Going Wireless: Connecting You to the World - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 33
Title:
Going Wireless: Connecting You to the World
Description:
The requires a wireless antenna in the hearing aid. Which ... The wireless accessory communicates via a digital induction to the antenna in the hearing aids ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:115
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Going Wireless: Connecting You to the World
1
Going WirelessConnecting You to the World
Shelly Boelter, AuD Phonak Hearing Systems Peter
Succo, AuD Eugene Hearing Speech Center
2
Going Wireless.
- What we hope to accomplish today
- Wireless specific advancements in Hearing Aids
- New accessories available
- Answer the question, What is Bluetooth?
- Discuss how Bluetooth works
- Examples of how to apply the new technology
- Anything else?
3
What has changed?
- Technology is moving more and more in the
direction of wireless and hands free - Hearing aid manufacturers have identified this
problem and over the last several years have been
releasing products to help!
4
So what exactly are you talking about?
- Weve made hearing aids wireless! They can
communicate
- Between two hearing instruments
- Between a bluetooth accessory, the hearing
instruments and the world of communication
devices
5
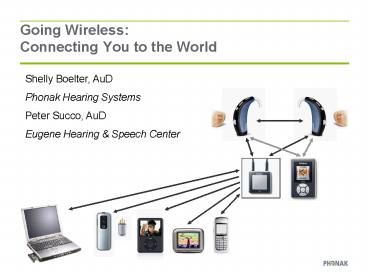
How do we make Hearing Aids Wireless?
- Wireless technology means the instruments are
able to transmit and receive wireless commands
and stream external audio signals. - The requires a wireless antenna in the hearing
aid.
6
Which Hearing Aids are Wireless?
- Phonak and other manufacturers have been making
wireless instruments 3 years - Any style of the new technology hearing aids can
be made wireless-- as long as we can fit that
antenna inside! - Standard behind the ear
- Mini behind the ear
- Most custom products except the completely in the
canal (CIC) - Premium, Advanced, and Basic technology levels as
well!
7
Once you have wireless hearing aids.
- The possibilities are endless!
- Allows for the addition of wireless accessories
- Gives access to so many more features to help in
challenging listening situations!! - Wireless accessories vary with your listening
goals
8
Digital Wireless Accessories
- myPilot remote control
- ClicknTalk cell phone accessory
- Streamer communication interface
9
Digital Wireless AccessorymyPilot remote
control
- Control over hearing system functionality
- Easy and intuitive
- Time, date and alarm functions
- Bi-directional capabilities allow display of
hearing instrument status - Zoomcontrol
10
ZoomControl
Blah
- ZoomControl lets you hear the sound from one side
in both ears. Useful for - Car
- Cell phone
- Work environments
sh
sh
Blah
Blah
11
Digital Wireless AccessoryClick'nTalk cell
phone accessory
- Just Plug in and go!
- Compatible with wireless Phonak products
- Compatible with 50 Sony Ericsson cell phones
- No pairing, No charging
12
Digital Wireless Accessory Bluetooth Streamers
Communication Interface
13
Streamers
- The wireless accessory communicates via a digital
induction to the antenna in the hearing aids - Sends the sound to both ears
- Can be a stereo sound quality
- Streamers have different built in features
- Audio input
- Remote control capabilities
- FM interface
14
Digital Wireless AccessoryCommunication
Interface
Wireless connection to the Bluetooth world
Wireless connection to the FM world
Wired connection to audio sources
15
Lets back up for a minute and talk
BluetoothWhat is Bluetooth?
- Bluetooth is a short-range wireless setup used to
create personal networks - Developed in 1996 to have a standard for cell
phone and computer communication - It uses an unlicensed radio frequency bandwidth
of 2.4 2.485GHz - Is omni-directional and is able to penetrate
solid objects
16
What is Bluetooth?
- Bluetooth is used for a variety of applications,
such as - Wireless control and communication between a
mobile phone and a wireless headset - Wireless communication between computers and
input devices, such as keyboards, printers and
mice - Wireless replacement of serial port applications,
such as GPS receivers and medical devices (i.e.
HiPro boxes/ NoahLinks) - Wireless networking of computers, where small
amounts of information exchange occur - Wireless transfer of contact information and
calendar details
17
Digital Transmission Technologies
- Power efficiency measure power / data rate
- Bluetooth 100 ?W/kbit/s
- Inductive 5 ?W/kbit/s
18
Bluetooth Different Profiles
- Think of profiles as capabilities or features
- Both devices have to support the same profile for
a feature to work - There are many different profiles available
19
Bluetooth Profiles to know about
- Profiles important to you include
- Headset Profile (HSP)
- Hands-Free Profile (HFP)
- Advanced Audio Distribution Profile (A2DP)
20
Bluetooth HSP
- Headset Profile (HSP)
- This is the most commonly used profile and allows
mobile phones to communicate with wireless
headsets - It only allows to ability to ring, adjust the
volume, answer a call and hang up
21
Bluetooth HFP
- Hands-Free Profile (HFP)
- This is commonly used to allow communication with
a car hands free system - The extra features that HFP allows are last
number redial, call waiting and voice dialing - Most Bluetooth headsets support both HSP and HFP
profiles.
22
Bluetooth A2DP
- Advanced Audio Distribution Profile (A2DP)
- This profile is used to define how high quality
mono and stereo audio information is streamed
from one device to another - Example
- Audio from a television or stereo to a wireless
headset
23
Bluetooth TermsGrouping, Pairing Connecting.
Oh My!
- There are three terms that are frequently
interchanged, however, need to be clearly
defined. - Grouping occurs in the hearing aid software. It
is when an iCom/ Streamer is attached to hearing
instruments to create a hearing system. - Pairing is when a trusted relationship is
established between two Bluetooth devices. The
devices place each other on their buddy list - Connecting is when two previously paired devices
recognize each other and start talking.
24
Bluetooth Pairing
- Pairing occurs when two devices agree that it is
safe to communicate with one another and create a
connection - To pair two compatible devices, a shared passkey
(password) is needed - Many devices use the standard 0000, especially
those without keyboards for manual number input - Once two devices are paired, they need not be
re-paired unless either device is reset or the
pairing has been deleted
25
Bluetooth Pairing
- The pairing process is
- Device A (ex cell phone) searches for other
Bluetooth devices - Device B (streamer) is found by Device A
- Device A asks for a passkey (any user generated
code) and sends it to Device B - Device B sends the passkey back to Device A and
creates a trusted pairing if both passkeys are
the same - Connected!
26
Other Considerations
- Bluetooth is a one-to-one connection. Two
receiving devices cannot be connected to two
devices at the same time. - For example, a husband and wife, each with their
own iCom, would each need their own television
transmitter.
27
So how do we apply all of this?
Endless possibilities!
?
The World!
Wireless HAs
Streamer
28
Scenario 1
- Joe cannot hear the television clearly.
- Solution Wireless hearing aids streamer TV
package - Hook the bluetooth adapter to the television
- Pair the bluetooth adapter to the streamer
- Watch TV at a comfortable volume (for everyone)
- Joe was able to hear a stereo sound through both
hearing aids and everyone could watch TV in the
same room!
29
Samsung SPD-50P91FHD
30
Scenario 2
- Jill wanted to hear cell phone better and to use
her iPod. - Solution Wireless hearing aids streamer
- Pair the streamer to the cell phone (must have
bluetooth) - Can either plug the iPod into her streamer or
pair it via a bluetooth adapter - Can now hear cell phone with both ears
- Listens to her iPod at the gym
31
Scenario 3
- Claire wants to hear better on her work phone
which is a landline. - Solution Wireless hearing aids streamer
bluetooth phone adapter (Jabra 7010) - Hook adapter up to the phone OR purchase a new
bluetooth phone - Pair to the streamer
- Claire was able to hear beautifully on the phone
and an added benefit was the ability to talk
hands free!
32
ATT EP5632 Bluetooth home phone
33
Questions?