NOTES: 12.2 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
NOTES: 12.2
Description:
NOTES: 12.2 12.3 DNA Structure & Replication 12.2: DNA Structure it was known that DNA was made up of nucleotides joined into long strands by covalent bonds but ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:123
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: NOTES: 12.2
1
NOTES 12.2 12.3DNA Structure Replication
2
12.2 DNA Structure
- ? it was known that DNA was made up of
nucleotides joined into long strands by covalent
bondsbut HOW were they connectedwhat was the
structure?
3
DNA Structure
- ? Made up of nucleotides (monomer)
- ? Each nucleotide composed of 3 parts
- 5-carbon sugar (DEOXYRIBOSE)
- Phosphate group
- Nitrogen-containing base
- ? Adenine (A)
- ? Thymine (T)
- ? Guanine (G)
- ? Cytosine (C)
4
Chargaffs Rules
Percentage of Bases in Four Organisms Percentage of Bases in Four Organisms Percentage of Bases in Four Organisms Percentage of Bases in Four Organisms Percentage of Bases in Four Organisms
Source of DNA A T G C
Streptococcus 29.8 31.6 20.5 18.0
Yeast 31.3 32.9 18.7 17.1
Herring 27.8 27.5 22.2 22.6
Human 30.9 29.4 19.9 19.8
- What do these data suggest to you?
5
- ? A T (A pairs with T)
- ? C G (C pairs with G)
6
What DNA Looks Like
- ? Rosalind Franklin used X-ray diffraction
patterns to discover that DNA strands twisted
around each other like a HELIX
7
- ? Watson Crick while trying to build a 3-D
model of DNA, Watson saw Franklins photograph
and measurements and within weeks, he and Crick
figured out the structure of DNA
8
DNA Structure DOUBLE HELIX (twisted ladder)
- ? Backbone
- deoxyribose phosphate group of each nucleotide
- ?Steps of Ladder
- bases (A, G, C, T)
- ? Any base sequence is possible!
9
(No Transcript)
10
(No Transcript)
11
Whats holding the strands together?
- ? HYDROGEN BONDS!!!
- ? Hydrogen Bonds form between A and T base pairs
as well as between C and G base pairs
12
12.3 - DNA Replication
- Vocabulary
- Chromatin
- Replication
- DNA polymerase
- Key Concept
- What happens during DNA Replication?
13
The Review
- ? Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus
- DNA molecules are located in the cytoplasm
- Usually a circular DNA molecule and it is
referred to as the cells chromosome - ? Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus
- Can have 1000x more DNA than prokaryotic cells
- DNA is located in the form of a number of
chromosomes - of chromosomes varies widely from species to
species
14
DNA molecules are longhow does DNA fit in the
nucleus?
- ? It forms chromosomes!
- ? DNA coils around proteins called histones and
then this chromatin supercoils around itself
until chromosomes form
15
DNA Replication
- ? before a cell divides, it must copy its DNA so
that all cells have a copy of the genetic
instructions - ? this process involves A LOT of ENZYMES!
- ? each half of the DNA double helix can serve as
a "template" for the replication of another DNA
double helix molecule - The strands are said to be complementary
16
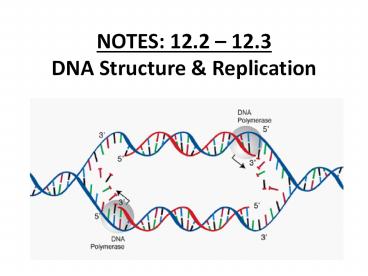
DNA REPLICATION THE PROCESS
- 1) An enzyme unwinds "unzips" DNA (separates
the 2 DNA strands) by breaking the hydrogen bonds
between base pairs
Hydrogen Bonds Breaking!
17
- 2) a complementary base is inserted to each side
of the DNA strand with the help of DNA POLYMERASE
Why does the blue always pair with the green?
18
(No Transcript)
19
(No Transcript)
20
(No Transcript)
21
- 3) The sugar-phosphate groups are covalently
bonded to the growing DNA chain (new "backbone")
1 nucleotide
COVALENT BOND
22
(No Transcript)
23
- 4) an enzyme (DNA polymerase) will "proof-read"
the order of bases make corrections
24
A SIMPLIFIED VERSION
25
A Little More Complicated