Attachment Theory - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 13
Title:
Attachment Theory
Description:
But babies are born with different temperaments. Some children are easier to parent than others ... Attachment styles tend to be stable and long-lasting ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:2062
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Attachment Theory
1
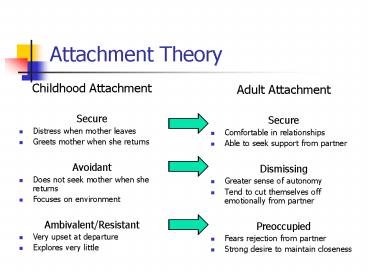
Attachment Theory
- Childhood Attachment
- Secure
- Distress when mother leaves
- Greets mother when she returns
- Avoidant
- Does not seek mother when she returns
- Focuses on environment
- Ambivalent/Resistant
- Very upset at departure
- Explores very little
- Adult Attachment
- Secure
- Comfortable in relationships
- Able to seek support from partner
- Dismissing
- Greater sense of autonomy
- Tend to cut themselves off emotionally from
partner - Preoccupied
- Fears rejection from partner
- Strong desire to maintain closeness
2
- But babies are born with different temperaments
- Some children are easier to parent than others
- Thus, the quality of care they receive might be
based on the childs personality - But temperament has only a moderate effect on
parenting/care (Vaughn Bost, 1999)
3
- Experience seem to play a large role in
determining the styles we bring to relationships - Mothers attachment styles predict the attachment
style of their babies with 75 accuracy before
they are even born it is argued that babies
come to share their style (Fonagy, Steele,
Steele, 1991) - The parenting adolescents receive as 7th graders
predicts how they will behave in their own
romances when they are young adults (Conger, Cui,
Bryant, Elder, 2000)
4
Attachment stability
- Attachment styles tend to be stable and
long-lasting - May lead people to create new relationships that
reinforce existing tendencies (Scharfe
Bartholomew, 1997) - E.g. Avoidant people may never learn that people
can be trusted
5
- But attachment styles can change
- A bad breakup can make a formerly secure person
insecure - A good relationship can make an avoidant person
less so (Kirkpatrick Hazan, 1994) - As many as 1/3 of us may encounter a real change
in our attachment styles over a two year period
(Fuller Fincham, 1995)
6
Relationship functioning
- Secure individuals tend to be more trusting,
committed, and satisfied than insecure
individuals (Simpson, 1990) - They experienced more positive emotions than
negative - There are also differences in the ways in which
these couples respond to interpersonal distress
7
Attachment Activation
- Role of conflict
- Partner availability
Partner perceived as available
Primary strategy (secure attachment)
Partner perceived as unavailable
Secondary strategy (insecure attachment)
Proximity seeking as viable or non-viable
8
Secondary Strategies
- Preoccupied attachments
- Hyperactivating strategies
- Hypervigilant attention to ones partner
- Rapidly detect disapproval, rejection
- Intensify negative emotional responses
- Dismissing attachments
- Deactivating strategies
- Active inattention to threatening aspects of the
relationship - Increased self-reliance
9
Expression and Regulation of Negative Affect
- Communication of attachment-figure unavailability
- Consistent rejection
- Criticism and hostility
- Specific predictions about the types of behaviors
individuals might exhibit
10
- Secure express themselves calmly and seek
comfort and support from their partners in a
constructive fashion - Dismissing tend to withdraw from their
partners may become hostile - Preoccupied tend to become excessively anxious
and fretful (Simpson, Rholes, Nelligan, 1992)
11
Perceptions
- Secure individuals are more likely to make
relationship-enhancing attributions (Collins,
1996) - They are more likely than insecure people to
remember positive past events (Miller Noirot,
1999) - More likely to remain open to new information
when they judge their partners (Mikulincer, 1997) - Insecure people tend to rely on existing beliefs
and assumptions
12
- Secure people tend to understand their partners
better than insecure people (Mikulincer, Orbach,
Iavnieli, 1998) - Preoccupied individuals tend to overestimate how
much they have in common with their partners - Preoccupied people are also good at guessing
their partners feelings when it may be costly to
them - E.g. when looking at pictures of attractive
potential partners
13
Attachment and jealousy
- Preoccupied individuals seek closeness but also
may be chronically worried about their partners
returning that love - Preoccupied individuals do experience more
jealousy than the other attachment styles (Buunk,
1997) - Secure people are also fearful when a valued
relationship is imperiled - Dismissing individuals dont tend to worry about
being abandoned