Pediatric Nursing - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Pediatric Nursing
Description:
Pediatric Nursing Module 6 Caring for Children with Alterations in Neurosensory Functions Neurological Assessment Assessment indirect measurements children under 2 ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:3702
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Pediatric Nursing
1
Pediatric Nursing
- Module 6
- Caring for Children with Alterations in
Neurosensory Functions
2
Neurological Assessment
- Assessment
- indirect measurements
- children under 2 years
- normal growth and development parameters
- parents evaluation of their child
- developmental milestones
- history
- prenatal
- birth history
- post natal
3
Neurological Assessment
- Behavior
- personality, affect, level of activity, social
interaction, attention span - Motor function
- muscle - size, tone, strength
- abnormal movements
- Sensory function
- discrimination of touch with eyes closed
4
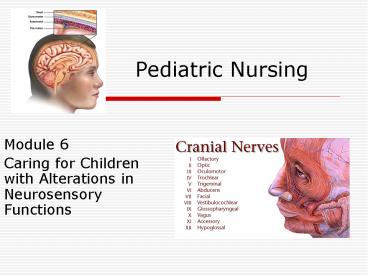
Neurological Assessment
- Cranial Nerves
- Olfactory - smell
- Optic - light perception visual acuity
- peripheral vision
- Ocular motor - 6 cardinal positions of gaze
PERRLA - Trochlear - have child look down and in
- Trigeminal nerves - bite down and try to
- open jaw, sensation to face
5
Neurological Assessment
- Abducens- look toward temporal side
- Facial - make a funny face or smile
- Acoustic - hearing and balance
- Glossopharyngeal - gag reflex, taste
- Vagus - uvula is midline, swallow
- Accessory - shrug shoulders against mild applied
pressure - Hypoglossal - move tongue in all directions
6
Video - Neurological exam in children
- http//video.google.com/googleplayer.swf?docid331
4499774483652601hlenfstrue
http//video.google.com/googleplayer.swf?docid7
363212422012619904hlenfstrue
http//video.google.com/googleplayer.swf?docid-72
8577715202828264hlenfstrue
7
(No Transcript)
8
Increased Intracranial Pressure
- Causes
- tumors
- accumulation of fluid within the ventricular
system - bleeding
- edema in cerebral tissues
- early signs and symptoms are often subtle and
assume many patterns
9
Assess for signs of Increased Intracranial
Pressure
- Level of consciousness (LOC)
- earliest indicator of changes in neurological
status - 1. Alertness
- arousal-waking state
- ability to respond to stimuli
- 2. Cognitive abilities
- process stimuli
- produce verbal and motor responses
10
Increased Intracranial PressureSigns/symptoms
- Lack of painful stimuli is abnormal and is
reported immediately - as ICP increases LOC decreases
- 3. Vital Signs
- pulse
- variable, may be rapid or slow, bounding or
feeble - B/P
- normal or elevated with a widening pulse
pressure, at shock level - Respiration's
- varies
11
Increased Intracranial PressureSigns/symptoms
- Temperature
- elevated especially with infections and
intracranial bleeding - subnormal in a coma of toxic origin
- Pupils
- size and reactivity
- bilateral vs unilateral
- sudden fixed and dilated pupils is a
neurosurgical emergency - pressure from herniation of the brain through the
tentorium
12
Neuromuscular - Signs/symptoms
- Neuromuscular Movement
- strength, spontaneous movements
- asymmetric or absent movements
- tone
- may be increased or decreased
- tremors, twitching, spasms
- purposeless flapping
- hyperactive or flaccid
13
Increased Intracranial Pressure Signs/symptoms
- Posturing
- decorticate
- adduction and flexion
- decerebrate
- rigid extension and pronation
14
Diagnosis Procedures
- Lumbar puncture
- measure pressure and sample for analysis
- Subdural tap
- r/o subdural effusions, relieves ICP
- EEG
- measures electoral activity
- detects abnormalities
15
Diagnosis Procedures
- Computer Tomography (CT)
- visualizes horizontal and vertical cross section
of the brain - distinguishes density
- MRI
- permits tissue discrimination unavailable with
other techniques - Transillumination
- localized glowing seen in abnormal fluid
16
Diagnosis Procedures
- Labs
- CSF
- blood glucose
- electrolytes
- Ca, Mg, Na
- clotting studies
- liver function tests
- blood cultures
- drug titre
17
Cerebral TraumaHead Injury
- Etiology
- falls, MVA, bicycle injuries
- head is larger, heavier
- children curious
- incomplete motor development
- Concussion
- Contusion/laceration
- Fracture
18
Shaken Baby Syndrome
coup
countrecoup
19
- Fatal bacterial
- meningitis
20
Meningitis
- Inflammation of the meninges
- Spread
- vascular dissemination
- OM or URTI
- exudate covers the brain
- brain becomes hyperemic and edematous
21
(No Transcript)
22
Meningitis
- Causative Organism
- H. Influenza, type B
- S. Pneumoniea
- N. Meningitis
- Meningococcus
- Signs and Symptoms
- FUO
- lethargy
23
MeningitisSigns/symptoms
- irritable
- vomiting and/or diarrhea
- signs of meningeal irritation
- guarding of the neck
- nuchal rigidity
- cries when moved
- poor feeding
24
MeningitisDiagnosis
- Labs
- CSF
- culture, glucose, protein, cell count, gram stain
- Blood Culture
- r/o sepsis
- Urine Culture
- r/o UTI
- Chemistry panel
- electrolytes, glucose, BUN, creatinine
25
MeningitisTreatment
- Antibiotics
- administer within 1 hour of diagnosis
- type is based on age and causative organism
- neonate - ampicillin / claforan
- 3 months to 3 years - ampicillin / ceftriaxone
- older children - penicillin / chloramphemicol
26
MeningitisTreatment
- Fluid Management
- fine balance between dehydration and cerebral
edema - child may be dehydrated due to v/d, poor po,
fever - 2/3 maintenance of IV replacement
- fluid restriction
27
MeningitisNursing Care
- PC Neurological dysfunction
- cerebral hypoxia
- seizures
- increased ICP
- PC Seizure
- High Risk for spread of infection
- needs resp. isolation for first 24 hrs of
antibiotic therapy
28
MeningitisNursing Care
- Fluid Volume Deficit less than body
requirements r/t dehydration - NPO/fluid restriction
- I O
- daily weights
- Labs
- specific gravity and electrolytes
- IV fluid - careful, conservative replacement
29
MeningitisNursing Care
- PC Neurological damage
- seizures
- sequelae to meningitis
- seizures
- hydrocephalus
- visual/hearing deficits
30
Reye Syndrome
- Toxic encephalopathy with additional organ
involvement - Etiology
- follows viral illness, ASA
- Signs and Symptoms
- fever
- decrease LOC
- hepatic dysfunction
- Prognosis
- good
31
Febrile Convulsions
- Age
- most common between 6 months and 3 years
- Occurrence
- Seizure accompanied by fever without CNS
infection - Occurs during the temperature rise
- Treatment
- fever - tylenol
- seizure - ativan, valium
32
- Tonic clonic seizure
- Tonic stiff
- Clonic - jerking
- Rescue position
33
- Assessment
- seizure precautions
- emergency treatment
- rescue position
- Nursing Care
- protect from injury
- open airway
- accurately observe and record happenings
34
Hydrocephalus
35
Hydrocephaly
- Abnormal condition characterized by an increase
volume of normal cerebrospinal fluid under
increased pressure with in the intracranial
cavity - Communicating
- obstruction is located in the subaranoid cistern
or within the subarachnoid space - Non-communicating
- blockage is within the ventricles
36
Hydrocephaly - Pathology
- 3 possible mechanisms leading to hydocephalus
- 1. Over production of CSF
- 2. Defective absorption of CSF
- 3. Obstruction of CSF
- 3 major causes
- inflammation
- congenital malformations
- tumors
37
HydrocephalusSigns/symptoms
- Signs of increased fluid pressure
- tense or bulging anterior fontanel
- scalp becomes thin and shiny
- vein dilate
- cranial suture lines begin to separate
- Other clinical symptoms
- vomiting
- wide bridge between eyes
- bulging eyes - sunset eyes
38
HydrocephalusSigns/symptoms
- Severe Form
- head size increases rapidly
- infants cry is shrill, high pitched
- hyperirritability, restlessness
- Older Children
- no head enlargement ataxia
- papilledema Alter mental status
- spasticity strabismus
- H/A
39
HydrocephalusTreatment
- Surgical
- VP (ventriculo-peritoneal) Shunt
- Nursing Care
- Pre-op
- assessments
- daily head circumference
- size and fullness of anterior fontanel
- behavior
- nutrition - vomiting
40
Hydrocephalus - Nursing Care
- fluid and electrolyte needs
- positioning
- prevent pressure ulcers
- support the neck
- good skin care
- neuro assessments
- LOC
- irritable child/infant
- vital signs
- observe for seizures
41
Hydrocephalus
- Nursing Care
- Post-op
- monitor feeding and behavior patterns
- assess for increasing ICP and cerebral
irritability - HOB flat or set elevation
- Shunt observation
- infection - along the line or cerebral
- abdominal girth
- valve function, blockage, separation
- emotional needs - hold and cuddle
- teaching
42
Cerebral Palsy
- Non-specific disorder characterized by early
onset of movement and posture impairments - abnormal muscle tone and coordination
- Spastic
- hypertonicity, stiff
- Dyskinectic
- slow, worm-like movement
43
Spina bifia - myelomeningocele
- Failure of the neural tube to close during early
development - Treatment
- early surgical closure
- Associated Problems
- hydrocephalus
- paralysis
- bone deformity
44
- Andrew, age 10 was a passenger in a MVA 3 weeks
ago, he sustained a closed head injury from the
impact. He is unconscious in the E.R. - What are is needs in the Emergency Room?
- What are his priority nursing interventions?
45
- He was admitted to the PICU, now transferred to
your Pediatric Unit. He tracks his parents
movement, he is receiving 02 via trach collar,
has G-tube with enteral feedings, is incontinent
of urine and stool, is able to nod his head
appropriately. - Why do you think Andrew has a trach?
- Why do you think Andrew has a G-tube?
46
- What risk factors predispose Andrew to infection?
- Why is he on these medications?
- ranitidine 70mg bid - zantac
- metoclopramide 3.5 mg qid - reglan
- phenytoin sodium 70mg bid - dilantin
- How can you intervene to help met Andrews growth
and development needs?















![Download ⚡️[EBOOK]❤️ Wong's Essentials of Pediatric Nursing 10th Edition PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10074231.th0.jpg?_=20240708125)
![[PDF] Foundations and Adult Health Nursing 9th Edition Android PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10076360.th0.jpg?_=20240710094)
![[PDF] Foundations of Nursing 8th Edition Free PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10078622.th0.jpg?_=202407151211)
![[PDF] Foundations of Nursing 9th Edition Android PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10078635.th0.jpg?_=20240715017)
![[PDF] Mosby's Pocket Guide to Pediatric Assessment (Nursing Pocket Guides) 5th Edition Full PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10081974.th0.jpg?_=20240719057)





![[PDF] Pediatric Nursing Certification Practice Q&A 1st Edition, Kindle Edition Free PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10085935.th0.jpg?_=20240726013)


![[PDF] School Nursing: A Comprehensive Text Third Edition Free PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10098837.th0.jpg?_=202408140411)

![[PDF] Study Guide for Wong's Essentials of Pediatric Nursing 11th Edition Free PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10101197.th0.jpg?_=20241106066)