Prokaryotes - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Prokaryotes
Description:
If the bacteria possesses a cell capsule, it will retain a pink color. ... live in hot, acidic environments such as hot springs and hydrothermal ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:66
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Prokaryotes
1
Prokaryotes
2
Prokaryotes
- Classification of prokaryotes has dramatically
changed due to analysis of the genomes of various
types of cells - The description of these organisms as members of
Kingdom Monera, has been abandoned and replaced
with a three domain system. These Domains are as
follows - Domain Bacteria
- Domain Archaea
- Domain Eukarya
- The domains bacteria and archaea contain the
prokaryotic organisms. - Domain Eukarya include the protists and the other
multicellular kingdoms.
3
General Bacterial Structure
4
General Characteristics
- Bacteria are the smallest "living" organisms
- Are prokaryotic cells
- Lack Nucleus
- DNA is naked. - a single loop - not bound into a
chromosome. - May contain plasmids (small circular fragments of
DNA) - Lack membrane-bound organelles
- Usually have an outer Cell Wall.
- Sometimes have an Outer Capsule - These stain red
in a Gram Stain test and are called Gram Negative
bacteria. - Those without an outer capsule stain blue in the
gram stain test and are called Gram Positive
Bacteria
5
BACTERIAL CLASSIFICATION
- Bacteria are classified generally by 3
characteristics - The bacterial cell shape
- The bacterial cell arrangements
- Ability to accept a Gram stain
6
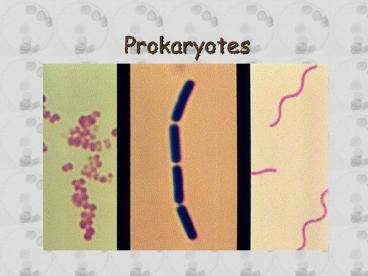
Bacterial Shape
- Bacteria have 4 basic shapes
- Spherical - cocci
- Rod-shaped bacilli
- Bent rod shaped - Vibrios
- Spiral spirilli
7
Bacterial Arrangement
- Bacteria have 3 basic arrangements
- Occurring singly Mono arrangement
- Occurring in pairs Diplo arrangement
- Occurring in long chains Strepto arrangement
- Occurring in clusters Staphlo arrangement
8
Gram Staining
- Bacteria can be categorized by their ability to
accept a gram stain. - Bacteria are exposed to several staining agents
Crystal Violet, Grams Iodine, and safranine. - If the bacteria possesses a cell capsule, it will
retain a pink color. This is referred as to a
Gram Negative bacteria - If the bacteria lacks a cell capsule it will
retain a blue color. This is referred to as a
Gram Positive bacteria
Gram Negative Bacteria
Gram Positive Bacteria
9
How Bacteria obtain energy
- Two major categories
- Autotrophs - Make their own energy - 2 types
- Phototrophic autotrophs - Get energy from
sunlight - Chemotrophic autotrophs - Get energy from
inorganic molecules (eg. Sulfides) - Heterotrophs - Energy obtained from other
organisms - Chemotrophic heterotrophs - obtain energy by
dissolving/absorbing organic material - Phototrophic heterotrophs - meet some energy
needs from photosynthesis, but must absorb
organic compounds.
10
Bacterial Respiration
- 3 major categories
- Obligate aerobes. - Must have O2 in order to live
- Obligate anaerobes - Must live in an O2 free
environment - Facultative anaerobes - Can live with or without
O2.
11
Bacterial Reproduction
- Bacteria reproduce through binary fission.
- Can engage in primitive sexual reproduction
called conjugation. - A bridge is formed between 2 bacteria
- Plasmids are shared across bridge, thus
exchanging genetic information. - In times of harsh conditions, bacteria can form
endospores, to encapsulate themselves in a
dormant state, until conditions improve.
12
Motility
- Some bacteria are motile - can move by either
thrashing, secreting lubricating secretions or
through use of a flagellum
13
Archaea
- Evolutionary Relationships
- Analysis of molecules found within the cells
suggests that eukaryotes are more closely related
to archaea than to bacteria.
14
Major Groups of Archaea
- Three major groups of archaea are found in
extreme habitats. - Methanogens are found in anaerobic
environments.such as marshes and in the
intestinal tracts of animals. They produce
methane as a result of cellular respiration. - Halophiles are found in environments with high
salt concentration such as the great salt lake or
soil with a high salt concentration. - Thermoacidophiles live in hot, acidic
environments such as hot springs and hydrothermal
vents.