14'1 Kinetics of Angular Motion - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 17
Title:
14'1 Kinetics of Angular Motion
Description:
14.1 Kinetics of Angular Motion : centripetal : tangential. Chap. ... 14.1 Kinetics of Angular Motion (continued) Example : A gymnast on the high bar (continued) ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:85
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: 14'1 Kinetics of Angular Motion
1
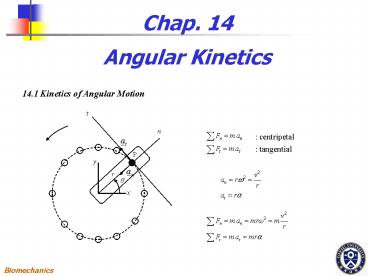
Chap. 14 Angular Kinetics
14.1 Kinetics of Angular Motion
centripetal
tangential
2
14.1 Kinetics of Angular Motion (continued)
- Example A gymnast on the high bar
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
(a) Energy conservation between 1 and P
3
14.1 Kinetics of Angular Motion (continued)
- Example A gymnast on the high bar (continued)
(a) Energy conservation between 1 and i
(b) Angular velocities
(c) Normal (radial) component of linear
accelerations
4
14.1 Kinetics of Angular Motion (continued)
- Example A gymnast on the high bar (continued)
(d) Forces applied on the gymnasts arm
compressive
tensile
5
14.1 Kinetics of Angular Motion (continued)
- Example A gymnast on the high bar (continued)
(e) Tangential component of linear accelerations
(f) Angular accelerations
6
14.2 Torque and Angular Acceleration
Bolt and wrench
In general,
7
14.3 Mass Moment of Inertia
Mass moment of inertia
Particle mass
Rigid body
radius of gyration
8
14.3 Mass Moment of Inertia (continued)
Mass moment of inertia
Rectangular prism
Solid cylinder or disk
Solid sphere
9
14.4 Parallel-Axis Theorem
Mass moment of inertia
If the moment of inertia of a body about a
centroidal axis is known, then the moment of
inertia of the same body about any other axis
parallel to than centroidal axis can be
determined using the parallel axis theorem.
10
14.6 Segmental Motion Analysis
Example 14.3 Knee extension
Fig 14.3 Knee extension
(a) the net torque produced about the knee
joint (b) the tension in the patellar tendon (c)
the reaction force at the knee joint
11
Example 14.3 Knee extension
- Quadriceps is the primary muscle group for knee
extension. - Patellar tendon is attached to the tibia at A
- Intended direction of motion is CCW.
Fig. 14.3(a) Forces acting on the lower leg
12
Example 14.3 Knee extension
(a) Net torque produced by the knee joint
(b) Tension in the patellar tendon
Fig. 14.3(a) Forces acting on the lower leg
13
Example 14.3 Knee extension
(c) the reaction force at the knee joint
Fig. 14.3(b) Free-body diagram of the lower leg
14
Example 14.3 Knee extension
(c) the reaction force at the knee joint
Fig. 14.3(b) Free-body diagram of the lower leg
15
14.7 Rotational Kinetic Energy
For a rotational motion of a rigid body,
translational kinetic energy
rotational kinetic energy
16
14.8 Angular Work and Power
Angular work done
Angular work done Torque ? Angular displacement
For const torque,
Using the chain rule,
Work-Energy theorem in rotational motion
Power in rotational motion
17
14.8 Angular Work and Power (continued)
Example Knee extension
? 0 to ? 90o for 0.5sec
Average kinetic energy
Average work done
Average power