Fluorescent proteins - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 41
Title:
Fluorescent proteins
Description:
Fluorescent proteins Biological Questions on GPCR Dimer/oligomerization Ligand induced Conformational change G protein coupling Second messenger signaling cAMP/PKA ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:368
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Fluorescent proteins
1
Fluorescent proteins
2
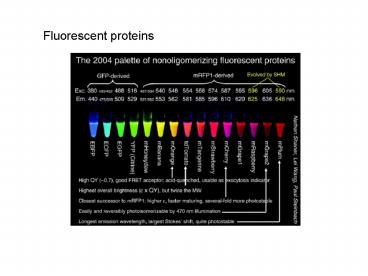
Excitation and Emission Wavelengths of AFP
proteins
3
Strategy of FRET between CFP and YFP
4
Biochemical Modulation of AFP fluorescence
5
The General Design of FRET-based Fluorescent
Probes
6
Some early indicators for second messenger
7
Using fluorescence protein to imaging signaling
transduction
8
Biological Questions on GPCR
- Dimer/oligomerization
- Ligand induced Conformational change
- G protein coupling
- Second messenger signaling
- cAMP/PKA, PKC, DAG, IP3, Ca2
- Scaffold protein/signal complex
9
(No Transcript)
10
(No Transcript)
11
(No Transcript)
12
Biological Questions on GPCR
- Dimer/oligomerization
- Homo/hetreo dimer
- Constitutive vesus ligand induced dimer
- Dimer in receptor maturation in ER
- New agonism
- Functional diversity and Signaling integration
13
(No Transcript)
14
(No Transcript)
15
(No Transcript)
16
(No Transcript)
17
Biological Questions on GPCR
- Ligand induced Conformational change
- Structural functional study
- Agonism/antagonism
- Receptor activation
18
(No Transcript)
19
(No Transcript)
20
(No Transcript)
21
Biological Questions on GPCR
- G protein coupling
- Real time activation
- Screen model for drug discovery
- Signaling/function co-relation.
- Single cell study, instead of biochemical assay
of GTPgS binding
22
(No Transcript)
23
Biological Questions on GPCR
- Second messenger signaling
- cAMP/PKA, PKC, DAG, IP3, Ca2
- Spatial and temporal resolution
- Localized signaling properties, specificity and
efficiency. - Specific function
24
Restricted cAMP signaling in cardiac myocytes
cAMP indicator
25
Promiscuous G protein Coupling by GPCR
26
(No Transcript)
27
Go-CFP resistant to PTX, Cell pretreated with PTX
28
CFP 43012.5nM 46520nM YFP 50010nM
53515nM FRET 43012.5NM, 53515nM
29
Control
CFP 43012.5nM 46520nM YFP 50010nM
53515nM FRET 43012.5NM, 53515nM
30
CFP 43012.5nM 46520nM YFP 50010nM
53515nM FRET 43012.5NM, 53515nM
31
(No Transcript)
32
514nM laser line bleach YFP about
70-90 Concomitant CFP bleach about 7-10
33
(No Transcript)
34
Figure 6, Quantitative Analyses of FRET
a2A-YFP Go-CFP
a2A-YFP Gs-CFP
Donor(Go)acceptor(receptor) at 11, a proportion
of receptor is not coupled to G protein Increaing
the ration leads to higher degree of precoupling.
In physiological conditions, G proteins are in
significant excess compared to receptor, thus a
large majority of receptor are precoupled.
35
(No Transcript)
36
(No Transcript)
37
(No Transcript)
38
(No Transcript)
39
(No Transcript)
40
(No Transcript)
41
(No Transcript)