
Capture Recapture
N
N2
N1
C
17
Estimert antall feil igjen
18
Adams data