Acoelomate PowerPoint PPT Presentations
All Time
Recommended
Acoelomate Bilateral Animals Acoelomate Bilateral Animals Consist of phyla: Phylum Platyhelminthes Phylum Nemertea And others Acoelomate Bilateral Animals Simplest ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
... (Dracunculus medinensis): transmitted by infected copepods in drinking water larvae move into the body cavity female adult migrates to the subcutaneous ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
The body consists of an anterior scolex solely for attachment to the host's gut and a string of proglottids, each of which possesses both male and female organs aka ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
How do the acoelomates fit in? Nemertea Platyhelminthes acoelomate Complete digestive system acoelomate Closed circ. system Ladder-like nervous system
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
... Acoelomate Body Plan Body Wall Exchanges with the Environment Reproduction and Development Class Trematoda Subclass Digenea Class Cestodia: ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
patterns of organization 1. asymmetrical, radial, or bilateral 2. unicellular, diploblastic, or triploblastic 3. acoelomate, psuedocoelomate, or coelomate
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Usually flattened dorsoventrally Triploblastic Acoelomate Bilaterally symmetrical Unsegmented worms Incomplete gut (absent in tapeworms) Somewhat cephalized, with ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Unit 4 - Phylums Platyhelminthes and Nematoda Flatworms and Roundworms * * Phylum Platyhelminthes Largest group of acoelomate (no body cavity) worms Flatworms with ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Invertebrate Animals (MOST Animals -- 95%!) Animal Phylogeny Porifera (Sponges) Simple, ALMOST Colonial No Symmetry No Gut 2 Tissue Layers Acoelomate ( Spongocoel ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Chapter 12 Part 2 The Worms Platyhelminthes, Nematoda & Annelida Phylum: Platyhelminthes Examples: Flatworms, Planaria sp., tapeworms and blood flukes Acoelomate ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Trends in Animal Evolution Symmetry ... deuterostome Digestive system None gastrovascular cavity complete digestive system Body cavities acoelomate pseudocoelomate ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Animal Phyla Chart Platyhelminthes (flatworms) Miscellaneous: -Symmetry -Body cavity -Number of germ cell layers Bilateral symmetry Acoelomate 3 germ cell layers ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
(Plat = flat) There are three classes: Turbellaria Trematoda Cestoda Characteristics of Flatworms They are acoelomates (they don t have body cavities) ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Coelom: Fluid-filled body cavity lined by cells from the mesoderm In mammals it forms the peritoneal, pleural and pericardial cavities Acoelomate Pseudocoelomate ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Outline Evolutionary Relationships Acoelomates (sort of ) Phylum Platyhelminthes Phylum Nemertea Gnathiferans Phylum Rotifera Phylum Acanthocephala
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Coelom: Fluid-filled body cavity lined by cells from the mesoderm In mammals it forms the peritoneal, pleural and pericardial cavities Acoelomate Pseudocoelomate ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
PLATYHELMINTHES & NEMATODA. The answers will be shown when you click the mouse so ... Label the coelom types. Acoelomate Pseudocoelomate Coelomate. Fill in the blanks ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Acoelomate no body cavity coelom- solid mesenchyme (mesoderm) First phylum to show a definite cellular mesoderm. Bilaterally symmetrical ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Cnidarians. Protostome Phyla. Deuterostome Phyla (except ... Sponge, Cnidarian. Ectoderm. Endoderm. spongocoel. Acoelomate. Mesoderm. 2-layered. Planarian ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Phylum Platyhelminthes Characteristics Flatworms Soft body Flattened Have tissue Have internal organ systems Bilateral symmetry Acoelomates Many are parasites Body ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Coelom. Acoelomates. Pseudocoelomates. Coelomates. Two Views of Animal Diversity. Animal Evolution ... 1st Eukaryotes. 1st Colonial Eukaryotes. 1st Multi ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Phylum Porifera Phylum Porifera Sponges are the simplest animals Radially symmetrical Acoelomate Body resembles a perforated sac. Has inner cavity called spongocoel ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Adult flatworms develop from the gastrula with an ectoderm, ... body cavity is called a coelom - flatworms do not have a coelom. flatworms are acoelomates ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Fig. 14.10 ACOELOMATE ANIMALS 14.1. General Features A. Cephalization 1. Sessile animals survive well with radial symmetry. 2. Concentrating the sense organs on the ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Phylum Porifera Phylum Porifera Sponges are the simplest animals Radially symmetrical Acoelomate Body resembles a perforated sac. Has inner cavity called spongocoel ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
The exam schedule is different from that for the reviews. ... Coelom Formation. Acoelomates - PHYLUM Platyhelminthes - PHYLUM Nemertina. Pseudocoelomates ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Title: Platyhelminthes (Flatworms) Author: bvn Last modified by: bvn Created Date: 1/27/2003 7:19:26 PM Document presentation format: On-screen Show
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Chapter 33 Lower Invertebrates Animals 1 million species of animals 95% are invertebrates! 34-36 phyla of the Animal Kingdom 1. Phyla Calcarea & Silicea ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Kingdom Animalia Invertebrates Phylum Porifera Phylum Cnideria SPONGES Sponges Phylum Porifera (pore-bearers)/ simplest animal Body Symmetry/Shape: Asymmetrical ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
The Kingdom ANIMALS Eukaryotic cells Multicellular Heterotrophic by ingestion External Fertilization vs Internal Fertilization a. Invertebrate Chordates: Tunicates ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Phylum : Platyhelminthes General Characteristics Free-living or parasitic Bilaterally symetrical, and dorso-ventrally flattened Epidermis has cilia or cuticle Coelom ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Phylum Nematoda: The Round Worms Over 80000 species Cylindrical pseudocoeloemates Have effective hydroskeleton and musculature Inhabit aquatic areas.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
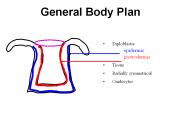
General Body Plan Diploblastic epidermis gastrodermis Tissue Radially symmetrical Cnidocytes
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Non-Coelomate Animals Porifera Simplest metazoan Cell level of organization Few cell types No true tissues Feed on material suspended in water Motile as larva ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Some other diploblastic creatures Ctenophores Attributes of ctenophores Diploblastic Comb jellies--eight rows of ciliated plates Lack true nematocysts Active ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
General Body Plan Diploblastic epidermis gastrodermis Tissue Radially symmetrical Cnidocytes
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Reproductive system is not well understood: Only female reproductive organs have been identified. ... Pigs become infected by eating grubs.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
KINGDOM ANIMALIA Chapter 26
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
By definition, in true coelom- mesentery. tissue connects organs to body cavity wall ... Also, by definition coelom is fluid-filled body. cavity, found in ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
... No two kinds of animals have the same binomial name Every animal has one correct name International Code of Zoological Nomenclature Genus ... microbes live in ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Chapter 39. Primitive Invertebrates. Animal Kingdom. SubKingdom-Parazoa: Phylum:Porifera ... Acolomates (no body Cavity) Bilateral Symmetry ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Introduction to Kingdom Animalia Characteristics of Animals Heterotrophic Multicellular Movement Eukaryotic Basic Embryology Define: Zygote Embryo Blastula Gastrula ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Rather inefficient outside of their normal environment Another form of pseudocoelomate Rotifera Muscles for body contraction--inch worm kind of pattern of motion ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Animal Bauplan Symmetry and complexity Chapter 3: Animal Architecture * * * * * * * * * * * * III. Symmetry Radial symmetry: body parts organized about a center axis ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Chapter 32 Introduction to Animal Evolution
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
... but the two species which infect man are T. saginata and T. solium External Features: Tatnia saginata has four large muscular suckers; no mouth or hooks exist.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Tricininella spiralis causes trichinosis in humans from under cooked pork ... Guinea Worms: Elephantiasis (Filarial worm) Life Cycle of Filarial Worm. Trichinosis ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
1 $100 Which of the following describes flatworms? Platyhelminthes Nematoda Coelom Asexual fission 1 $100 Which of the following describes flatworms?
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
1 $100 Which of the following describes flatworms? Platyhelminthes Nematoda Coelom Asexual fission 1 $100 Which of the following describes flatworms?
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Hydras - Jellyfish - Anemones - Corals. II. Animal Diversity. B. Radiata ... Hydra and jellies alternate between polyp and medusa stages; coral and anemones ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Kingdom Animalia Characteristics of Animals Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and membrane bound organelles Heterotrophic must ingest their food Diploid two ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Fig. 32-2-3 Zygote Cleavage Eight-cell stage Cleavage Blastula Cross section of blastula Blastocoel Gastrulation ... Cleavage (b) Coelom formation Coelom Key Ectoderm ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
These animals are also triploblastic they have three embryonic germ layers. Organ-system level of organization more division of labor among their organs.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Phylum Platyhelmenthes (the flatworms) General characteristics Eumetazoa - animals with tissue Bilateria - have bilateral symmetry Head end-cephalization
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Phylum Porifera. Phylum Porifera. Sponges are the simplest animals. Radially ... produce a flow of H20 into the sponge through pores in through the body wall, ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Animal gametogenesis and embryology (chapters 25, 32, 47) What is an animal? ... nervous and muscle tissues are unique. distinctive stages of development ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view