Coherent Scattering - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 7
Title:
Coherent Scattering
Description:
... with an electron in an atom and bounces off at some _thus being scattered away ... Physics 108 Lecture 33: X-ray Interactions with Matter. Most Common ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:688
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Coherent Scattering
1
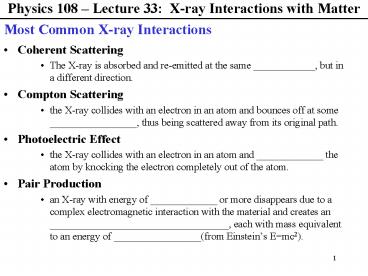
Physics 108 Lecture 33 X-ray Interactions
with Matter
Most Common X-ray Interactions
- Coherent Scattering
- The X-ray is absorbed and re-emitted at the same
____________, but in a different direction. - Compton Scattering
- the X-ray collides with an electron in an atom
and bounces off at some _________________, thus
being scattered away from its original path. - Photoelectric Effect
- the X-ray collides with an electron in an atom
and _____________ the atom by knocking the
electron completely out of the atom. - Pair Production
- an X-ray with energy of _____________ or more
disappears due to a complex electromagnetic
interaction with the material and creates an
___________________________________, each with
mass equivalent to an energy of
_________________(from Einsteins Emc2).
2
Coherent Scattering
Diagram
Equations
Relative Likelihood
Medium for low energy X-rays Low for medium to
high energy X-rays
Compton probability
X-ray energy (MeV)
3
Compton Scattering
Diagram
Equations (can be derived by combining energy
and momentum conservation)
Relative Likelihood
High for low energy X-rays Medium for high
energy X-rays
Compton probability
X-ray energy (MeV)
4
Photoelectric Effect
Diagram
Equation
K, L, M edge explanation
Ebinding - Specific values for each material K
shell (most energy loss) L shell (less energy
loss) M shell (not much energy loss)
Relative Likelihood
High for low energy X-rays Low for high energy
X-rays
Photoelectric probability
X-ray energy (MeV)
5
Pair Production
Diagram
Equation
Explanation of equation
E1 Total incident photon energy 1.022 MeV
energy lost to make e-/e pair Energy loss is
divided equally among e-/e pair
Relative Likelihood
Zero below 1.022 MeV Low to medium for
low-medium energy X-rays High for high energy
X-rays
Pair Prod. probability
X-ray energy (MeV)
6
Example (X-ray interactions with matter) Three
identical X-rays of energy 1.5MeV enter a
patient. One undergoes Compton scattering at
25?, one undergoes the photoelectric effect with
a K-shell electron in a Calcium atom, and one
undergoes pair production. Find the final energy
of all the particles after the interaction.
Given Path
Want Conversions/Equations
7
Example (X-ray interactions with matter)
CONTINUED
Given Path
Want Conversions/Equations