Diseases of Snap Bean - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 29
Title:
Diseases of Snap Bean
Description:
syringae - brown lesions of varying size, lack halos. common blight - Xanthomonas campestris pv. ... halo blight - Pseudomonas syringae pv. phaseolicola ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:642
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Diseases of Snap Bean
1
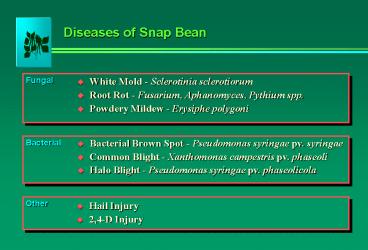
Diseases of Snap Bean
- White Mold - Sclerotinia sclerotiorum
- Root Rot - Fusarium, Aphanomyces, Pythium spp.
- Powdery Mildew - Erysiphe polygoni
- Bacterial Brown Spot - Pseudomonas syringae pv.
syringae - Common Blight - Xanthomonas campestris pv.
phaseoli - Halo Blight - Pseudomonas syringae pv.
phaseolicola
- Hail Injury
- 2,4-D Injury
2
Bacterial Bean Problems
3
Common Blight
4
Bacterial Brown Spot
5
Bacterial Brown Spot - Pod
6
Bacterial Brown Spot - Pod
7
Halo Blight
8
Halo Blight
9
Bacterial Diseases of Snap BeanKey Points
- Pathogens and symptoms
- bacterial brown spot - Pseudomonas syringae pv.
syringae - brown lesions of varying size, lack
halos - common blight - Xanthomonas campestris pv.
phaseoli - lesions become large, dry, dark brown,
coalesce - halo blight - Pseudomonas syringae pv.
phaseolicola - small brown lesions, surrounded by
large chlorotic halo - Survival and transmission
- all three may be carried via the seed
- pathogens enter host plants through both wounds,
natural openings - inoculum disseminated by wind driven rain and
irrigation - pathogens survive on a number of leguminous hosts
10
Bacterial Diseases of Snap BeanControl Strategies
- Eliminate weeds and volunteer bean hosts
- Use pathogen-free seed or resistant varieties
- Use a two-year rotation with a non-host crop
- For commercial production use currently
registered chemical controls
11
White Mold
12
White Mold
13
White Mold
14
White Mold
15
White Mold
16
White Mold
17
White Mold
18
White Mold
19
Birds Nest Fungus
20
Snap Bean Diseases - White MoldKey Points
- Pathogen Sclerotinia sclerotiorum
- infects over 360 species of plants
- Symptoms and signs
- lesions on leaves, stems and pods - initially
water-soaked, drying to papery tan appearance - lesions girdling stems result in death of stem or
entire plant - white cottony mycelium and black sclerotia often
associated with lesions - Sclerotia produced by the fungus survive in soil
up to five years or longer - Dense canopy of plant tissue that creates cool
moist microclimate favors plant infection - Senescent flowers are most common site of initial
infection
21
Snap Bean Diseases - White Mold Control
Strategies
- Varieties with more upright, open structure less
likely to be infected - Plant crop to promote rapid drying of tissue
after wetting - Plant rows parallel to prevailing winds
- Wide row spacing
- Rotation with non-host crops such as corn and
small grains - Use currently registered fungicides during the
flowering period
22
Common Root Rot
23
Common Root Rot
24
Common Root Rot
25
Snap Bean Diseases - Bean Root RotKey Points
- Pathogen Complex of fungi
- May involve Fusarium, Aphanomyces, Pythium
species - soil inhabiting pathogens which can attack bean
roots at any time during the growing season - Symptoms
- stunting and wilting of plant
- discoloration and death of roots and lower
portion of stem - lower portion of stem may become mushy
- Generlly most severe in moist soil but
temperature requirements differ for the different
pathogens - Pathogen resting structures allow long-term
survival - Root exudates from host stimulate fungal growth
and infection - Severity can increase if more than one fungus
present
26
Snap Bean Diseases - Bean Root RotControl
Strategies
- Have soil tested for root rot potential before
deciding which fields will be planted to beans - Minimize soil compaction
- Plant in well-drained, light soil. In the home
garden, raised beds may help with control - Chemical seed treatment is effective for Pythium
root rot, but not for rot caused by Fusarium or
Aphanomyces
27
Powdery Mildew
28
Hail Injury
29
2,4-D Injury