VE7124: Session 3: The syntaxsemantic interphase: Semantic roles - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 9
Title:
VE7124: Session 3: The syntaxsemantic interphase: Semantic roles
Description:
[request for object which is the exit /entrance to be put into a position so that ... they strolled in the park. she walked to the bus stop. they ran down the street ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:40
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: VE7124: Session 3: The syntaxsemantic interphase: Semantic roles
1
VE7124 Session 3 The syntax-semantic
interphase Semantic roles
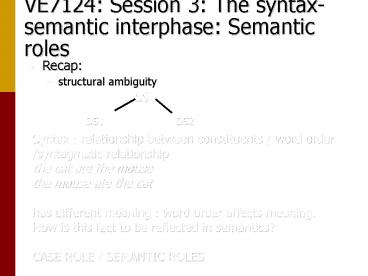
- Recap
- structural ambiguity
SS
DS1
DS2
- Syntax relationship between constituents / word
order /syntagmatic relationship - the cat ate the mouse
- the mouse ate the cat
- has different meaning word order affects
meaning. - How is this fact to be reflected in semantics?
- CASE ROLE / SEMANTIC ROLES
2
- Please open the door
- request for object which is the exit /entrance
to be put into a position so that we can leave or
come in - Implicature
- DI proposition
- II command
- Presupposition that there is a door, and the
door is currently not open - Hussien accused Minah of writing the letter
- Hussien criticised Minah for writing the letter
3
CASE ROLE / SEMANTIC ROLE
The cat ate the mouse P1 The mouse ate the cat
P2 P1 P2 We can identify two elements in the
proposition entities and predicate
Aziz broke the window with a rock The rock broke
the window The window broke
Participant entities (rock, window) Agent
(Aziz) predicate (break) specify the relationship
between the entities, agents etc.
4
What are the roles?
- AGENT the doer of the action
- AFFECTED entity upon which the action is carried
out on - INSTRUMENT the means by which the action is
carried out - BENEFICIARY, PATIENT,
- ADVERBIAL CASE FUNTIONS LOCATION, TIME,
PROCESS, CONTINGENCY, MODALITY, DEGREE - regardless of the order a word appears, if it has
a similar semantic role, we can understand the
exact function that it plays in the semantics if
the sentence.
5
- Representation / Notation
- Aziz broke the window with a rock
- a BREAK w r
- The rock broke the window
- r BREAK w
- The window broke
- w BREAK
- no matter where window appears (syntactically),
the way in which the window participates (or the
role of the window) in the act of breaking is the
same the window is the object AFFECTED in the
situation - case roles -defined semantically in terms of
meanings of sentences and not in terms of
position in the sentence (grammatical role) - cf. Grammatical role subject, object,
complement - the factory was torched by the gang
- The bomb destroyed the bridge
6
- Work this out!
- NATO destroyed the town with air-to-surface
missiles - The missiles destroyed the town
- The town was destroyed
- more roles LOCATION, BENEFICIARY
- They met in Kuala Pilah
- He died on the peak of Mt. Kinabalu
- Kuantan is wet in December
- She made Vin a cake
- I bought a bike for my son
- role markers - prepositions - by, for, with, at,
in (Guess what roles each might mark)
7
- Possible to make finer semantic role distinctions
e.g. - Location position, direction, distance, source
- he sat on the chair
- they strolled in the park
- she walked to the bus stop
- they ran down the street
- They drove 100 miles
- They came from the store
8
- Some problems with roles
- Jamal bought a car from Nik
- Nik sold a car to Jamal
- not clear as to whether an entity can bear more
than one role in relation to the verb in a
particular context - how many roles are there in total? And how do we
determine what they are? - This shoe are dirty
- That animal is a chihuahua
- Pedication - not limited to verbs, prepositions
can also serve to predicate. - The book is in the bag
9
Semantic roles of adverbial (Quirk et al. 1985
479ff.)
LOCATION (SPACE), TIME, PROCESS, CONTINGENCY,
MODALITY, DEGREE MODALITY (emphasis,
approximation, restriction) Aziz broke the
window. Aziz for sure, broke the window Aziz,
probably, broke the window Aziz broke only the
window CONTINGENCY (cause, reason, purpose,
result, condition, concession) she died of JE he
volunteered because of his interest he
volunteered so as he can be near her he
volunteered, so he acquired the experience if he
volunteered, he will acquire some
experience Though he didnt volunteer, he still
helped