Encryption - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Encryption
Description:
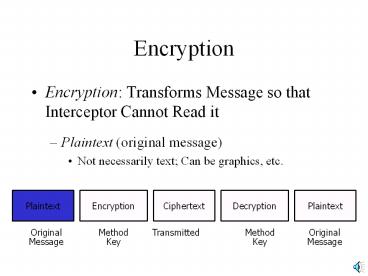
Encryption Encryption: Transforms Message so that Interceptor Cannot Read it Plaintext (original message) Not necessarily text; Can be graphics, etc. – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:341
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Encryption
1
Encryption
- Encryption Transforms Message so that
Interceptor Cannot Read it - Plaintext (original message)
- Not necessarily text Can be graphics, etc.
Plaintext
Encryption
Ciphertext
Decryption
Plaintext
Method Key
Method Key
Transmitted
Original Message
Original Message
2
Encryption
- Encryption Transforms Message so that
Interceptor Cannot Read it - Ciphertext (transformed) for transmission
- Stream of ones and zeros for transmission
Plaintext
Encryption
Ciphertext
Decryption
Plaintext
Method Key
Method Key
Transmitted
Original Message
Original Message
3
Encryption
- Encryption Transforms Message so that
Interceptor Cannot Read it - Receiver decrypts ciphertext back to plaintext
Plaintext
Encryption
Ciphertext
Decryption
Plaintext
Method Key
Method Key
Transmitted
Original Message
Original Message
4
Encryption
- Encryption Requires a Method and a Key
- Encryption method is the specific transformation
process - Key is a string of bits used in the method
- Get different ciphertext with different key
Plaintext
Encryption
Ciphertext
Decryption
Plaintext
Method Key
Method Key
Transmitted
Original Message
Original Message
5
Encryption
- Encryption Requires a Method and a Key
- Method cannot be kept secret
- Key must be kept secret
Plaintext
Encryption
Ciphertext
Decryption
Plaintext
Method Key
Method Key
Transmitted
Original Message
Original Message
6
Encryption Key Length
- Key can be guessed by exhaustive search
- Try all possible keys
- See which one decrypts the message
7
Encryption Key Length
- Long keys make exhaustive search difficult
- Key is a string of bits (11000100010101)
- If length is n bits, 2n tries may be needed
- On average, need half this many
- If key length is 8 bits, only 256 tries maximum
8
Encryption Key Length
- Long keys make exhaustive search difficult
- Weak security Today lt 100 bits
- Strong security Today gt 100 bits
- Need for length will grow over time
- Laws may limit export of strong security, sending
strongly encrypted messages internationally
9
Methods and Algorithms
- Encryption Method Categories
- Two general ways of doing encryption
- Symmetric key versus public key encryption
- Encryption Method Algorithms
- Specific ways of doing encryption
- With symmetric key encryption DES, 3DES, AES,
IDEA, Blowfish, and RC5 algorithms - With public key encryption RSA, elliptical curve
cryptosystem (ECC), El Gamal
10
Symmetric Key Encryption
- Both sides use a single key to encrypt decrypt
- When A send to B
- A encrypts with the key, B decrypts with the key
- When B sends to A
- B encrypts with the key, A decrypts with the key
B
A
Symmetric Key
11
Symmetric Key Encryption
- Symmetric key encryption and decryption processes
are simple enough for fast encryption/decryption - Fast enough for long messages
B
A
Symmetric Key
12
Symmetric Key Encryption
- Problem 1 Symmetric key must be distributed
secretly between partners or interceptors can
read subsequent messages
Key A
A
Key B
B
13
Symmetric Key Encryption
- Problem 2 Need a different symmetric key for
each business partner - Or other partners could read messages
- Complicates symmetric key distribution
Key A
A
Key B
B
14
Symmetric Key Encryption
- Problem Need a different symmetric key for each
business partner - If there are N partners
- And if each needs to communicate with all others
- Then N(N-1)/2 keys must be distributed
Key A
A
Key B
B
15
Symmetric Key Encryption
- Data Encryption Standard (DES)
- Extremely popular symmetric key algorithm
- DES breaks the plaintext into blocks of 64 bits
- It then encrypts each block of plaintext using a
64-bit key - However, it is proper to say that DES uses a
56-bit key, because 8 of the key bits are
redundant (can be computed from the other 56) - 56-bit key is small, giving inadequate strength
for important transactions (OK for small ones)
16
Symmetric Key Encryption
- Triple DES (3DES)
- Applies DES three times to encrypt
- With 3 keys, get 168-bit effective key length
- Encrypt block with first key
- Decrypt (yes, decrypt) result with second key
- Encrypt result with third key Send this
ciphertext - Decryption
- Decrypt ciphertext with third key
- Encrypt (yes, encrypt) result with second key
- Decrypt result with third key
17
Symmetric Key Encryption
- Note Encryption and Decryption often are
Reversible - Usually, encrypt to get ciphertext and then
decrypt to restore the plaintext - Some algorithms also can decrypt to get
ciphertext and encrypt to restore plaintext - Both approaches transform the plaintext into
ciphertext to give confidentiality (privacy),
then unscramble the ciphertext back to the
original plaintext
18
Symmetric Key Encryption
- Triple DES (3DES)
- Can be done with 2 keys for 112-bit effective key
length - Encryption
- Encrypt block with first key
- Decrypt (yes, decrypt) result with second key
- Encrypt result with first key again Send this
ciphertext - Decryption
- Decrypt received ciphertext with first key
- Encrypt (yes, encrypt) result with second key
- Decrypt result with first key again
19
Symmetric Key Encryption
- DES is an old algorithm
- Developed in 1970s
- 3DES is merely a way of extending its life
- Advanced Encryption System (AES)
- Being developed by the U.S. National Institutes
for Standards and Technology - Will be much stronger with longer keys
20
Public Key Encryption
- There are Two General Encryption Method
Categories - Symmetric key encryption (just seen)
- Public key encryption (next)
21
Public Key Encryption Methods
- Different keys for encryption and decryption
- Encryption with receivers public key
- Decryption with receivers private key
- Once encrypted, sender cannot decrypt the
ciphertext does not have receivers private key
Plaintext
Encryption
Ciphertext
Decryption
Plaintext
Public Key
Private Key
22
Public Key Encryption
- Everyone has a public and private key
- Keep the private key secret
- Distribute the public key to everybody without
security
Public Key
Private Key
Public Key
23
Public Key Encryption
- Then anyone can encrypt messages to you using
your public key - But only you can decrypt the messages
Encryption
Public Key
Private Key
Public Key
24
Public Key Encryption
- Four Keys Needed for Two-Way Communication
- Each side has a public and a private key
- Each sends public key to other unsecurely
B
A
Bs Pub Key
Bs Priv Key
As Priv Key
As Pub Key
25
Public Key Encryption
- Four Keys Needed for Two-Way Communication
- Encrypt with other partys public key
- Decrypt with own private key
B
A
Bs Pub Key
Bs Priv Key
As Priv Key
As Pub Key
26
Public Key Encryption
- Four Keys Needed for Two-Way Communication
- Never refer to public and private keys without
saying to whose public or private key you are
referring
B
A
Bs Pub Key
Bs Priv Key
As Priv Key
As Pub Key
27
Public Key Encryption
- No need for separate secret key for each business
partner - Greatly simplifies key management
28
Public Key Encryption
- Unfortunately, highly processing-intensive
- 100 times slower than symmetric key encryption
- So can only encrypt small messages
- Also, often can only encrypt messages about the
size of the public key (typically a few thousand
bits)
29
Combining Public, Symmetric Key
- Not competitors--Used Together in Practice
- Public key is easy to distribute but can only be
used for small messages - Symmetric key has key distribution problems but
can be used for long messages - They have complementary strengths and weaknesses
30
Combining Public, Symmetric Key
- Symmetric Key Encryption and Public Key
Encryption are Complementary, not Competitors - Often, partners first communicate with public key
encryption - Including initial authentication
B
A
Public Key Authentication
31
Combining Public, Symmetric Key
- Then one sides generates a symmetric key
- Encrypts symmetric key with partners public key,
sends to partner - Now, both sides have the symmetric key
Public Key Encryption
B
A
Symmetric Session Key
32
Combining Public, Symmetric Key
- Afterward, both sides communicate with the
symmetric key - This symmetric session key is good only for
this session--single flow of communications
Symmetric Session Key
B
A
33
Public Key Algorithms
- Public Key Encryption is a Method Category
- Must Use a Specific Public Key Algorithm
- RSA
- Most widely used public key algorithm
- Patented, but public domain in October 2000
- Elliptical Curve Cryptosystem (ECC)
- Can use smaller keys than RSA with same degree of
protection
34
Public Key Encryption
- If know someones public key, there is no known
way to compute their private key faster than
exhaustive search - If there was, public key encryption would be
useless - This is a general concern for public key
encryption because there is no proof that there
is no possible way to compute the private key
rapidly if a public key is known