Planes of the Body - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 23
Title:
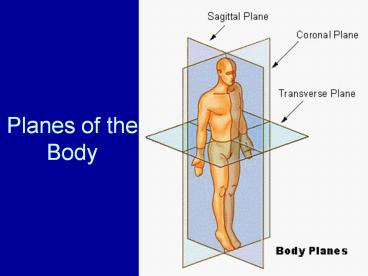
Planes of the Body
Description:
A. Eversion - Turning the sole of the foot outward. or laterally. ... combinations. For example, one could have. plantar flexion and eversion at. the same time. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:258
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Planes of the Body
1
Planes of the Body
2
Specific Joint Movements
The following terms describe motions at specific
joints.
3
(No Transcript)
4
Ankle and Foot Movements
A. Eversion - Turning the sole of the foot
outward or laterally.
Example Standing with the weight on the inner
edge of the foot.
B. Inversion - Turning the sole of the foot
inwardly or medially.
Example Most ankle sprains are inversion type
ankle sprains.
In what plane of motion do inversion and eversion
occur? Frontal Plane
5
(No Transcript)
6
Ankle and Foot Movements
C. Plantarflexion - Extension movement of the
ankle that results in the foot and toes
moving away from the body.
Example A diver will plantar flex his/her
foot as much as possible when entering the water.
7
Ankle and Foot Movements
D. Dorsiflexion - Flexion movement of the ankle
that results in the top of the foot moving
toward the anterior tibia.
In what plane of motion do plantar flexion
and dorsal flexion occur?
Sagittal plane
8
(No Transcript)
9
Radioulnar Joint Movements
A. Pronation - Internally rotating the radius,
where it lies diagonally across the ulna,
resulting in the palm down position of the
forearm.
B. Supination - Externally rotating the radius
where it lies parallel to the ulna,
resulting in the palm up position of the
forearm.
In what plane of motion do pronation and
supination occur?
Transverse plane
10
Scapular Motions
A. Elevation - Superior movement of the scapula
Example Shrugging the shoulders
B. Depression - Inferior movement of the scapula
Example Opposite of shrugging shoulders.
In what plane of motion do elevation and
depression take place?
Frontal plane
11
Scapular Motions
C. Protraction - Forward movement of the
scapula away from the spine. Abduction of the
scapula.
Example Putting hands on hips and moving
elbows anteriorly.
- Retraction - Backward movement of the scapula
- toward the spine. Adduction of the
- scapula.
Example Putting hands on hips and moving elbows
posteriorly.
12
Scapular Motions
In what plane of motion do protraction and
retraction occur?
Transverse plane
E. Downward rotation - Rotary movement of the
scapula with the inferior angle of the scapula
moving downward or medially.
Example Putting arm behind back and reaching
down.
13
Scapular upward and downward rotation
14
Scapular Motions
F. Upward rotation - Rotary movement of the
scapula with the inferior angle of the scapula
moving laterally and upward.
Example Reaching arm over and across the head.
In what plane of motion do upward and downward
rotation occur?
Frontal plane
15
Horizontal Abduction and Horizontal Adduction
16
Glenohumeral Joint Motions
A. Horizontal abduction - Movement of humerus
in the transverse plane away from the midline
of the body. Also called horizontal
extension or transverse abduction.
Example Spread arms from outstretched together
to a T.
B. Horizontal adduction - Movement of the
humerus in the transverse plane toward the
midline of the body. Also known as horizontal
flexion or transverse adduction.
17
Glenohumeral Joint Motions
- Flexion anterior and superior movement
- Extension posterior and superior movement
- Abduction lateral movement
- Adduction medial movement
- Internal Rotation elbow at 90 degrees, move arm
medially - External Rotation elbow at 90 degrees, move arm
laterally
18
(No Transcript)
19
Spinal Joint Movements
A. Lateral Flexion - Also known as side
bending. Movement of the head and or trunk
laterally away from the midline. Abduction
of the spine.
Plane of motion?
Frontal
B. Reduction - Return of the spinal column to
the anatomic position from lateral flexion.
C. Flexion - Reducing the angle of the spine.
Curling the spine as in doing sit-ups.
20
Spinal Joint Movements
D. Extension - Widening of the angle of the
spine. Uncurling of the spine.
Example - lying prone on the floor, raising the
head and legs.
In what plane of motion do flexion and extension
occur?
Sagittal plane
21
Wrist and Hand Joint Movements
A. Radial flexion - Abduction movement at the
wrist of the thumb side of the hand toward
the forearm.
Also known as radial deviation.
22
Wrist and Hand Joint Movements
C. Flexion and extension of the wrist.
D. Opposition of the thumb - touching the
various fingers of the hand with the thumb.
23
Note Joint movements can occur in
combinations. For example, one could have
plantar flexion and eversion at the same time.