Aldoseketose interconversion - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 13
Title:
Aldoseketose interconversion
Description:
Keto-enol tautomerism. C. H. C. O. Keto form. C. C. O. H. Enol form. 4. Group transfer reactions ... (e.g. acetate or phosphate) from one substance to another. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:410
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Aldoseketose interconversion
1
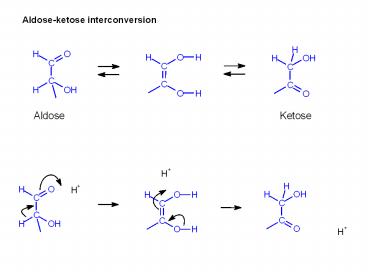
Aldose-ketose interconversion
O
H
C
C
H
O
H
Aldose
2
Keto-enol tautomerism
3
4. Group transfer reactions involve transfer of a
group (e.g. acetate or phosphate) from one
substance to another.
e. g. formation of glucose 6-phosphate in
glycolysis.
Imine formation involves group transfers and is
common in amino acid metabolism.
4
Carbonyl groups readily react with amines to form
imines.
5
Glycolysis and the TCA cycle
The carbon atoms of glucose are gradually
oxidised to CO2. The energy released is captured
as NADH, ATP, FADH, and GTP
Intermediates in carbohydrate catabolism also act
as precursors for biosynthesis of amino acids.
6
A. Metabolism consists of hundreds of reactions,
but only a few different types of reactions.
- Most reactions in metabolism are simple chemical
- transformations that are catalysed by enzymes.
7
Isomerisation
Group transfer
Moving the carbonyl group facilitates aldol
cleavage later on. This gives two trioses.
8
Isomerisation
Aldol cleavage
9
Oxidation
Oxidation of the aldehyde is coupled to formation
of two high-energy compounds NADH and an acyl
phosphate.
10
Group transfer
11
Isomerisation
Elimination
PEP is a very high-energy compound -phosphate on
C2 locks pyruvate into the enol tautomer.
12
Group transfer
13
Pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction C-C bond
cleavage, oxidation.