Analogous and Vestigial Structures - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 30
Title:
Analogous and Vestigial Structures
Description:
Analogous and Vestigial Structures Write in complete sentences! Don t talk during the Catalyst! Catalyst Cougars eat Bucaneers, which have decreased in population ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:1000
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Analogous and Vestigial Structures
1
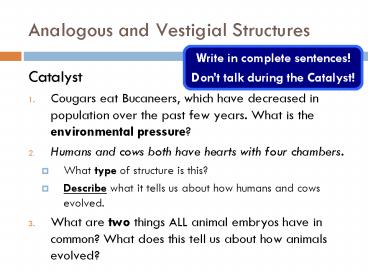
Analogous and Vestigial Structures
Write in complete sentences! Dont talk during
the Catalyst!
- Catalyst
- Cougars eat Bucaneers, which have decreased in
population over the past few years. What is the
environmental pressure? - Humans and cows both have hearts with four
chambers. - What type of structure is this?
- Describe what it tells us about how humans and
cows evolved. - What are two things ALL animal embryos have in
common? What does this tell us about how animals
evolved?
2
Objectives
- By the end of today, all SWBAT
- Explain how analogous structures support the
theory of evolution - Explain how vestigial structures support the
theory of evolution
3
Agenda
- Review
- Structures
- Analogous
- Vestigial
- Guided Practice
- Independent Practice/Homework
- Closing
- Exit Questions
4
Catalyst Review
- Cougars eat Bucaneers, which have decreased in
population over the past few years. What is the
environmental pressure? - The environmental pressure is the decrease in
population of the Bucaneers. - WHY?
5
Catalyst Review
- Humans and cows both have hearts with four
chambers. What type of structure is this, and
what does it tell us about how humans and cows
evolved? - Human and cow hearts are homologous structures.
- This shows that humans and cows evolved from a
common ancestor with a four-chambered heart.
6
Catalyst Review
- What are two things all animal embryos have in
common? What does this tell us about how animals
evolved? - All animal embryos have gill slits and tails.
- This is evidence that all animals evolved from
the same common ancestor.
7
Homework Review
- What are homologous structures? Provide two
examples of homologous structures. - What is an embryo?
- What is a common ancestor? Give an example.
- All animal embryos start off looking very
_______________. For example, they all have
_______________ and _______________. These traits
are examples of _______________ structures.
8
Homework Review
- Lions and tigers have similarly structured tails.
What type of structures are these? EXPLAIN how
these structures support the theory of evolution.
(Hint use the phrases evolve and common
ancestor!) - How can we use the appearance of cat and horse
embryos to support the theory of evolution?
(Hint use the phrases evolve and common
ancestor!)
9
Comparative Anatomy
- Scientists can compare the anatomy of different
organisms to figure out how closely they are
related. - Anatomy body structure
10
Analogous Structures
- Analogous structure Parts of different species
that have the same function, but EVOLVED
SEPARATELY - Key Point 1 Analogous structures show that
unrelated species will evolve similar
adaptations in response to similar environmental
pressures - Natural selection selects for (keeps around)
mutations that increase fitness in the specific
environment. - If organisms they live in similar environments,
they will evolve similar structures.
11
Insect, bird, and bat wings evolved completely
separately. Unrelated organisms will evolve
similar adaptations in response to similar
environmental pressures!
- No recent common ancestor!!!
12
Seals and penguins both have streamlined bodies,
and store fat to keep them warm in the cold
water. Unrelated organisms will evolve similar
adaptations in response to similar environmental
pressures!
13
Vestigial Structures
- Vestigial structure Part of an organism that is
no longer used for anything - Key Point 2 Vestigial structures show that a
species used to live in a different environment. - Organism moved into a new environment, where the
vestigial structure decreases fitness - No longer needed, waste of energy
- Risk of disease
14
Letter c hind legs of a baleen whale skeleton
- Vestigial no longer used!!!
15
Blind salamanders have eye sockets!?!?
16
So, what about me?
17
Guided Practice Notes Reflection
- How do analogous structures provide evidence for
evolution? - Analogous structures show that unrelated
organisms will evolve similar adaptations in
response to similar environmental pressures
ADD IT!!!
If you cant find the answer
18
Guided Practice Notes Reflection
- How do vestigial structures provide evidence for
evolution? - Vestigial structures show that the species used
to live in a different environment - Organism moved into a new environment where the
vestigial structure decreased fitness so it
started to degrade
ADD IT!!!
If you cant find the answer
19
Study!
- This practice will cover yesterdays lesson
(homologous structures) as well as todays
(analogous and vestigial structures). - Take three minutes to study your notes from
yesterday and refresh your memory before we
proceed.
20
Guided Practice (GP)
Are these structures (A) Homologous, (B)
Vestigial, (C) Analogous?
- Human embryos and cat embryos both have gill
slits.
HOMOLOGOUS
21
Guided Practice (GP)
Are these structures (A) Homologous, (B)
Vestigial, (C) Analogous?
- Birds and insects both have wings, but they
developed in completely different ways.
ANALOGOUS
22
Guided Practice (GP)
Is this structure (A) Homologous, (B) Vestigial,
(C) Analogous?
- Snakes dont have legs, but they do have hip and
leg bones.
VESTIGIAL
23
Guided Practice (GP)
Is this structure (A) Homologous, (B) Vestigial,
(C) Analogous?
- The human appendix a small organ next to the
intestines doesnt seem to do anything at all.
VESTIGIAL
24
Guided Practice (GP)
Are these structures (A) Homologous, (B)
Vestigial, (C) Analogous?
- Cat embryos and human embryos both have tails.
HOMOLOGOUS
25
Guided Practice (GP)
Are these structures (A) Homologous, (B)
Vestigial, (C) Analogous?
- Dolphins and sharks both have fins, but they
evolved completely differently.
ANALOGOUS
26
Guided Practice (GP)
Are these structures (A) Homologous, (B)
Vestigial, (C) Analogous?
- Alligators and bats have the same bone structure
in their forelimbs (front legs for alligators,
wings for bats).
HOMOLOGOUS
27
Guided Practice (GP)
Is this structure (A) Homologous, (B) Vestigial,
(C) Analogous?
- Humans have wisdom teeth (third molars), even
though they are not needed to chew up food.
VESTIGIAL
28
Guided Practice (GP)
Are these structures (A) Homologous, (B)
Vestigial, (C) Analogous?
- Humans and squids both have eyes, but they
evolved in completely different ways.
ANALOGOUS
29
Independent Practice (IP)
- Get an early start on the homework.
30
Key Point Wrap-Up
- Key Point 1 Analogous structures show that
unrelated species will evolve similar
adaptations in response to similar environmental
pressures - Key Point 2 Vestigial structures show that a
species used to live in a different environment. - Organism moved into a new environment, where the
vestigial structure decreases fitness
31
Exit Question Choose one optionWrite in
complete sentences!
- All humans have a tail bone, but we dont have
tails. - What type of structure is this?
- EXPLAIN how this structure provides evidence for
evolution.
- Dogs and alligators both have long snouts that
allow their jaws to open wide. However, they
evolved in completely different ways. - What type of structure is this?
- EXPLAIN how these structures provide evidence for
evolution.