Chapter 21: Metamorphism - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 12
Title:
Chapter 21: Metamorphism
Description:
... enough, cross through a sequence of facies. Facies Series/Field Gradient ... Facies concept leads to idea that metamorphic petrologists try to reconstruct ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:99
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Chapter 21: Metamorphism
1
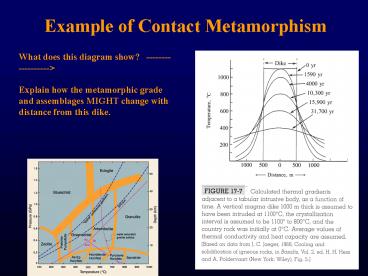
Example of Contact Metamorphism
What does this diagram show? ------------------gt
Explain how the metamorphic grade and
assemblages MIGHT change with distance from this
dike.
2
Facies Series/Field Gradient
- A traverse up grade through a metamorphic terrane
should follow one of several possible metamorphic
field gradients, and, if extensive enough, cross
through a sequence of facies
3
Mid-ocean Ridge metamorphism
4
Fig. 25-3. Temperature-pressure diagram showing
the three major types of metamorphic facies
series proposed by Miyashiro (1973, 1994). Winter
(2001) An Introduction to Igneous and Metamorphic
Petrology. Prentice Hall.
5
Subduction zone metamorphism
6
Fig. 25-3. Temperature-pressure diagram showing
the three major types of metamorphic facies
series proposed by Miyashiro (1973, 1994). Winter
(2001) An Introduction to Igneous and Metamorphic
Petrology. Prentice Hall.
7
Pressure-Temperature Time Paths
- Facies concept leads to idea that metamorphic
petrologists try to reconstruct CONDITIONS of
metamorphism. - Also important is TIME. Time tells us about the
RATES of processes.
8
Regional Metamorphism
3 stages Burial/crustal thickening--why does
trajectory have steep slope? Heating
stage Uplift stage
9
Isotherms in a subduction zone
10
Regional Metamorphism
What are prograde vs. retrograde metamorphic
paths or reactions?
11
(No Transcript)
12
Fig. 25-9. Typical mineral changes that take
place in metabasic rocks during progressive
metamorphism in the medium P/T facies series. The
approximate location of the pelitic zones of
Barrovian metamorphism are included for
comparison. Winter (2001) An Introduction to
Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology. Prentice Hall.