Some Serious Reflection - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 19
Title: Some Serious Reflection
1
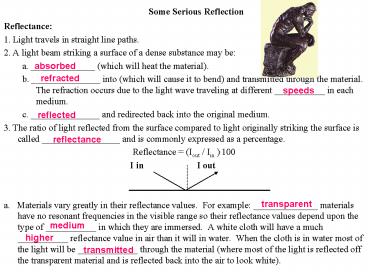
Some Serious Reflection
- Reflectance
- 1. Light travels in straight line paths.
- 2. A light beam striking a surface of a dense
substance may be - a. ______________ (which will heat the material).
- b. _______________ into (which will cause it to
bend) and transmitted through the material. The
refraction occurs due to the light wave traveling
at different ___________ in each medium. - c. _______________ and redirected back into the
original medium. - 3. The ratio of light reflected from the surface
compared to light originally striking the surface
is called _________________ and is commonly
expressed as a percentage. - Reflectance (Iout / Iin ).100
- I in I out
- a. Materials vary greatly in their reflectance
values. For example ______________ materials
have no resonant frequencies in the visible range
so their reflectance values depend upon the type
of ___________ in which they are immersed. A
white cloth will have a much ___________
reflectance value in air than it will in water.
When the cloth is in water most of the light will
be _____________ through the material (where most
of the light is reflected off the transparent
material and is reflected back into the air to
look white).
absorbed
refracted
speeds
reflected
reflectance
transparent
medium
higher
transmitted
2
- b. Glass reflects 4 of visible light, the rest
is transmitted through the glass therefore it has
a reflectance of ______. - Water reflects 2 of visible light and transmits
the rest. - Most materials that are black even have some
reflectance values for they dont ___________
all light that strikes them (they have
reflectance values up to 5). - The material with the highest reflectance is
magnesium oxide ( ) which has a
reflectance of 98. - ____________ silver surfaces have reflectance
values as high as 95 and make good surfaces for
___________ (bring in a shiny spoon tomorrow for
a homework bonus). - 4. When our eyes perceive an object, they do so
by collecting light which is ______________ from
the surface of the material. - Greek philosophers such as Socrates and ________
believed that vision resulted from streamers of
light being emitted from the eye and making
contact with the object. - http//www.tufts.edu/as/wright_center/lessons/pdf/
docs/activities/stained_glass.pdf - b. Other philosophers believed that light
traveled as particles from the object to the eye.
- c. So some thought of light as a particle and
others thought of light as a wave. We know that
light has a _________ nature in that it acts as a
particle and a wave. - Metals as Reflectors
- Metals are not only good reflectors of light but
they are good __________________ of heat and
electricity. The reason for all of these
properties is that metals contain loosely held
_____________ electrons (electrons in the
___________ shell of the atom).
4
absorb
MgO
Polished
mirrors
reflected
Plato
dual
conductors
valance
outer
3
- 2. When light shines on a metallic material, the
energy is not transferred from atom to atom but
is _________________ by the free-floating valence
electrons. - 3. The free-floating valence electrons are the
reason for metals appearing ______________. - 4. The metals aluminum (___) and silver (___)
have almost no ______________ frequencies in the
visible range so they reflect almost all light
from their surfaces and are therefore used as
mirrors. - Law of Reflection
- Recall that the Law of Reflection states that
the angle of incidence is ___________ to the
angle of reflection where each angle is measured
relative to the __________ of the surface. - Regular (Specular) and Diffused Reflection
- 1. Regular (_____________) reflection occurs
when parallel incident light beams strike a
surface and are reflected in _______________.
This type of reflection occurs on ___________
surfaces. - 2. Diffuse reflection occurs when parallel
incident light beams strike a surface and are
_______ reflected in parallel. This type of
reflection occurs on ____________ surfaces.
Apply diffuse and specular reflection to explain
why it is much more difficult to drive at night
on a ______ road. The wet road provides a
__________ surface which reflects light
____________ from you, while the dry road (which
is very rough) will ______________ light back at
you due to being reflected in __________
directions. Remember your perception of objects
arises due to light being reflected to your eye
from objects.
reflected
shiny
resonant
Al
Ag
equal
normal
specular
parallel
smooth
not
rough
wet
smooth
away
reflect
diffuse
4
- Both regular (______________) and diffuse
reflection follow the Law of Reflection. - When you shine a light on a smooth piece of
paper, the light is _______________ reflected.
This is due to the paper, on a microscopic level,
being rough and visible light having a relatively
___________ wavelength (___). Therefore, the
material is very __________ compared to the very
short wavelength. If it were not for this fact,
you could not read print on a page from more than
1 angle. - An open-mesh parabolic dish can act as a diffuse
reflector of light (due to the _________
wavelength of light) and a regular (specular)
reflector of radio waves (due to the _________
wavelength of radio waves). The longer the
wavelength the ______________ the surface. - Further reflection on this material tomorrow
- with mirrors.
specular
diffusely
short
?
rough
short
long
smoother
5
- Mirrors
- Mirror Terminology
- 1. Object Source of light reaching the mirror.
- 2. Real Image
- a. For mirrors this image appears to be in
_________ of the surface of the mirror and will
always be _____________. - b. This image is a result of reflected light
rays ____________ and passing through the image. - c. This image can be _____________ onto a
screen. - 3. Virtual Image
- a. Image appears to be __________ the surface of
the mirror. - b. This image will always be ____________.
- c. This image comes from points where light rays
appear to ____________ from. - See figure 28.7 pg. 533
- 4. Magnification (M) Ratio of size of the
__________ (hi) compared to the size of the
__________ (ho). hi is __ for an inverted image
and ___ for an upright (also called erect) image. - 5. Object distance ( ) The distance of the
__________ from the surface of the mirror. - 6. Image distance ( ) The distance of the
__________ from the surface of the mirror. - M -di/do hi/ho di - (virtual) di
(real image) do (always )
front
inverted
converging
projected
behind
upright
diverge
image
object
-
do
object
di
image
6
- Plane (_____) Mirrors
- 1. These create ___________ images. It appears
to be __________ the mirror. - 2. The image is the ___________ size as the
object. (Magnification ____) - 3. The image is as far ___________ the mirror as
the object is in front of the mirror. (-di do) - 4. The right and left sides of the object and the
image are __________. - 5. How tall does a mirror need to be in order to
see your full height? Answer ___ of your
height. In the figure above the man is 1.68 m
tall and the distance from his eyes to the top of
his head is 0.08 m. How tall must the mirror be?
_______ Prove this using the law of
reflection. fig 29.5 pg. 445 (old book) Distance
from the mirror doesnt matter. - Curved Mirrors
- 2 Types Convex and Concave (see figure 28.9 pg.
534) - Terminology
- 1. Vertex ( ) the geometric center of the
mirror. - 2. Center of Curvature ( ) point
equidistant to all points on the sphere. - 3. Principal axis straight line connecting ___
and ___. - 4. Radius - distance from ___ to ___.
- 5. Focal Point ( ) point at which incident
light rays ___ to the principal axis will reflect
through (for light rays are __________ to the
principle axis).
flat
behind
virtual
1
same
behind
reversed
½
0.84 m
V
C
C
V
C
V
F
close
7
- a. Spherical aberration - as parallel light
beams strike the mirror _________ from the
principal axis (for spherical mirrors with a
large aperture or mouth) the beams no longer
converge at ___. - b. The convergence of the ___ rays further from
the principal axis not reflecting through F with
those that are close to the principal axis going
through F results in images being __________. - c. In order to reduce spherical aberration, you
can decrease the aperture angle to ____ or less
or a __________ mirror could be used that will
converge all ___ light rays to the principle axis
through ___. - 6. Focal length ( ) - ___ of the radius (or
½ the distance between C and V which is equal to
the distance between F and V).
further
F
blurred
10o
parabolic
F
½
f
8
- Construction of an Image from a point on an
Object - Any object will __________ light rays in all
directions. In forming an image from a mirror
some of the light beams strike the mirror and
converge somewhere else (which can form a
__________ image) or appear to diverge from some
point behind the mirror (to form a __________
image). - To create an image from a concave mirror, __
light rays are helpful in determining the
location and height of the image. We will look
at these 3 rays as they leave the _____ of the
object. - (Note that all reflected rays obey the Law of
Reflection) - Light Ray 1 The incident ray to the mirror is
___ to the principal axis and reflects through
___. - Light Ray 2 The incident ray to the mirror
passes through ___ and reflects ___ to the
principal axis.
reflect
real
virtual
3
top
F
This arrow represents the object
F
9
- Light Ray 3 The incident ray enters from or
through ___ and __________ back on itself. - If light rays 1,2 and 3 are superimposed and
converge, they do so at the ____ of the image.
If the 3 diverge they will appear to do so from
the _____ of the image. - 6 Useful object positions for determining images
- (Note object distance ( ) and image distance
( ) at each position.) - Position 1 Object lies at a distance
infinitely far from the mirror relative to the
size of the mirror. Image is ________ and
appears as a ________ of light in front of the
mirror. (See figure below)
C reflects
top
top
do
di
real
point
do 8 (di f) (real image)
Case 1
10
Position 2 Object lies outside of C (but not
infinitely far away). The image is ______,
_________ and has a magnification _____________
-1 and 0. (See figure below)
real
inverted
between
Case 2 8 gt do gt r (r gt di gt f) -1lt M
lt0 (real image)
The red arrow is the image. This must be shown in
your ray diagrams
Position 3 Object lies on C (the center of
curvature). The image is ______, ___________
and has a magnification of ____. (See figure
below)
real inverted
-1
Case 3 do r (di r) M -1 (real
image)
11
Position 4 Object lies between C and F.
real inverted
less
Image is _____, ___________ and has a
magnification ________ than -1.
Case 4 r gt do gt f (8 gt di gt r)
Mlt-1 (real image)
Position 5 Object lies on F (the focal point).
____ image is formed. All light rays leave ___
to each other. Application Flashlights and
headlights place the bulbs on the focal points of
parabolic mirrors
No
Object is a point source
Normal Object
12
Position 6 Object lies between F and V (the
Vertex).
The reflected rays do not converge but seem to
diverge from a point behind the mirror. This
creates a ___________ image. The image is
___________ and has a magnification _____________
than 1.
virtual
upright
greater
Case 6 do lt f (di lt 0)
Mgt1 (virtual image)
Your eye projects diverging rays back to what
appears to be the point of emanation.
13
- Convex Mirrors
- Any incident light ray ___ to the principal
axis will be reflected away (diverge) from the
__________ point. - Any incident light ray directed toward the
focal point is reflected back _____ to the
principal axis. - Any ray directed at the center of curvature (
) will be reflected back on _________. - 4. The rays ________ so the eye projects them
back to the point where they seem to emanate.
focal
C
itself
diverge
focal point and center of curvature are behind
the surface of the mirror
F C
The image will always be ________ and ________
with a magnification between 0 and 1
virtual
upright
14
2 positions for images forming Position 1
Object an ____ distance away. Image appears as a
_________ located at the focus. (See figure
below)
8
point
Case 1 do 8 (di f)
Position 2 Object less than 8 distance away.
Image is virtual, __________ and has a
magnification between ___ and 1. (See figure
below)
upright
0
Case 2 do lt 8 0ltMlt1
15
Solving Reflection Problems Law of Reflection-
angle of reflection is equal to the angle of
_____________ with respect to the normal of the
surface. Object distance ( ) distance of
object to the mirror. This is always a __
number. Image distance ( ) distance of the
image to the mirror. di is a __ number for a
virtual image (image behind mirror) and a __
number for a real image (in front of
mirror). Focal Point ( ) point where ___
lines to the principal axis converge. Focal
Length ( ) distance from F to V (vertex).
This is always a ___ number for a concave mirror
and a ___ number for a convex mirror. Equations
(For concave and convex mirrors) 1 1 1
M hi -di f 1 r 1 0
1 8
incidence
do
-
di
F
f
-
f do di ho do
2 8 0 (focal
length) Convex Concave Virtual image Real image
radius is always positive regardless f is
- f is di -
di of sign of focal length
hi hi -
16
- Example Problems
- 1 Sitting in her parlor one night Ellie May
sees the reflection of her cat, Whiskers, in the
living room window. If the image of whiskers
makes an angle of 40.º with the normal, at what
angle to the normal does Ellie May see Whiskers
reflected? - cats image
-
window - cat
- Ellie May
400
400
17
- 2 Radio sees his reflection when he gazes into
a Christmas ornament from a distance of 15 cm. - a. What is the focal length of the ornament if
he b. What is the radius of the - can see his reflection 4.0 cm behind the surface
ornamental ball? - of the ornamental ball?
- 1/f 1/do 1/di
- 1/ f 1/ 15 cm 1/ -4.0 cm
- f -5.5 cm
- c. What is the magnification? M
-di / do - M - (-4.0 cm) / 15 cm
- M 0.27
- d.
f ½ r r 2 f r 2 (5.454 cm) r 11 cm
18
- 3 With his face 6.0 cm from his empty water
bowl, Odie sees his reflection 12 cm behind the
bowl. - a. What is the focal length of the bowl?
b. What is the magnification? - 1/f 1/do 1/di
- 1/ f 1/ 6.0 cm 1/ -12 cm
- f 12 cm
- c. Draw the ray diagram
M -di / do M - (-12 cm) / 6.0 cm M
2.0
19
- 4a. How far from a curved mirror with a radius
of 10. cm should an object be placed to produce
an inverted image that is 10. times the size of
the object? - M -di / do
- -10. -di / do
- di 10. d0
1/f 1 / di 1/do 1 / 5.00 cm 1 / (10. do )
1 / do 1/5.00 cm 1/(10. do) 10 /
(10do) 1/5.00 cm 11 / (10. d0) do / 5.00 cm 11
/ 10. do 5.00 cm(11) / 10. do 5.5 cm
4b. How far from a curved mirror with a radius
of 10. cm should an object be placed to produce
an upright image that is 10. times the size of
the object? M -di / do 10. -di / do di
-10. d0
1/f 1 / di 1/do 1 / 5.00 cm 1 / (-10. do )
1 / do 1/5.00 cm 1/(-10. do) -10 /
(-10do) 1/5.00 cm - 9 / (-10. d0) do / 5.00 cm
-9 / -10. do 5.00 cm (9) / 10. cm do 4.5
cm