The Trigonometric Parallax - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 13
Title:
The Trigonometric Parallax
Description:
The Trigonometric Parallax. B. p. B = 1 AU = 1.496*1013 cm. d = (1/p[arcsec]) parsec ... The magnitude scale system can be extended towards negative numbers ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:326
Avg rating:4.0/5.0
Title: The Trigonometric Parallax
1
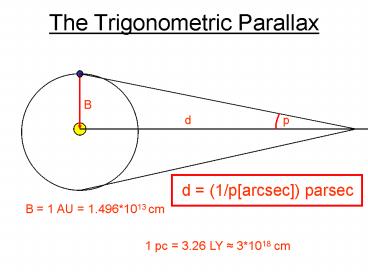
The Trigonometric Parallax
0
B
p
d
d (1/parcsec) parsec
B 1 AU 1.4961013 cm
1 pc 3.26 LY 31018 cm
2
The Moving Cluster Method
0
v
q
vf
vr
q
f
x
3
0
The magnitude scale system can be extended
towards negative numbers (very bright) and
numbers gt 6 (faint objects) Sirius (brightest
star in the sky) mv -1.42 Full moon mv
-12.5 Sun mv -26.5
4
Color and Temperature
0
Stars appear in different colors, from blue
(like Rigel) via green / yellow (like our sun)
to red (like Betelgeuze). These colors tell us
about the stars temperature.
Orion
Betelgeuze
Rigel
5
Blackbody Radiation (I)
0
The light from a star is usually concentrated in
a rather narrow range of wavelengths. The
spectrum of a stars light is approximately a
thermal spectrum called Blackbody Spectrum.
6
Blackbody Radiation
0
Fsurf s Teff4 s 5.6710-5 erg/(cm2 s
K4) Wiens displacement law lmax 0.29 cm /
TK (TK temperature in Kelvin).
7
The Color Index (I)
0
B band
V band
The color of a star is measured by comparing its
brightness in different wavelength bands The
blue (B) band and the visual (V) band. We define
B-band and V-band magnitudes just as we did
before for total magnitudes.
8
Optical Wavelength Bands
0
U l0 3650 Å
B l0 4400 Å
V l0 5500 Å
9
The Color Index
0
- We define the Color Index
- B V
- (i.e., B magnitude V magnitude)
- The bluer a star appears, the smaller the color
index B V. - The hotter a star is, the smaller its color index
B V.
B - V
Temperature
10
Example
0
For our sun Absolute V magnitude 4.83 Absolute
B magnitude 5.51
gt Color index B V 0.68
From standard tables B V 0.68 gt T
5800 K.
11
The Color-Color Diagram
0
B0
-1.0
-0.5
Blackbody
0.0
A0
U - B
F0
G0
0.5
K0
1.0
M0
1.5
-0.5
1.5
1.0
0.5
0.0
2.0
B - V
12
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
0
Log(L)
Most stars are found along the Main Sequence
M
Zero-Age Main Sequence (ZAMS)
Teff
B - V
13
Radii of Stars in the Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
0
Rigel
Betelgeuze
10,000 times the suns radius
Supergiants
Polaris
Giants
100 times the suns radius
Sun
White Dwarfs
As large as the sun
100 times smaller than the sun