INDUSTRIAL ROBOTS - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 15
Title:
INDUSTRIAL ROBOTS
Description:
Definition 2: A robot is a reprogrammable, multi functional manipulator designed ... fireman working in hazardous applications -sea bottom surveying etc. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:4080
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: INDUSTRIAL ROBOTS
1
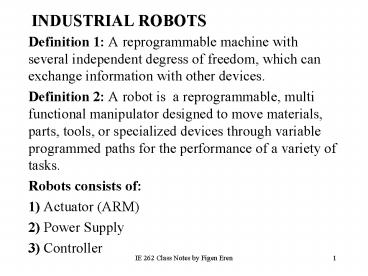
INDUSTRIAL ROBOTS
- Definition 1 A reprogrammable machine with
several independent degress of freedom, which can
exchange information with other devices. - Definition 2 A robot is a reprogrammable, multi
functional manipulator designed to move
materials, parts, tools, or specialized devices
through variable programmed paths for the
performance of a variety of tasks. - Robots consists of
- 1) Actuator (ARM)
- 2) Power Supply
- 3) Controller
2
(No Transcript)
3
- Classification of Robots
- 1) Antropological (human like) Used for
- -escorting blind
- -serving handicapped
- -driving moving chairs
- -entertainment
4
- Classification of Robots (cont.)
- 2) Animal likeBody structures looks like animals
or insects - -Snake like mechanism used in medical field
- -fly eye etc.
5
- Classification of Robots
- 3) Industrial Usually in arm structures used to
- -pick and place tasks
- -welding
- -painting
- -assembly
- -inspection
6
(No Transcript)
7
- Continue...
- 4) Non-IndustrialUsed for
- -to assist bed ridden patients
- -fireman working in hazardous applications
- -sea bottom surveying etc.
8
(No Transcript)
9
- Robot Geometries
- 1) Cartesian (3 linear axes)
- 2) Polar (Spherical)(1 linear and 2 rotational
axes) - 3) Cylindrical (2 linearand one rotational axis)
- 4) Articulated (3 rotary axes)
- Note that the most successful articulated one is
SCARA (SelectiveComplience Articulated Robotic
Actuator)
10
(No Transcript)
11
- Continue...
- Robot Applications
- - Hazardous work environment (welding, spray
painting, etc.) - - Repetitive work cycle
- - Part or tool handling which are difficult for
human - - Multishift operations
- - Material handling (loading-unloading)
- - Process operations
- - Assembly and inspection
12
- Continue...
- Robot Power Sources
- 1) Hydraulic Most powerfull drive.
- 2) PneumaticEasy to supply air pressure. Used in
simple geometries like pick and place, or fixed
end cycle operations. Clean. - 3) ElectricalPopular in precision jobs. Has two
types Stepper motor drives and DC Servo drives.
In stepper motor drives slippage can occur which
cause the loss of the route. Servo drives are
more popular. - 4) Mechanical gearsLow cost, low speed, hard
programmed.
13
- Continue...
- Robot Control Systems
- 1) Limited Sequence Control Simple cycles, not
require microprocessor and usually be implemented
using limit switches and mechanical stops. Often
pneumatically actuated. - 2) Playback with Point-to Point (PTP)
ControlPoints recorded into memory and played
back during execution of the program. The path is
not controlled. - 3) Playback with Continuous Path (CP)
ControlSimilar to PTP, instead of points, paths
stored in the memory. - 4) Inteligent ControlSensors and amchine
visions makes decisions when things go wrong.
Need powerfull micro processeors.
14
- Continue...
- Typical Robot Arm Characteristics
- Hand must grip or release a work piece
- Arm must be able to move the hand in three
planes - Wrist has three articulations (roll-pitch-grib)
- Limb power to lift and manipulate
- limb must be operated manually
- Error involved in repeated positioning must be
minimized - It has a computer interface
- It can run automatically in programmed mode as
well as after being tought the process sequence
15
- Continue...
- Gripper Types
- Mechanical Fingers or jaws or
antropomorphically designed hands - Magnetical If object being grasped are metallic
and not effected by magnetic field we can use
this type. - By Vacuum If vibrational shock is not important
- By Piercing Punctures the component as in
clothing application - By Adhesion Using sticky tape or other adhesives








![Forecast on China Industrial Robot Industry[2015-2019] PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/8334715.th0.jpg?_=20190501113)
![Market Report on China Industrial Robot Industry [2015-2019] PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/8336262.th0.jpg?_=201512240310)




















