Covalent Bonding - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 14
Title:
Covalent Bonding
Description:
... NH3 has 3 bond pairs & 1 lone pair of electrons & is trigonal pyramidal in shape. ... PCl5 : trigonal bipyramidal. OF2 : V-shaped. Covalent Bonding ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:82
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Covalent Bonding
1
Covalent Bonding
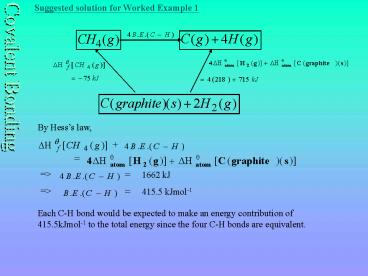
Suggested solution for Worked Example 1
By Hesss law,
gt
1662 kJ
gt
415.5 kJmol-1
Each C-H bond would be expected to make an energy
contribution of 415.5kJmol-1 to the total energy
since the four C-H bonds are equivalent.
2
Covalent Bonding
Suggested solution for Worked Example 2
By Hesss law,
-84.6 6B.E.(C-H) B.E.(C-C) 6(218) 2(715)
gt B.E.(C-C) 6(218) 2(715) 84.6 - 6(415.5)
gt B.E.(C-C) 6(218) 2(715) 84.6 - 6(415.5)
329.6kJmol-1
3
Covalent Bonding
Suggested solution for Worked Example 3
348 6(412) 2820 kJmol-1
4
Covalent Bonding
Suggested solution for Worked Example 4
By Hesss law,
5
Covalent Bonding
Suggested solution for Worked Example 5
a)
(1)
(2)
B.E.(H-H) 4(B.E.(C-H)) B.E.(CC) -
6(B.E.(C-H)) B.E.(C-C)
436 4( 414 ) 620
- 6( 414 ) 347
2712 - 2831 -119 kJmol-1
b)
The enthalpy of reaction calculated in (2) is
only an estimate because he bond energies used
are average values. The enthalpy of reaction
calculated in (1) is more accurate.
6
Covalent Bonding
Suggested solution for Worked Example 6
Net enthalpy change is equivalent to
The breaking of 1 mole of bonds
2 moles of H-H bonds requires 813 2(435)
1685 kJ
The formation of 1 mole of C-C bonds 4 moles of
C-H bonds releases 346 4(413) 1998 kJ
Enthalpy of hydrogenation of ethyne 1685 1998
-313 kJmol-1
7
Covalent Bonding
Suggested solution for Worked Example 7
The reaction involves the breaking of 2 moles of
C-H bond the formation of 1 mole of C-C bond
1 mole of H-H bond.
Enthalpy required to break 2 moles of C-H bond in
hexane
2 (413) 826 kJ
Enthalpy released when 1 mole of C-C bond 1
mole of H-H bond are formed in the product 347
436 783 kJ
Enthalpy of reaction 826 - 783 43 kJmol-1
8
Covalent Bonding
Suggested solution for Worked Example 8
(a)
Bond dissociation energy decreases with
increasing molecular mass (/size) of the hydrogen
halides. This is because the H-X bond lengths
increase as the atomic radii of the halogens
increases. The longer the bond length, the weaker
the bond is the bond dissociation energy is
smaller as a result.
(b)
H-I has the smallest bond dissociation energy,
the activation energy for its decomposition is
lowest. Therefore, it is most easily
decomposed. HBr HCl do not decompose at
temperature above 400K. HI has a positive
enthalpy of formation whereas those of other
hydrogen halides have negative values. That means
HI is less stable than the elements making it
while the other halides are more stable than the
elements making them. HI is the most unstable
hydrogen halide in relation to decomposition to
its elements.
9
Covalent Bonding
Suggested solution for Worked Example 9
Cl-Cl bond is stronger than Br-Br bond because
bond energy decreases on descending a group since
the distance between the nuclear protons
bond-pair electrons (bond length) increases. This
results in a smaller attractive force between the
atoms hence weaker bond strength. In contrast,
F-F bond is weaker than Cl-Cl bond due to
non-bonding electron repulsion between lone pairs
of electrons on the F nuclei. The repulsion
weakens the bond strength in F2 molecules.
10
Covalent Bonding
Suggested solution for Worked Example 10
(a)
Going down any group of the Periodic Table, the
covalent radius increases because as the number
of filled inner shells increases, the screening
effect on the outermost electrons increases/the
effective nuclear charge on the outermost shell
electrons decreases.
(b)
Going across any period, the covalent radius
decreases because the effective nuclear charge on
the outermost shell electrons increases. The
electrons are drawn closer towards the nucleus.
11
Covalent Bonding
Suggested solution for Worked Example 11
Both tetrachloromethane, CCl4, ammonia, NH3,
have 8 valence (outermost) electrons or 4
electron pairs around the central atoms (C in
CCl4 N in NH3). CCl4 has 4 bond pairs of
electrons is therefore tetrahedral in shape,
whereas NH3 has 3 bond pairs 1 lone pair of
electrons is trigonal pyramidal in shape.
12
Covalent Bonding
Suggested solution for Worked Example 12
(c)
(b)
(a)
OF2 V-shaped
SiF4 tetrahedral
PCl5 trigonal bipyramidal
13
Covalent Bonding
Suggested solution for Worked Example 13
BF3 has 6 valence electrons (i.e. 3 bond pairs)
around the central atom (i.e. B), forming 3
equivalent bonds. Its shape is triangular planar.
14
Covalent Bonding
Suggested solution for Worked Example 14
(a)
In CC bond, there are 2 pairs of electrons
making up the bond whereas there is only one pair
of electron in C-C bond. The electrostatic
attraction between the carbon atom the shared
electrons is therefore greater in CC bond. This
results in the greater strength of CC bond.
(b)
The 2 pairs of electrons in between the carbon
atoms in CC bond repel each other slightly
weakens the bond.