Counting Rules - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 12
Title:
Counting Rules
Description:
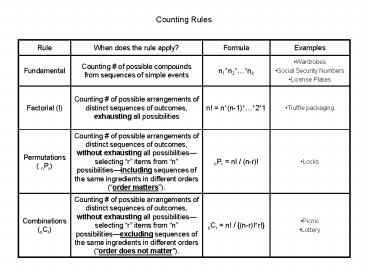
Counting # of possible arrangements of distinct sequences of ... Bivariate distribution example with covariance calculation -247.94. 1201.19. 58.19. 32.25 ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:76
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Counting Rules
1
Counting Rules
2
Probability Distributions
- Describe entire populations
- X all items in the probability space
- P(X) probabilities are relative frequencies for
all outcomes in the probability space - 0 P(X) 1, for each outcome in the probability
space - SP(X) 1, over all outcomes in the probability
space - Population mean, m S XP(X)
- Population variance, s2 SX2P(X) m2
3
Example of a discrete probability distribution
Population variance s2 7.1 4 3.1
4
Example 2 of a discrete probability distribution
Population variance s2
5
Bivariate distribution example with covariance
calculation
Covariance is negative because X and Y are
inversely related
6
Correlation, r
- r Cov(X,Y) (Var(X)Var(Y))(1/2)
- For example, in the previous page, for X and Y
- r -247.94 / (58.191012.19)(1/2)
- r -93.8 ? X and Y are strongly and negatively
correlated.
7
Binomial Populations
- Discrete, numerical population
- Counts of successful trials in a mutually
exclusive sequence of length n. - The sequences are made of n independent and
identical binomial trials. - Binomial trials are categorical simple events
- Binomial trials have 2 complement outcomes
- Identical trials means that each trial has the
same probability, p, of a success.
8
Binomial example
A baseball player has a probability of hitting a
homerun in each at bat of (p) .08. In a given
road trip, this player gets (n) 15 at bats.
9
Binomial populations in excel
- Binomial probability formula
- P(x) binomdist(x,n,p,false)
- x of successes in n trials
- n of trials in the binomial sequence
- p probability of a success in a trial
- false logical value to compute marginal, rather
than cumulative probability.
10
Binomial example
- A baseball player has a probability of hitting a
homerun in each at bat of (p) .08. In a given
road trip, this player gets (n) 15 at bats. - Question what is the probability that this ball
player hits 2 homeruns in this road trip? - Answer plug in excel the following information
binomdist(2,15,.08,false) - and you will get . 0.227306
11
Binomial parameters
- Population mean, m
- m np
- Population variance, s2
- s2 np(1-p)
12
Examples of parameter computations
- For the baseball player in the previous example,
we expect the player to hit an average of 1.2
(15.08)homeruns during his road trip, give or
take 1.05 (square root of 15.08.92) homeruns.




![[PDF] READ Free The Hi-Lo Card Counting System: A Complete G PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10105486.th0.jpg?_=20240823108)

























