Regulation of AcidBase Balance - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 12
Title:
Regulation of AcidBase Balance
Description:
Regulation of Acid-Base Balance. Principles of Acid-Base Physiology ... of foodstuffs. Digestion, absorption. CO2 blown. off by lungs. Depleted. HCO3 replaced ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:230
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Regulation of AcidBase Balance
1
- Regulation of Acid-Base Balance
- Principles of Acid-Base Physiology
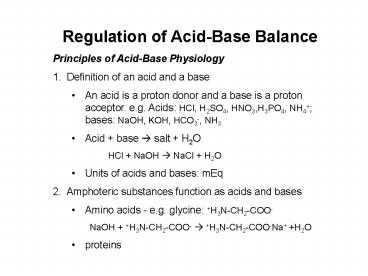
- Definition of an acid and a base
- An acid is a proton donor and a base is a proton
acceptor. e.g. Acids HCl, H2SO4, HNO3,H3PO4,
NH4 bases NaOH, KOH, HCO3-, NH3 - Acid base ? salt H2O
- HCl NaOH ? NaCl H2O
- Units of acids and bases mEq
- Amphoteric substances function as acids and bases
- Amino acids - e.g. glycine H3N-CH2-COO-
- NaOH H3N-CH2-COO- ? H3N-CH2-COO-Na H2O
- proteins
2
- The acid dissociation constant
- HA ??H A-
- HA --------?H A-
- H A- ------?HA
- K1 HA K2 H A-
- H A-/HA K1 / K2
- Dissociation constant Ka K1 / K2
- Logarithmic form of Ka
- pKa - log Ka ? pKa log (1/ K a)
- 4. The pH values of aqueous solutions
- pH - log (H) log (1/ (H))
- pH is inversely related to free H
- pH scale 0-14
- The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
- pH pKa log (A-/HA)
- When A- HA, the solution pH pKa
K1
K2
3
- Buffers promote stability of pH
- A pH buffer minimizes a change in pH
- A pH buffer weak acid/conjugate base or
conjugate acid/weak base - H2PO4- ?? HP O42-- H
- HCO3 ?? HCO3- H
- NH4 ?? NH3 H
- pH pKa log (conjugate base/acid)
- HCl Na2HPO4 ? NaH2PO4 NaCl
- NaOH NaH2PO4 ? Na2HPO4 H2O
- Titration Curve
- Two factors determine the effectiveness of a
buffer - pKa of the buffer in relation to the desired pH
- the amoount of buffer present
4
(No Transcript)
5
- Regulation of Extracellular pH Buffering
Mechanisms in the body - Buffering mechanisms
- chemical buffers in ECF, ICF and bone
- lungs
- kidneys
- Chemical pH buffers
- Phosphate
- proteins
- the bicarbonate-CO2 system
6
Food intake
Digestion, absorption
Cell metabolism of foodstuffs
CO2
Sulfate, chloride, phosphate anions
Depleted HCO3 replaced by kidneys
CO2 blown off by lungs
Sulfate, chloride, phosphate excreted by kidneys
H soaked up by chemical buffer bases (e.g., HCO3-
H combined with urinary buffers excreted by
kidneys
Fig. 25-2, pg791
7
- The lungs dispose CO2
- CO2 expired in the lungs matches CO2 production
- effect of hyperventilation
- effect of hypoventilation
- Concentration of a fixed acid is not affected by
lung function - Peripheral and central chemoreceptors
- The kidneys buffer blood pH by excreting H
- Urinary acidification
- reabsorption of filtered bicarbonate
- excretion of titratable acid
- excretion of ammonia
8
CO2
(HCO3) 14 mmoles per liter (dissolved CO2)
11.2 mmoles per liter (PCO2 373 mm Hg) pH 6.20
(HCO3) 24 mmoles per liter (dissolved CO2)
1.2 mmoles per liter (PCO2 40 mm Hg) pH 7.40
(b) Closed system (after adding 10 mmoles strong
acid per liter)
(a) Normal condition
CO2
CO2
(HCO3) 14 mmoles per liter (dissolved CO2)
0.90 mmoles per liter (PCO2 30 mm Hg) pH 7.29
(HCO3) 24 mmoles per liter (dissolved CO2)
1.2 mmoles per liter (PCO2 40 mm Hg) pH 7.17
(d) Open system hyperventilation (after adding
10 mmoles strong acid per liter)
(c) Open system (after adding 10 mmoles strong
acid per liter)
Fig. 25-3, pg792
9
Reclaimed
filtered
Carbonic anhydrase
High PCO2 speeds Low PCO2 slows
(a) Reabsorption of filtered bicarbonate
New
Carbonic anhydrase
(b) Formation of titratable acid
Glutamine
?-ketoglutarate2-
Glucose or CO2
Carbonic anhydrase
New
Fig. 25-4, pg795
(c) Excretion of ammonia
10
- Disturbances of Acid-Base Balance
- Respiratory acidosis
- Damage to respiratory centers
- Decrease of lungs' ability to eliminate CO2
- Respiratory alkalosis
- Psychoneurosis
- Physiological type of respiratory alkalosis
11
- Metabolic acidosis
- Renal tubular acidosis
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Diabetes Mellitus
- Ingestion of acid
- Chronic renal failure
- Metabolic alkalosis
- Diuretics (except for the carbonic anhydrase
inhibitors) - Excess aldosterone
- Vomiting
- Ingestion of alkaline drugs
12
Metabolic alkalosis
Chronic respiratory acidosis
Acute respiratory acidosis
Acute respiratory alkalosis
Chronic respiratory alkalosis
PCO2(mmHg)
Metabolic acidosis
Fig. 25-5, pg801