Inclusion Dependency (IND) - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Inclusion Dependency (IND)
Description:
Normally every student must belong to a department. ... This tool is called 'Casanova et al.'s axiom system' We consider the following three rules: ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:503
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Inclusion Dependency (IND)
1
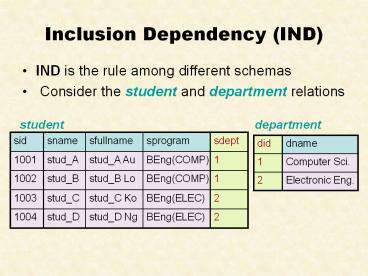
Inclusion Dependency (IND)
- IND is the rule among different schemas
- Consider the student and department relations
student
department
sid sname sfullname sprogram sdept
1001 stud_A stud_A Au BEng(COMP) 1
1002 stud_B stud_B Lo BEng(COMP) 1
1003 stud_C stud_C Ko BEng(ELEC) 2
1004 stud_D stud_D Ng BEng(ELEC) 2
did dname
1 Computer Sci.
2 Electronic Eng.
2
Inclusion Dependency (IND)
- In the student relation, we only have the student
ID of the student and his/her corresponding
department ID number. - Normally every student must belong to a
department. - There should not exist that the relation contains
a department with an unknown department identity
number, or that the department has no identity
number.
3
Inclusion Dependency (IND)
- Just the same as FD, there is a tool to formulate
the IND between schemas - This tool is called Casanova et al.s axiom
system - We consider the following three rules
- Reflexivity
- Projection and Permutation
- Transitivity
4
Inclusion Dependency (IND)
- Reflexivity
- If X is (are) attribute(s) in a schema R, we have
IND RX ? RX. - Example
- In student relation, IND studentsid ?
studentsid - It gives the basis of inclusion dependency.
5
Inclusion Dependency (IND)
- Projection and permutation
- If INDR1X?R2Y, then INDR1Xk?R2Yk where
Xk and Yk are projection and permutation on X and
Y - Example
- In the teach relation, course ID and the course
description are subset of records in the course
relation. If we use course ID as referential key
to the course relation, there must exist some
records in course relation for the same
description as the course description.
6
Inclusion Dependency (IND)
teach
course
course cdescription lecturer
COMP104 C 1
COMP104 C 2
COMP171 Algorithms 3
ELEC102 Electronics 4
ELEC151 Digital Circuit 5
ELEC151 Digital Circuit 6
course cdescription credit
COMP104 C 5
COMP171 Algorithms 3
ELEC102 Electronics 5
ELEC151 Digital Circuit 5
teachcourse, cdescription ? coursecourse,
cdescription, creditgt teachcdescription ?
coursecdescription
7
Inclusion Dependency (IND)
- Transitivity
- If INDR1X?R2Y and INDR2Y?R3Z, then
INDR1X?R3Z - Example
- In the pattern relation, it records what courses
a student needs to take and only the course ID is
known. It is trivial that the course ID is a
subset of the course ID in the teach relation. As
course ID in the teach relation is also a subset
of that in the course relation, from the pattern
relation, we can use the course ID as referential
key to the course relation.
8
Inclusion Dependency (IND)
If IND patterncourse ? teachcourse
pattern
teach
student dept course
1001 1 COMP104
1001 1 COMP171
1002 1 COMP104
1002 1 COMP171
1003 2 ELEC102
1003 2 ELEC151
1004 2 ELEC102
1004 2 ELEC151
course cdescription lecturer
COMP104 C 1
COMP104 C 2
COMP171 Algorithms 3
ELEC102 Electronics 4
ELEC151 Digital Circuit 5
ELEC151 Digital Circuit 6
9
Inclusion Dependency (IND)
and IND teachcourse ? coursecourse
teach
course cdescription lecturer
COMP104 C 1
COMP104 C 2
COMP171 Algorithms 3
ELEC102 Electronics 4
ELEC151 Digital Circuit 5
ELEC151 Digital Circuit 6
course
course cdescription dept
COMP104 C 1
COMP171 Algorithms 1
ELEC102 Electonics 1
ELEC151 Digital Circuit 1
10
Inclusion Dependency (IND)
then IND patterncourse ? coursecourse
pattern
student dept course
1001 1 COMP104
1001 1 COMP171
1002 1 COMP104
1002 1 COMP171
1003 2 ELEC102
1003 2 ELEC151
1004 2 ELEC102
1004 2 ELEC151
course
course cdescription dept
COMP104 C 1
COMP171 Algorithms 1
ELEC102 Electonics 1
ELEC151 Digital Circuit 1