Tuned Amplifiers - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 28
Title: Tuned Amplifiers
1
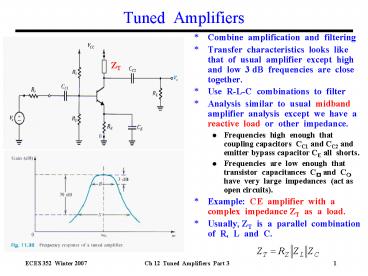
Tuned Amplifiers
- Combine amplification and filtering
- Transfer characteristics looks like that of
usual amplifier except high and low 3 dB
frequencies are close together. - Use R-L-C combinations to filter
- Analysis similar to usual midband amplifier
analysis except we have a reactive load or
other impedance. - Frequencies high enough that coupling
capacitors CC1 and CC2 and emitter bypass
capacitor CE all shorts. - Frequencies are low enough that transistor
capacitances C? and C? have very large
impedances (act as open circuits). - Example CE amplifier with a complex
impedance ZT as a load. - Usually, ZT is a parallel combination of R,
L and C.
ZT
2
Tuned Amplifiers
- Amplifier voltage gain
Vo
Rs
RZ
C
L
RL
RB
Vs
Rs
Vo
Vs
V?
RL
L
RZ
C
gmV?
RB
r?
_
This looks like a bandpass filter, but
with gain.
3
Tuned Amplifiers
Rs
Vo
Vs
RL
L
C
RZ
gmV?
RB
r?
Midband Gain
4
Example - Tuned Amplifier
Rs
Vo
Vs
RL
L
C
RZ
gmV?
RB
r?
Given
Analysis for RZ
Analysis
5
Example - Tuned Amplifier
Rs
Vo
Vs
RL
L
C
RZ
gmV?
RB
r?
Analysis for L
Analysis for C
6
Inductor Series Resistance
- To get accurate results from the above
analysis, we need to take into account the
series resistance of the inductor. - To do so, we will find an equivalent
circuit consisting of an ideal inductor with
a parallel resistance
7
Inductor Series Resistance - Example
Vo
Rs
C
Vs
L
RZ
RB
r?
gmV?
- What is the effect of this RP on our
tuned amplifier analysis? - RP appears in parallel with RL and RZ at
the output. - Must recalculate RZ taking into account RP
Given
Note C and L are unchanged !
8
Tuned Amplifier with LC at Input
RC5K
- Can also implement tuned amplifier with an
LC at the input .
ZT
Rs
Vo
Vs
RL
RC
L
C
gmV?
r?
RB
RP
9
Tuned Amplifier with LC at Input
Rs
Vo
Vs
V?
RL
RC
L
C
gmV?
r?
RB
RP
ZIn
- Amplifier voltage gain
This has the same form as a bandpass filter !
10
Tuned Amplifier with LC at Input
Rs
Vo
Vs
RL
RC
L
C
gmV?
r?
RB
RP
- Amplifier voltage gain
11
Summary of Tuned Amplifier Design
- Shown how use of reactive components
(capacitors and inductors) can be used to
produce a narrow band (tuned) amplifier. - Can use RLC as the load on the output.
- Get transmission at the resonance frequency
of the LC. - Bandwidth depends on the choice of resistor
sizes. - Can use LC combination on the input.
- Get transmission at the resonance frequency
of the LC. - Bandwidth depends on the choice of resistor
sizes. - Derived equations for including the finite
series resistance of the inductor in the
calculations.
RLC Load Tuned
ZT
Tuned LC on the Input
ZT
12
New High Frequency Commercial Applications
and Markets
- Mobile Cellular Communications
- Wi-Fi Local Area Networks
- Broadband Wireless Communications
- Satellite Telecommunications
- Automotive Applications
- Optical Communications
- Sensors and Radar
S. Curtis, Compound Semiconductor, p. 21, Jan/Feb
2005. R. A. Metzger, Compound Semiconductor vol.
1 (3), p. 21, Nov/Dec 1995. J. J. Liou and F.
Schwierz, Solid State Electronics, vol. 47, p.
1881 (2003).
13
World Wide Cell Phone Market
14
Communications Spectrum and Market
Opportunities
15
Spectrum of Millimeter Wave Applications
- International Technology Roadmap for
Semiconductors (2004).
16
State-of-the-Art SiGe Bipolar Transistors
IBM announces SiGe HBTs with gain up to 350 GHz
Current gain and power gain out to and above 100
GHz!
- J. S. Rieh et al., IEDM Tech. Dig., p.771 (Dec.
2002).
17
MOSFET and CMOS Evolution
http//www.intel.com/research/silicon/micron.htm
18
RF/Microwave CMOS
- As the gate length gets smaller, the
MOSFET gets faster. - Cutoff frequency fT is upper frequency limit
where transistors current gain goes to
unity (0 dB). - Cutoff frequency sets an upper limit on
transistor use in circuits since the
circuit cannot work faster than the devices
within it.
J. J. Liou and F. Schwierz, Solid State
Electronics, vol. 47, p. 1881 (2003).
19
Advanced Cellular Communications
- New cellular communication services
- Messaging services
- Locating/tracking
- Internet connections
- Email communications
- Picture acquisition and transmission
- Video games
- Fax
- Walkie-Talkie
- Voice recognition dialing
M. Hatcher and R. Stevenson, Compound
Semiconductor, p. 16, Jan/Feb 2005.
20
Mobile Cellular Communications
- 0.5-2 GHz frequencies
- Circuit applications
- Microwave circuits
- Voltage controlled oscillators and mixers
- Low noise amplifiers
- Filters
- Power amplifiers
- Digital circuits
- Multiplexers/demultiplexers
- Coders/decoders
- Digitizers
Filters
- L. E. Larson, IEEE J. Solid State Circuits, vol.
33, p. 387, March 1998. - T. Witaker, Compound Semiconductor, p. 24,
May 2003.
21
Wireless Communications
Filters
Compound Semiconductor, vol. 4(1), p. 30,
Winter 1998.
22
Bluetooth and Wi-Fi Applications
http//www.swedetrack.com www.bluetooth.com htt
p//accessories.us.dell.com
23
Satellite Radio
- S-band (2.3 GHz)
- GEO (geosynchronous earth orbit) satellites
- Digital audio radio
- Digital transmitters and receivers
- 100 channels
- Three broadcasters
- Sirius
- XM Satellite Radio
- WorldSpace
- Paid 80 M each for broadcast rights
- Monthly fee 10.
24
Global Positioning Systems (GPS)
- Utilizes satellite communications to
determine your location. - Uses 1.22 GHz and 1.58 GHz
- Series of 27 satellites in orbit
- Uses 3 to triangulate our position.
- Measures distance from you to each of
three satellites. - Used in cars, ships, planes and
individuals. - Can also combine with tracking (continuous
location monitoring) and with two way
communications.
25
Monolithically Integrated Inductors
Inductors
26
Recent Application Dual Band Receiver for
Wireless Applications
- Combine two narrow band receivers operating at
different frequencies into one dual-band
(concurrant) receiver.
Band Pass Filters
H. Hashemi and A. Hajimiri, IEEE Trans. Microwave
Theory and Techniques, vol. 50, p. 288 (Jan.
2002).
27
Recent Application Dual Band Receiver for
Wireless Applications
Amplifier Tuned for Gain at these two
frequencies.
Inductors
H. Hashemi and A. Hajimiri, IEEE Trans. Microwave
Theory and Techniques, vol. 50, p. 288 (Jan.
2002).
28
Commercial Development at Very High
Frequencies